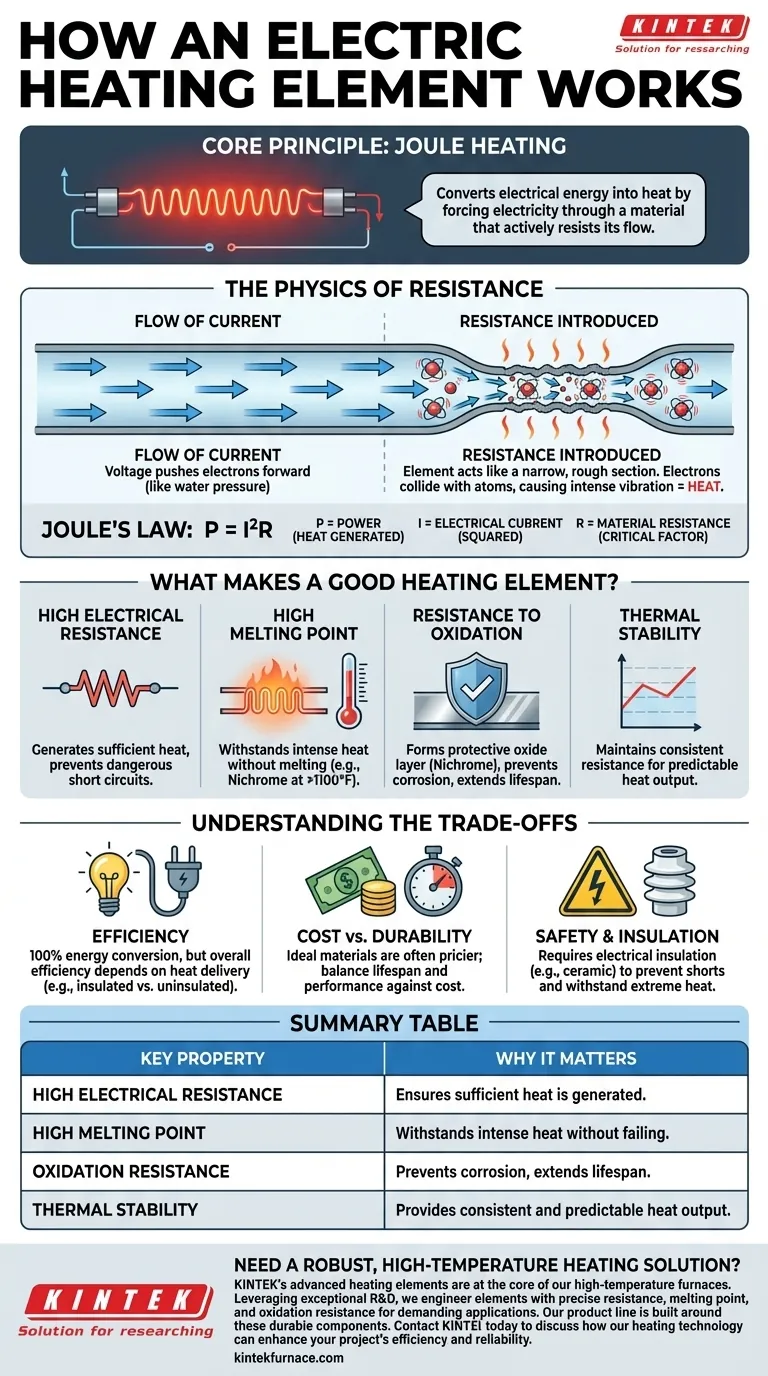
At its core, an electric heating element operates on a simple principle: it converts electrical energy into heat by forcing electricity through a material that actively resists its flow. This process, known as Joule heating, is the fundamental mechanism behind everything from electric stoves and toasters to industrial furnaces.
The key insight is not just that materials resist electricity, but that we can engineer specific materials with high, stable resistance to reliably and safely generate a predictable amount of heat from a standard electrical source.

The Physics of Electrical Resistance
To truly understand how a heating element works, we must first look at the physics of electricity and resistance at an atomic level.
The Flow of Current
Think of electricity as a flow of electrons through a conductor, similar to water flowing through a pipe. The voltage is the pressure pushing the electrons forward.
