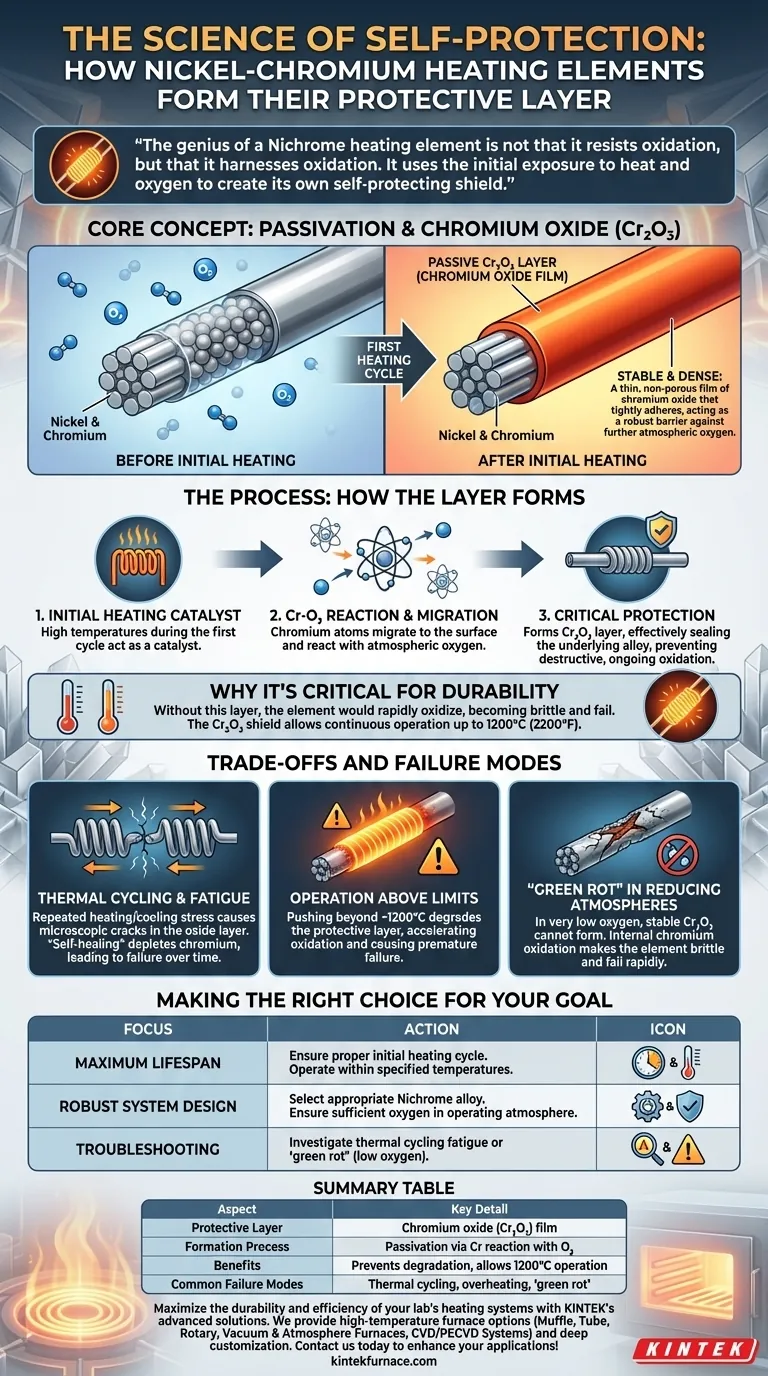
At its core, the protective layer on a Nickel-Chromium (Nichrome) heating element is a thin, stable film of chromium oxide. This layer forms automatically during the very first heating cycle as the chromium in the alloy reacts with oxygen from the air. This process, known as passivation, is what grants the element its remarkable resistance to degradation at high temperatures.
The genius of a Nichrome heating element is not that it resists oxidation, but that it harnesses oxidation. It uses the initial exposure to heat and oxygen to create its own self-protecting shield, preventing the destructive, ongoing oxidation that would otherwise cause it to fail.
The Science of Self-Protection: Passivation in Action
The durability of Nichrome wire is not an inherent property of the raw alloy but is created the moment it's first put into service. This self-protection mechanism is a controlled, beneficial form of oxidation.
The Initial Reaction: Forming Chromium Oxide
When the element is first heated, the high temperature acts as a catalyst. The chromium atoms within the alloy have a strong affinity for oxygen. They migrate to the surface of the wire and react with oxygen in the atmosphere.
This reaction selectively forms a passive layer of chromium oxide (Cr₂O₃) that tightly adheres to the surface.
The Nature of the Protective Layer
This newly formed chromium oxide layer is extremely thin, dense, and chemically stable. Unlike the flaky, porous rust that forms on iron, this layer is non-porous and acts as a robust barrier.
It effectively seals the underlying alloy—both the nickel and the remaining chromium—from further contact with atmospheric oxygen.
Why This Layer is Critical for Durability
Without this passive layer, the heating element would continue to oxidize rapidly at high temperatures, becoming thinner, more brittle, and quickly burning out.
The chromium oxide shield is what prevents this destructive cycle. It allows the element to operate continuously at temperatures up to 1200°C (2200°F) while maintaining its structural and electrical integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Failure Modes
While remarkably effective, the protective layer is not invincible. Understanding its limitations is key to maximizing the lifespan of a heating element.
Thermal Cycling and Fatigue
The most common cause of failure is repeated heating and cooling. This thermal cycling causes the element to expand and contract.
Over thousands of cycles, this stress can cause microscopic cracks to form in the protective oxide layer. While the element can "self-heal" by forming new oxide in these cracks, this process consumes chromium from the alloy. Eventually, the underlying alloy becomes depleted of chromium, and the element fails.
Operation Above Temperature Limits
Pushing the element beyond its specified operating temperature (typically around 1200°C) can cause the protective layer to degrade or become compromised. This accelerates oxidation and leads to premature failure.
'Green Rot' in Reducing Atmospheres
In environments with very low oxygen (known as reducing atmospheres), the stable chromium oxide layer cannot form properly.
Instead, a different oxidation process can occur, selectively oxidizing the chromium internally. This phenomenon, known as green rot, makes the element extremely brittle and leads to rapid failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the formation and function of this layer helps in designing and maintaining reliable heating systems.
- If your primary focus is maximum element lifespan: Ensure the element undergoes a proper initial heating cycle to form a quality oxide layer and always operate it within its specified temperature range.
- If your primary focus is designing a robust system: Select an appropriate Nichrome alloy for your target temperature and, critically, ensure the operating atmosphere has sufficient oxygen to maintain the protective layer.
- If you are troubleshooting frequent failures: Investigate for evidence of thermal cycling fatigue or signs of 'green rot', which points to operation in a low-oxygen environment.
By understanding this fundamental chemistry, you can ensure the long-term reliability and performance of your high-temperature heating applications.

Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Protective Layer | Chromium oxide (Cr₂O₃) film formed during initial heating |
| Formation Process | Passivation via chromium reaction with atmospheric oxygen |
| Benefits | Prevents degradation, allows operation up to 1200°C (2200°F) |
| Common Failure Modes | Thermal cycling fatigue, operation above limits, green rot in low-oxygen atmospheres |
Maximize the durability and efficiency of your lab's heating systems with KINTEK's advanced solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your high-temperature applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions



















