In short, the high thermal conductivity of silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements directly enhances process efficiency by enabling extremely rapid heat transfer. This allows your furnace or system to reach target temperatures faster and cool down more quickly, which in turn shortens process cycle times and increases overall throughput.
While speed is the obvious benefit, the true value of SiC's thermal conductivity lies in how it works with the material's other robust properties—like low thermal expansion—to enable aggressive, repeatable process cycles without sacrificing element longevity.
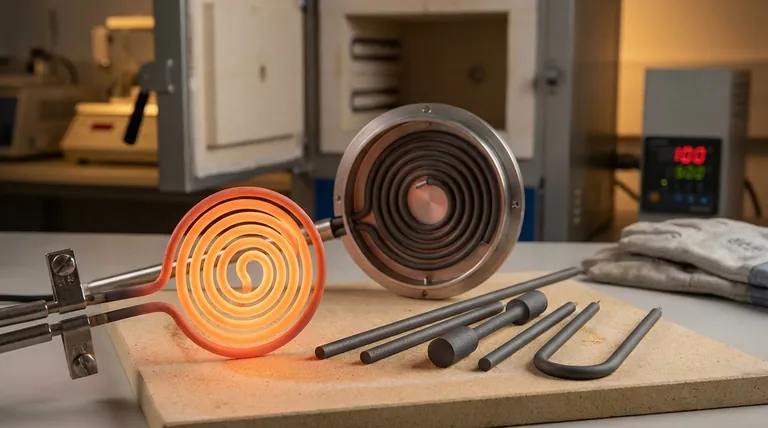

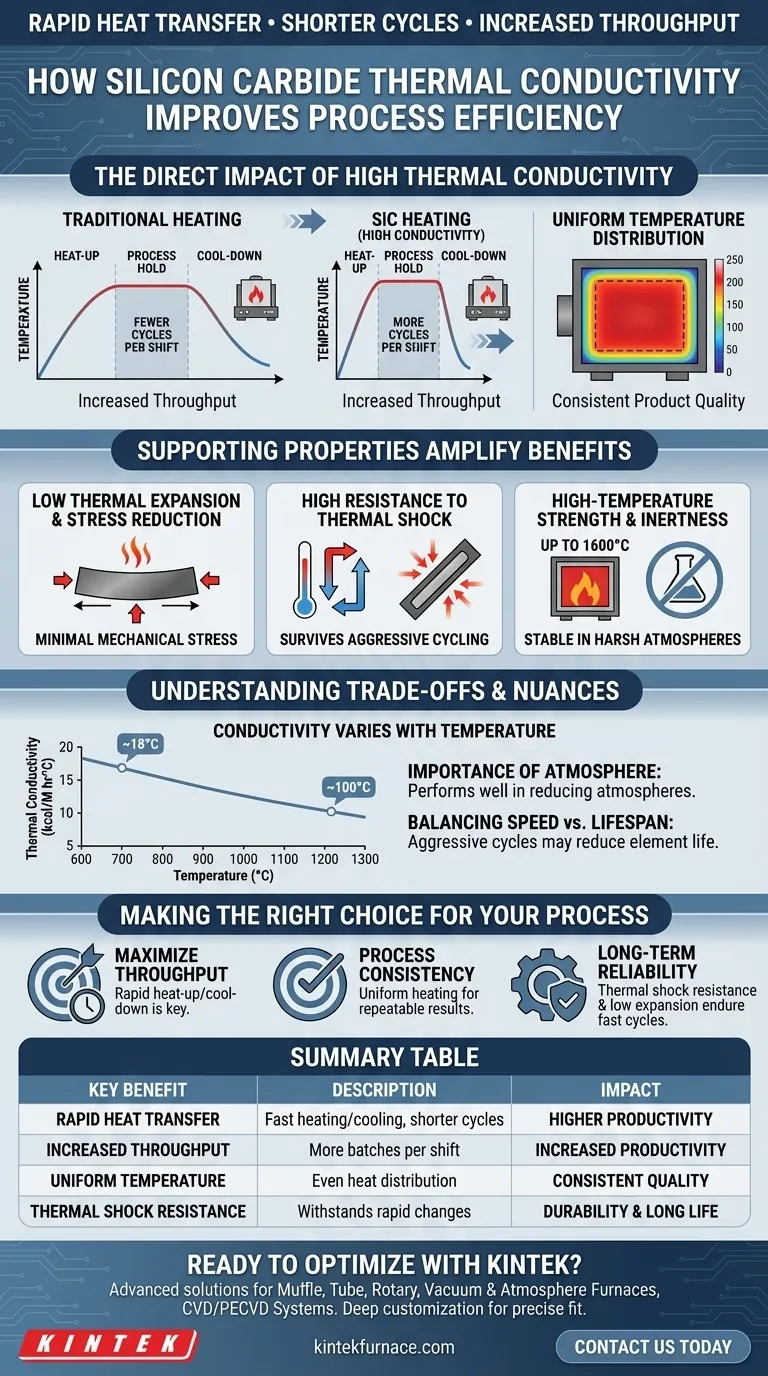
The Direct Impact of High Thermal Conductivity
The core advantage of silicon carbide is its ability to move thermal energy quickly and effectively. This physical property translates directly into measurable performance gains in an industrial or laboratory setting.