Introducing Resistance
A heating element acts like a deliberately narrow and rough section within that pipe. As electrons are forced through this resistant material, they collide with the atoms that make it up.
Atomic-Level Friction
These constant collisions cause the atoms of the element to vibrate intensely. This atomic-level vibration is what we feel and measure as heat. The material literally gets hot from the internal friction caused by the struggling electrons.
Quantifying the Heat (Joule's Law)
This relationship is described by Joule's first law (P = I²R). It tells us that the power (P), or heat generated, is a product of the electrical current (I) squared and the material's resistance (R). This formula shows why resistance is the most critical factor in designing a heating element.
What Makes a Good Heating Element?
Not just any material can be used. Heating elements are made from specialized alloys chosen for a specific combination of properties.
High Electrical Resistance
The material must have a sufficiently high resistance. If resistance is too low, the current will flow too easily, generating little heat and creating a dangerous short circuit.
High Melting Point
A heating element must be able to withstand the very high temperatures it creates without melting or deforming. A toaster element, for example, can glow red-hot at over 1,100°F (600°C).
Resistance to Oxidation
At high temperatures, many metals react with oxygen in the air, causing them to corrode and break down. Heating elements are often made of alloys like Nichrome (nickel and chromium) that form a protective outer layer of oxide, preventing further corrosion and extending their lifespan.
Thermal Stability
A good element maintains a relatively stable resistance even as its temperature changes dramatically. This ensures a consistent and predictable heat output throughout its operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the principle is simple, the engineering involves important trade-offs that affect performance, cost, and safety.
Conversion Efficiency vs. Application Efficiency
Joule heating is nearly 100% efficient at converting electrical energy into heat. The "inefficiency" in an appliance comes from how well that heat is delivered. An uninsulated space heater warms the room, but much of that heat is lost through walls and windows.
Material Cost and Durability
The ideal materials that offer high melting points and excellent oxidation resistance are often more expensive. Engineers must balance the desired lifespan and performance of an appliance against its final cost.
Safety and Insulation
Because heating elements operate at extreme temperatures, they must be properly supported and electrically insulated from their surroundings. This is often achieved using ceramic insulators, which are excellent electrical insulators and can withstand intense heat.
Applying This to Everyday Devices
Understanding this core principle helps demystify the technology you use daily.
- If your primary focus is understanding appliances: Recognize that the glowing wires in a toaster or oven are a high-resistance Nichrome alloy, engineered specifically to get hot without melting or breaking down.
- If your primary focus is electrical safety: Know that the immense heat is why elements require careful insulation and that a "short circuit" is simply a path with extremely low resistance, causing a dangerous surge of current and heat in an unintended location.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Remember that while the element itself is efficient, the overall appliance's efficiency depends entirely on how well it directs that heat to its intended target, like the food in an oven or the water in a kettle.
By understanding this principle of controlled resistance, you can see the simple, elegant physics at work in countless devices you use every day.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Why It Matters for a Heating Element |
|---|---|
| High Electrical Resistance | Ensures sufficient heat is generated from the electrical current. |
| High Melting Point | Allows the element to withstand the intense heat it produces without failing. |
| Oxidation Resistance | Prevents corrosion and extends the element's operational lifespan. |
| Thermal Stability | Provides consistent and predictable heat output during use. |
Need a robust, high-temperature heating solution for your lab or process?
KINTEK's advanced heating elements are at the core of our high-temperature furnaces. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we engineer elements with the precise resistance, melting point, and oxidation resistance required for reliable performance in demanding applications.
Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is built around these durable heating components. Combined with our strong deep customization capability, we can provide a heating solution that precisely meets your unique experimental or industrial requirements.
Contact KINTEL today to discuss how our heating technology can enhance your project's efficiency and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Ultra Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Connector Flange Power Lead for High Precision Applications
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using molybdenum-disilicide heating elements for aluminum alloy processing? (Rapid Heating Guide)
- What is the temperature range for MoSi2 heating elements? Maximize Lifespan in High-Temp Applications
- What types of molybdenum disilicide heating elements are available? Choose the Right Element for Your High-Temp Needs
- How can high temperature heating elements be customized for different applications? Tailor Elements for Peak Performance
- What is the temperature range where MoSi2 heating elements should not be used for long periods? Avoid 400-700°C to Prevent Failure














