At its core, the temperature capability of a continuous furnace is its defining advantage, enabling industrial processes that demand extreme, sustained heat at a large scale. This ability to operate consistently near the melting point of base metals allows for the high-volume manufacturing of materials with specific, advanced properties that are otherwise unattainable in other furnace types.
The true value of a continuous furnace isn't just its high temperature, but its capacity to maintain that heat across a continuous production line. This transforms demanding thermal processes like high-temperature sintering and metal treatment from batch operations into efficient, scalable manufacturing.
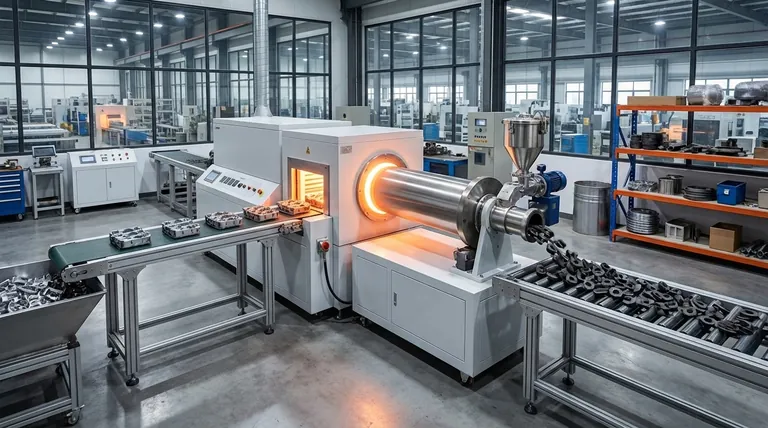

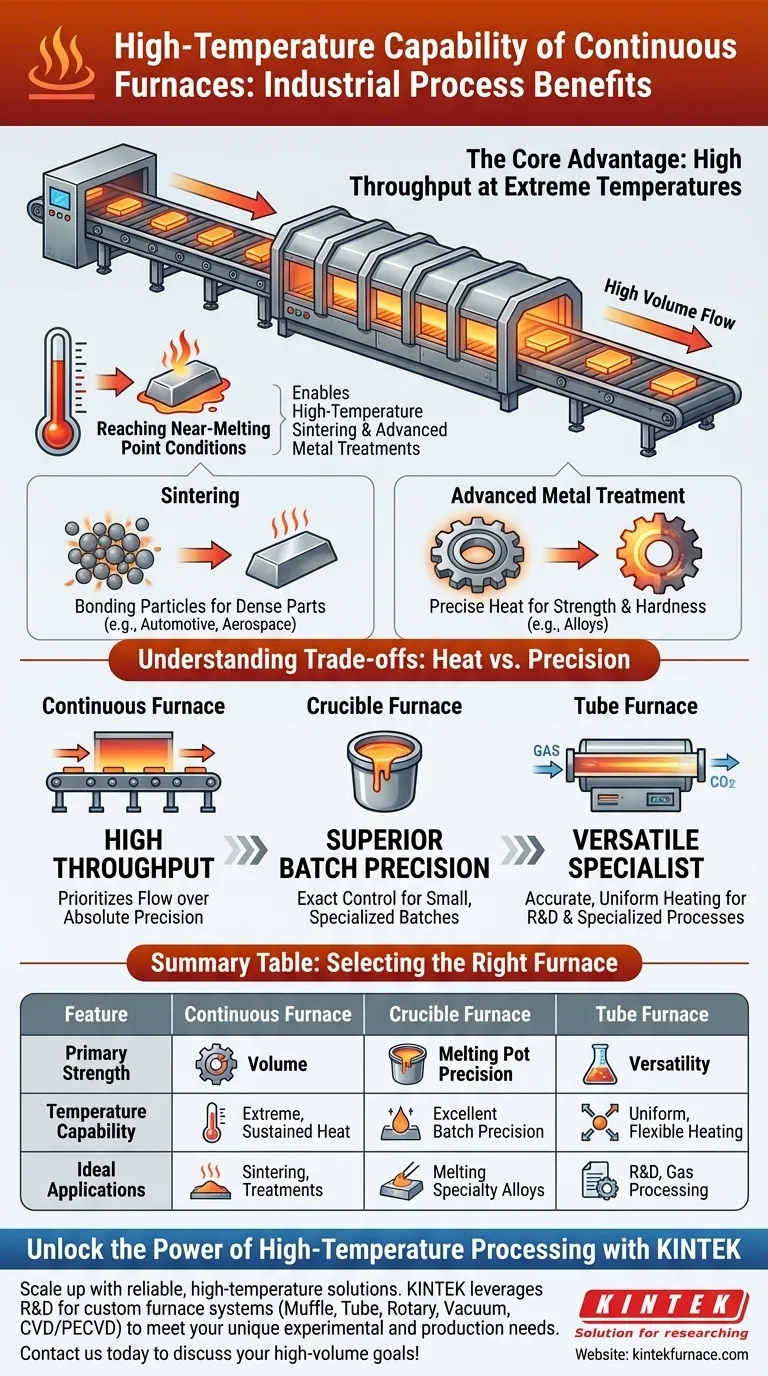
The Core Advantage: High Throughput at Extreme Temperatures
A continuous furnace is engineered as a production workhorse. Its design prioritizes moving a large volume of material through a consistently controlled, high-heat environment.
