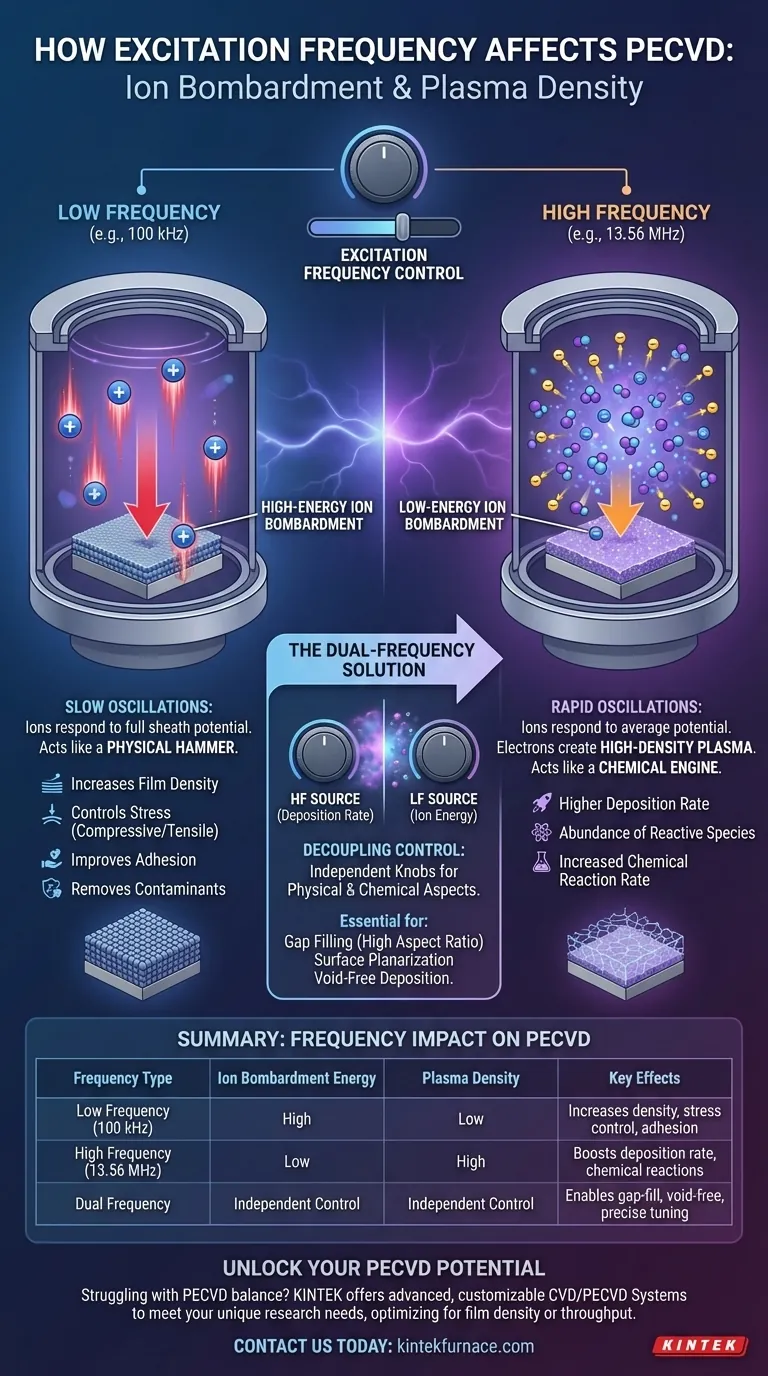
In Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD), excitation frequency is the fundamental control knob that dictates the energy of ion bombardment and the density of the plasma. In short, lower frequencies (like 100 kHz) produce high-energy ion bombardment, while higher frequencies (like the common 13.56 MHz) generate a higher-density plasma with lower-energy ions. This choice directly determines the physical properties and growth rate of the deposited film.
Excitation frequency is not just a process variable; it is the primary tool for balancing the physical and chemical aspects of deposition. Low frequency acts as a physical hammer to control film properties like density and stress, while high frequency acts as a chemical engine to control reaction rates and deposition speed.

The Physics of Frequency and Plasma
To control your PECVD process, you must first understand how ions and electrons behave differently in response to the alternating electric field. This behavior is dictated by the plasma sheath—a thin boundary layer between the main plasma and your substrate.
The Plasma Sheath: The Acceleration Zone
The plasma sheath is a region of strong electric fields that forms at all surfaces. It is within this zone that positive ions, extracted from the bulk plasma, are accelerated toward your substrate.
The voltage across this sheath, and how quickly it changes, determines the final energy of the ions as they strike the surface.
