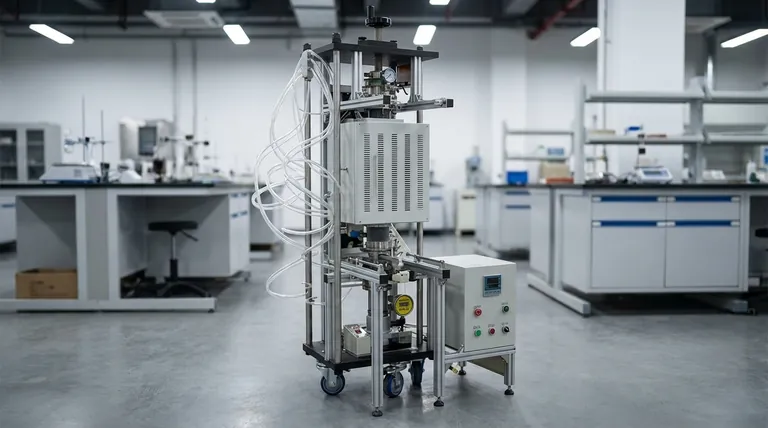
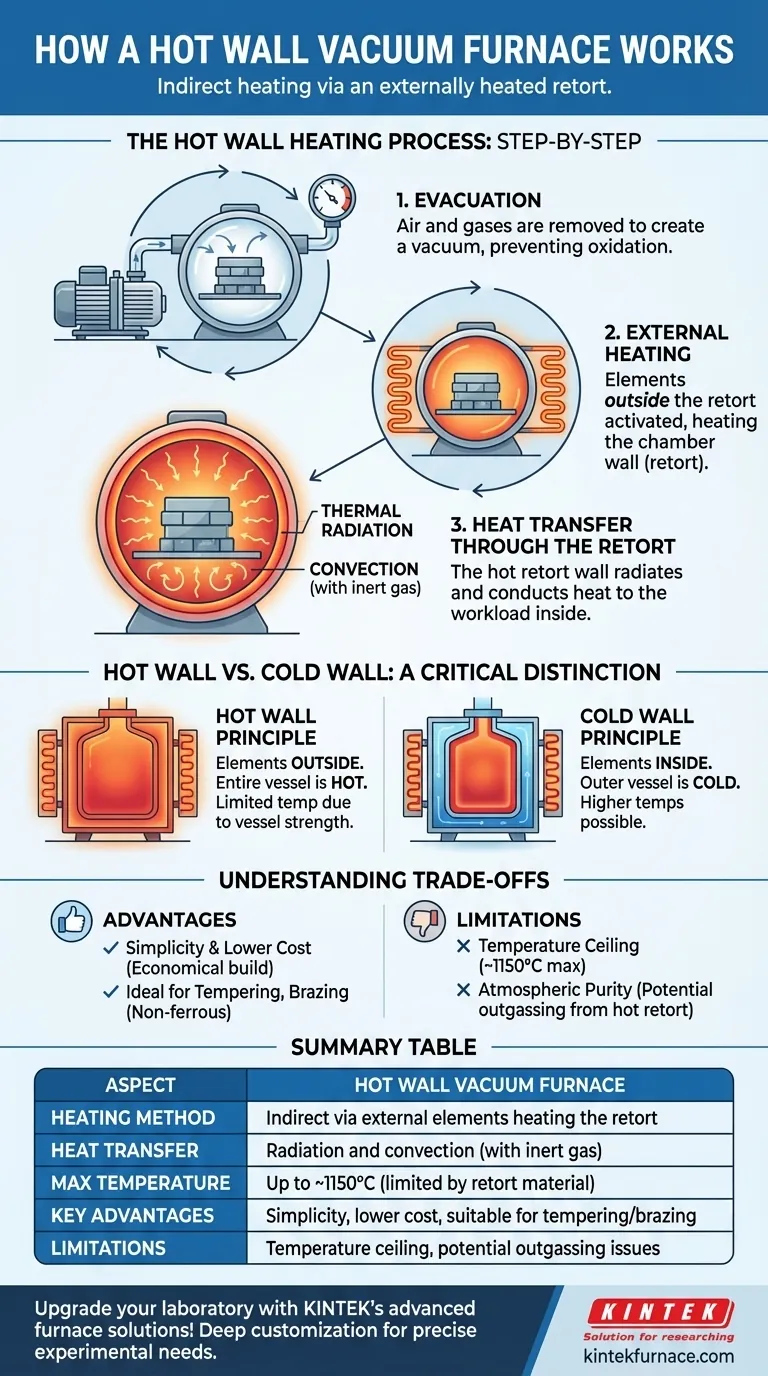
In a hot wall vacuum furnace, the heating process is indirect. Heating elements located outside the vacuum chamber first heat the chamber wall, known as the retort. This hot retort then radiates and conducts heat inward to the workload placed inside the vacuum environment.