Reaching Near-Melting Point Conditions
The ability to operate near the melting point of a base metal is critical. This extreme thermal energy is required to fundamentally alter the microstructure and properties of a material, which is the entire goal of many advanced heat treatment processes.
Enabling Key Industrial Processes
This high-heat capability is not theoretical; it is a prerequisite for specific, high-value applications.
- High-Temperature Sintering: This process involves heating compacted powder materials to just below their melting point to bond the particles together, creating a solid, dense object. Continuous furnaces make it possible to sinter parts for industries like automotive and aerospace on a mass scale.
- Advanced Metal Treatments: Certain treatments, such as solution annealing or specific hardening cycles for high-performance alloys, require precise exposure to extreme temperatures to achieve the desired strength, hardness, or corrosion resistance.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Heat vs. Precision
While powerful, a continuous furnace is not the universal solution for all heating applications. The optimal choice depends on the specific balance required between production volume, temperature uniformity, and process control.
Continuous Furnaces: Built for Volume
The primary strength of a continuous furnace is high throughput. They are designed for industrial-scale production where the goal is to process a large quantity of similar parts under consistent thermal conditions. While they maintain good temperature control, their design prioritizes flow over the absolute precision of a batch furnace.
Crucible Furnaces: Prioritizing Exact Control
In contrast, crucible furnaces excel at providing excellent and precise temperature control for a contained batch of material. This is crucial for applications like melting specialty alloys where even minor temperature deviations can negatively impact the final material properties. They sacrifice throughput for superior batch-level precision.
Tube Furnaces: The Versatile Specialist
Tube furnaces offer a unique blend of accurate temperature control, uniform heating, and process versatility, often for smaller or more specialized applications. They are workhorses in research and development, materials testing, and specialized chemical processes like pyrolysis or gas processing, where scalability and precision are both important.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct furnace technology is critical to meeting your production goals, quality standards, and budget. Your primary objective will guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of sintered parts or heat-treated metals: A continuous furnace is the ideal solution, designed specifically for efficient, large-scale throughput at extreme temperatures.
- If your primary focus is melting smaller, specialized batches with exacting material properties: A crucible furnace offers the superior temperature control necessary for ensuring consistent quality.
- If your primary focus is materials testing, R&D, or specialized gas processing: A tube furnace provides the necessary combination of precision, uniformity, and configuration flexibility for these applications.
Ultimately, understanding the unique strengths of each furnace type empowers you to select the right tool for your specific thermal processing objective.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Continuous Furnace | Crucible Furnace | Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Strength | High throughput for large-scale production | Precise temperature control for small batches | Versatile, accurate heating for R&D and specialized processes |
| Temperature Capability | Extreme, sustained heat near melting point | Excellent for contained batch precision | Uniform heating with configuration flexibility |
| Ideal Applications | High-temperature sintering, advanced metal treatments | Melting specialty alloys | Materials testing, pyrolysis, gas processing |
Unlock the Power of High-Temperature Processing with KINTEK
Are you looking to scale up your industrial processes with reliable, high-temperature solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnace systems tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements.
Whether you're in automotive, aerospace, or materials research, our furnaces can enhance your efficiency and output. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your high-volume production goals and deliver the perfect thermal solution for your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries
- What are the key features of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Control
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing



















