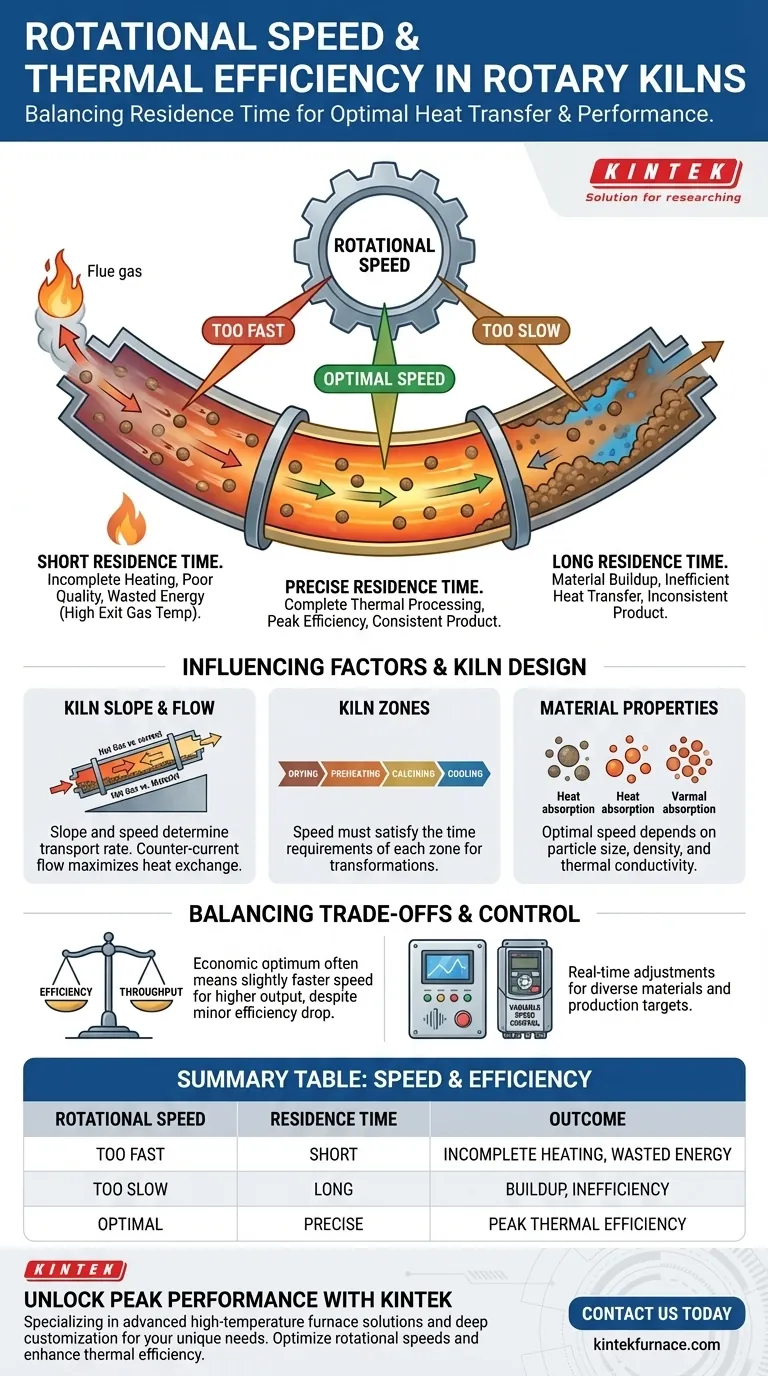
In short, rotational speed directly governs the thermal efficiency of a rotary kiln by controlling the material's residence time. An optimal speed ensures the material is exposed to heat for the precise duration needed for complete thermal processing. Speeds that are too high result in incomplete heating and wasted energy, while speeds that are too slow can cause material buildup and inefficient heat transfer, undermining both product quality and energy consumption.
The core challenge is not simply setting a speed, but continuously balancing it. Rotational speed is a dynamic control lever that must be harmonized with the material's properties and the kiln's other operational parameters to maximize heat transfer and achieve peak thermal efficiency.

The Core Mechanism: Residence Time and Heat Transfer
Rotational speed is arguably the most critical operational parameter you can control to influence kiln efficiency. Its primary effect is on the time your material spends traveling through the kiln, which dictates how能量 is absorbed.
Defining Residence Time
Residence time is the total duration a particle of material spends inside the kiln, from the feed end to the discharge end. This is directly and inversely proportional to the rotational speed. A faster rotation means a shorter residence time.
The "Too Fast" Problem: Incomplete Heat Exposure
When the kiln rotates too quickly, the material is transported palavras the heating zones before it can fully absorb the required thermal energy.