Low Frequency (LF): A Slow Push for High Energy
At low frequencies (e.g., below ~1 MHz), the electric field polarity reverses slowly. Ions are relatively heavy and can respond to these slow changes.
As a result, ions have enough time to accelerate across the full potential of the sheath during each cycle. This leads to high-energy ion bombardment, as the ions arrive at the substrate with nearly the maximum energy imparted by the RF voltage.
High Frequency (HF): A Fast Oscillation for Low Energy
At high frequencies (e.g., 13.56 MHz and above), the electric field reverses millions of times per second. The heavy ions cannot keep up with this rapid oscillation.
Instead of experiencing the full voltage swing, they respond only to the time-averaged voltage of the sheath, which is much lower. This results in low-energy ion bombardment.
Meanwhile, the light electrons are highly mobile and are efficiently energized by the oscillating HF field. These energetic electrons collide with gas molecules, creating a high-density plasma rich in reactive chemical species.
Leveraging Frequency to Control Film Properties
The choice between low and high frequency directly translates to different film characteristics. Understanding this allows you to tailor the deposition process to your specific goal.
Low Frequency (LF) for Physical Compaction
Using a low-frequency source is like using a physical hammer during deposition. The high-energy ion bombardment compacts the growing film.
This process increases film density, improves adhesion, helps remove contaminants, and can be used to control the film's intrinsic stress (compressive vs. tensile). It is ideal when mechanical or electrical integrity is paramount.
High Frequency (HF) for Chemical Throughput
Using a high-frequency source is like turning up the speed of a chemical engine. The high-density plasma generates a much larger flux of radicals and ions.
This abundance of reactive species dramatically increases the chemical reaction rate at the substrate surface, resulting in a higher deposition rate. This is ideal for applications where process throughput is the primary concern.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Dual-Frequency Solution
In a single-frequency system, ion energy and plasma density are coupled. Increasing RF power to get more plasma density also increases the sheath voltage, raising ion energy. This inherent coupling limits your process window.
The Limitation of Single-Frequency Systems
With a single frequency, you cannot independently control the physical (bombardment) and chemical (deposition rate) aspects of the process. You are forced into a trade-off: high deposition rate comes with low ion energy, and high ion energy comes with a lower deposition rate.
Decoupling Control with Dual-Frequency PECVD
Modern PECVD systems overcome this by using two simultaneous frequencies. A high-frequency source (e.g., >13.56 MHz) is used to control and sustain a high-density plasma, dictating the deposition rate.
A separate low-frequency source (e.g., <1 MHz) is then applied to control the bias on the substrate, independently tuning the ion bombardment energy. This gives you two separate knobs: one for deposition rate and one for film properties.
Practical Example: Gap Filling
In semiconductor manufacturing, dual-frequency PECVD is critical for filling high-aspect-ratio trenches. The HF component provides a high flux of depositing species, while the LF component provides controlled ion bombardment.
This bombardment sputters away the film as it builds up at the top corners of the trench, preventing the opening from "pinching off" and allowing for a void-free fill from the bottom up.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your choice of frequency configuration depends entirely on the desired outcome for your thin film.
- If your primary focus is film density, stress control, or adhesion: Favor a process with a strong low-frequency component to increase ion bombardment energy.
- If your primary focus is a high deposition rate: Favor a high-frequency source to maximize plasma density and the flux of reactive species.
- If your primary focus is complex tasks like gap-fill or surface planarization: A dual-frequency system is essential to independently control the deposition chemistry and the physical sputtering.
Ultimately, mastering excitation frequency transforms PECVD from a simple deposition tool into a precise materials engineering instrument.
Summary Table:
| Frequency Type | Ion Bombardment Energy | Plasma Density | Key Effects on Film |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Frequency (e.g., 100 kHz) | High | Low | Increases density, controls stress, improves adhesion |
| High Frequency (e.g., 13.56 MHz) | Low | High | Boosts deposition rate, enhances chemical reactions |
| Dual Frequency | Independent control | Independent control | Enables gap-fill, void-free deposition, and precise tuning |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your PECVD Process with KINTEK
Struggling to balance film density, stress control, and deposition rates in your PECVD applications? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, whether you're optimizing for high-density films or rapid throughput.
Contact us today via our contact form to discuss how our tailored PECVD solutions can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and achieve superior thin-film results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does PECVD contribute to semiconductor manufacturing? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Film Deposition
- What are the drawbacks of CVD compared to PECVD? Key Limitations for Your Lab
- What is PECVD specification? A Guide to Choosing the Right System for Your Lab
- How does chemical vapour deposition (CVD) differ from PVD? Key Differences in Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What are the advantages of using CVD? Achieve High-Purity, Conformal Thin Films for Your Applications



