The defining characteristic of a hot wall furnace is its external heating system. While this design is simple and cost-effective for many applications, it places a fundamental limit on the maximum achievable temperature, which is dictated by the material strength of the hot vacuum vessel itself.

The Hot Wall Heating Process, Step-by-Step
A hot wall furnace follows a precise sequence to ensure materials are treated correctly without contamination. The heating phase is just one part of this integrated process.
Step 1: Evacuation
Before any heating begins, a vacuum system removes air and other gases from the sealed chamber or retort. This step is critical because it prevents oxidation and other unwanted chemical reactions that would occur if the material were heated in the presence of oxygen.
Step 2: External Heating
Once the target vacuum level is reached, electrical heating elements surrounding the outside of the retort are activated. These heaters do not directly "see" the parts inside the furnace.
Step 3: Heat Transfer Through the Retort
The energy from the external heaters is absorbed by the retort wall, causing its temperature to rise significantly. The entire vacuum chamber becomes hot—hence the name "hot wall."
This hot retort then acts as the heat source for the workload inside. Heat is transferred from the hot inner surface of the retort to the parts primarily through thermal radiation. If a partial pressure of inert gas (like argon) is introduced, convection also plays a role in distributing heat more uniformly.
Hot Wall vs. Cold Wall: A Critical Distinction
To fully grasp the hot wall concept, it's essential to contrast it with its counterpart. The primary difference lies in the location of the heating elements.
The Hot Wall Principle
As we've established, the heating elements are outside the vacuum. The entire vessel gets hot and must be made from an alloy that can withstand high temperatures while under an external atmospheric pressure load.
The Cold Wall Principle
In a cold wall furnace, the heating elements and their insulation are located inside the vacuum chamber, surrounding the workload directly. The outer vessel is typically water-cooled and remains near room temperature, or "cold."
This design allows for much higher operating temperatures because the structural vessel is not exposed to heat. The internal hot zone is instead composed of high-temperature materials like graphite or refractory metals (molybdenum, tungsten).
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a hot wall design involves specific advantages and limitations that make it suitable for some processes but not others.
Advantage: Simplicity and Lower Cost
Hot wall furnaces are generally less complex and more economical to build and maintain. The design avoids the need for internal power feedthroughs and the sophisticated water-cooling circuits required for a cold wall vessel.
Limitation: Temperature Ceiling
The biggest constraint of a hot wall furnace is its maximum temperature. The retort material must maintain its structural integrity while hot and under vacuum. This typically limits hot wall furnaces to temperatures around 1150°C (2100°F) or lower, depending on the alloy used for the retort.
Limitation: Atmospheric Purity
Because the entire large surface of the retort is hot, it can release adsorbed gases—a phenomenon known as outgassing. This can make achieving the highest levels of vacuum or atmospheric purity more challenging compared to a cold wall design, where only the internal hot zone materials contribute to outgassing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision between a hot wall and a cold wall furnace is driven entirely by the requirements of your specific thermal process.
- If your primary focus is on processes like tempering, aging, or brazing of non-ferrous metals like aluminum: A hot wall furnace is often the most practical and cost-effective solution, as these processes fall well within its temperature capabilities.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature applications like sintering refractory metals, advanced ceramics, or brazing superalloys: A cold wall furnace is essential to reach the necessary temperatures (often exceeding 1200°C) and maintain the high-purity vacuum environment required.
Ultimately, understanding the heating mechanism is key to selecting the right tool for your engineering objective.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Hot Wall Vacuum Furnace |
|---|---|
| Heating Method | Indirect via external elements heating the retort |
| Heat Transfer | Radiation and convection (with inert gas) |
| Max Temperature | Up to ~1150°C (limited by retort material) |
| Key Advantages | Simplicity, lower cost, suitable for processes like tempering and brazing |
| Limitations | Temperature ceiling, potential outgassing issues |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and results. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can optimize your thermal processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of vacuum hot press furnaces? Achieve Superior Material Density & Purity
- How does a vacuum or protective atmosphere reduce oxidation in molten metals? Prevent Oxide Inclusions for Stronger Metals
- What is a vacuum hot press furnace? Unlock Superior Material Performance
- How does Vacuum Hot Press equipment contribute to the energy and power generation sector? Boost Efficiency and Durability
- How does precise temperature control affect Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Master Titanium Hot Pressing Accuracy



