This leads to two primary inefficiencies:
- Poor Product Quality: The material exits the kiln only partially processed, failing to meet quality specifications for chemical or physical changes.
- Wasted Energy: The heat generated by the burner does not have sufficient time to transfer to the material and instead exits with the flue gas, resulting in a higher exit gas temperature and dramatically lower thermal efficiency.
The "Too Slow" Problem: Buildup and Inefficiency
Conversely, a rotation that is too slow can be just as detrimental to efficiency. Extended residence time can cause material to overheat or create buildups along the refractory lining.
This creates insulating layers or "cold spots" within the material bed, preventing uniform heat distribution. The result is inconsistent product and wasted fuel, as you are spending energy to heat material that is no longer effectively absorbing it.
Rotational Speed in the Context of Kiln Design
A kiln is a system of interconnected variables. Rotational speed cannot be optimized in isolation; it must be considered alongside the kiln's fundamental design characteristics.
Interaction with Kiln Slope
Rotary kilns are installed at a slight inclination, typically between 1% and 4%, to facilitate the movement of material via gravity.
The speed of rotation and the kiln's slope work together to determine the material's overall transport rate. A steeper slope will require a slower rotational speed to achieve the same target residence time.
The Importance of Counter-Current Flow
Most modern kilns use a counter-current flow design for maximum thermal efficiency. In this setup, the hot combustion gases flow from the discharge end toward the feed end, opposite to the direction of the material.
This design ensures that the hottest, most energy-rich gases meet the hottest, most processed material, while cooler gases preheat the incoming cold material. Optimal rotational speed is crucial to maximizing the benefit of this design, ensuring material spends the correct amount of time in each temperature zone.
Aligning Speed with Kiln Zones
A kiln is not a uniform heating chamber but is divided into distinct zones: typically drying, preheating, calcining, and cooling. Each zone requires a specific temperature profile and duration for the necessary physical and chemical transformations to occur.
The total residence time, set by the rotational speed, must be long enough to satisfy the time requirements of each of these sequential zones.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
Achieving optimal thermal efficiency involves more than just a simple calculation. It requires navigating operational and material-specific trade-offs.
Efficiency vs. Throughput
There is an inherent conflict between maximizing thermal efficiency and maximizing production throughput.
A slower speed may yield the highest possible thermal efficiency per unit of material, but it reduces the total tons per hour the kiln can process. The economic optimum is often a slightly faster speed that accepts a minor hit in efficiency for a major gain in output.
The Role of Material Properties
The "correct" speed प्लांट-specific is highly dependent on a material's properties. Factors like particle size, density, and thermal conductivity influence how quickly it absorbs heat.
Processes can be validated using techniques like Thermal Gravimetric Analysis (TGA), which identifies the precise temperature ranges and times required for processes like vaporization or chemical decomposition. The kiln's residence time must be adjusted to match these scientifically determined requirements.
Modern Control Systems
Modern kilns often feature frequency conversion speed control. This technology allows operators to make precise, real-time adjustments to the rotational speed. This flexibility is critical for optimizing performance when changing feedstocks or adjusting production targets, turning speed into a truly dynamic control parameter.
Optimizing Rotational Speed for Your Goal
Your ideal rotational speed depends entirely on your primary operational objective. Use these principles as your guide.
- If your primary focus is maximum thermal efficiency: Opt for a slower rotational speed that ensures complete heat transfer and the lowest possible flue gas exit temperature, without causing material buildup.
- If your primary focus is maximum throughput: Carefully increase rotational speed while monitoring product quality and exit gas temperature to find the upper limit before efficiency and quality drop unacceptably.
- If your primary focus is handling diverse materials: Leverage variable speed controls to adjust residence time based on the specific thermal requirements of each feedstock, as determined by lab analysis.
Ultimately, mastering rotational speed transforms it from a simple mechanical setting into a precise tool for achieving operational excellence.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Influence on Thermal Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Rotational Speed | Controls material residence time in kiln |
| Too Fast | Short residence time, incomplete heating, wasted energy |
| Too Slow | Long residence time, material buildup, inefficient heat transfer |
| Optimal Speed | Ensures complete thermal processing, maximizes efficiency |
| Interaction with Kiln Slope | Affects transport rate and residence time |
| Counter-Current Flow | Enhances heat transfer when speed is optimized |
| Material Properties | Determines required residence time for specific heat absorption |
Unlock Peak Performance for Your Rotary Kiln with KINTEK
Struggling with inefficient heat transfer or inconsistent product quality in your rotary kiln operations? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your experimental and production requirements, helping you optimize rotational speeds and enhance thermal efficiency.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can boost your lab's performance and reduce energy costs—Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results



