Faster Heat-Up and Cool-Down Rates
High thermal conductivity means that as soon as electrical energy is applied, the heat is immediately and efficiently conducted through the element and radiated to your process load. The same is true for cooling; the element sheds heat rapidly once power is cut.
Reducing Cycle Times
This rapid heating and cooling capability directly shortens the time required for each batch or process cycle. For operations that rely on frequent temperature changes, this reduction is significant and cumulative.
Enhancing Throughput
By shortening each cycle, you can run more cycles within a given production shift. This directly increases the throughput of the furnace, boosting productivity without needing to invest in additional equipment.
Uniform Temperature Distribution
A secondary benefit of high thermal conductivity is more uniform heating. The element distributes heat evenly across its own surface, which helps eliminate hot and cold spots within the furnace chamber, leading to more consistent product quality.
How Supporting Properties Amplify the Benefits
Thermal conductivity does not operate in a vacuum. SiC's efficiency is only possible because its other physical characteristics allow it to withstand the stress of rapid temperature changes.
Low Thermal Expansion and Stress Reduction
All materials expand when heated and contract when cooled. The rapid cycling enabled by SiC's conductivity would create immense internal stress on a lesser material.
SiC has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion. This means it expands and contracts very little during temperature swings, minimizing mechanical stress and preventing cracks or premature failure.
High Resistance to Thermal Shock
This low expansion contributes directly to an exceptional resistance to thermal shock. The element can survive the rapid heating and cooling cycles that would cause many other ceramics to fracture, ensuring its durability and reliability.
High-Temperature Strength and Inertness
SiC maintains high mechanical strength even at extreme operating temperatures up to 1600°C. Furthermore, its chemical inertness makes it resistant to degradation in harsh process atmospheres, ensuring its conductive properties remain stable over a long operational life.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
To be a truly effective solution, it's crucial to understand the operating conditions and limitations of silicon carbide. Its properties are not static.
Conductivity Varies with Temperature
It is critical to know that SiC's thermal conductivity is not constant. It is actually highest at lower temperatures and decreases as the element heats up.
For example, a typical value might be 14-18 kcal/M hr°C at 600°C, but this can drop to 10-14 kcal/M hr°C at 1300°C. This must be factored into system design for precise temperature control.
The Importance of Atmosphere
While robust, SiC's performance can be affected by the process environment. It performs particularly well in reducing atmospheres, where it can be stronger than alternatives like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2).
Balancing Speed with Element Lifespan
Although SiC is designed for thermal cycling, more aggressive and frequent cycles will inevitably impose more stress than steady-state operation. There is always a balance between maximizing throughput and achieving the longest possible element lifespan.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific goal will determine which of silicon carbide's attributes is most valuable to your operation.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: The rapid heat-up and cool-down capability is your key advantage, allowing for more cycles per shift.
- If your primary focus is process consistency: The uniform heating provided by high conductivity is critical for ensuring repeatable, high-quality results.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability: The combination of thermal shock resistance and low thermal expansion ensures the element endures the very fast cycles it is designed to perform.
Ultimately, silicon carbide's thermal conductivity is the engine of efficiency, but its supporting physical properties are what make that performance reliable and sustainable.
Summary Table:
| Key Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Rapid Heat Transfer | Enables fast heating and cooling, reducing process cycle times. |
| Increased Throughput | Shortens cycles, allowing more batches per shift for higher productivity. |
| Uniform Temperature | Distributes heat evenly, minimizing hot/cold spots for consistent quality. |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Withstands rapid temperature changes, ensuring durability and long life. |
Ready to optimize your thermal processes with high-efficiency silicon carbide heating elements? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your unique needs, boosting throughput and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism



















