At its core, a vacuum induction melting (VIM) furnace operates by combining two key technologies. It uses non-contact electromagnetic induction to generate intense heat within a metal and a high-purity vacuum environment to eliminate contamination from the air. This dual process melts metals and alloys while preventing oxidation and removing dissolved gas impurities, resulting in materials with superior strength and purity.
A standard furnace melts metal in open air, introducing oxygen and other impurities that weaken the final product. A VIM furnace solves this by first creating a clean, controlled vacuum and then using efficient, non-contact heating to produce exceptionally pure, high-performance metals and alloys.
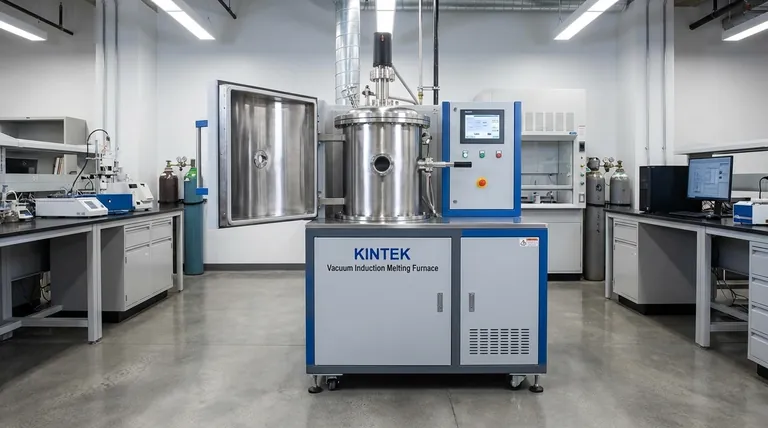

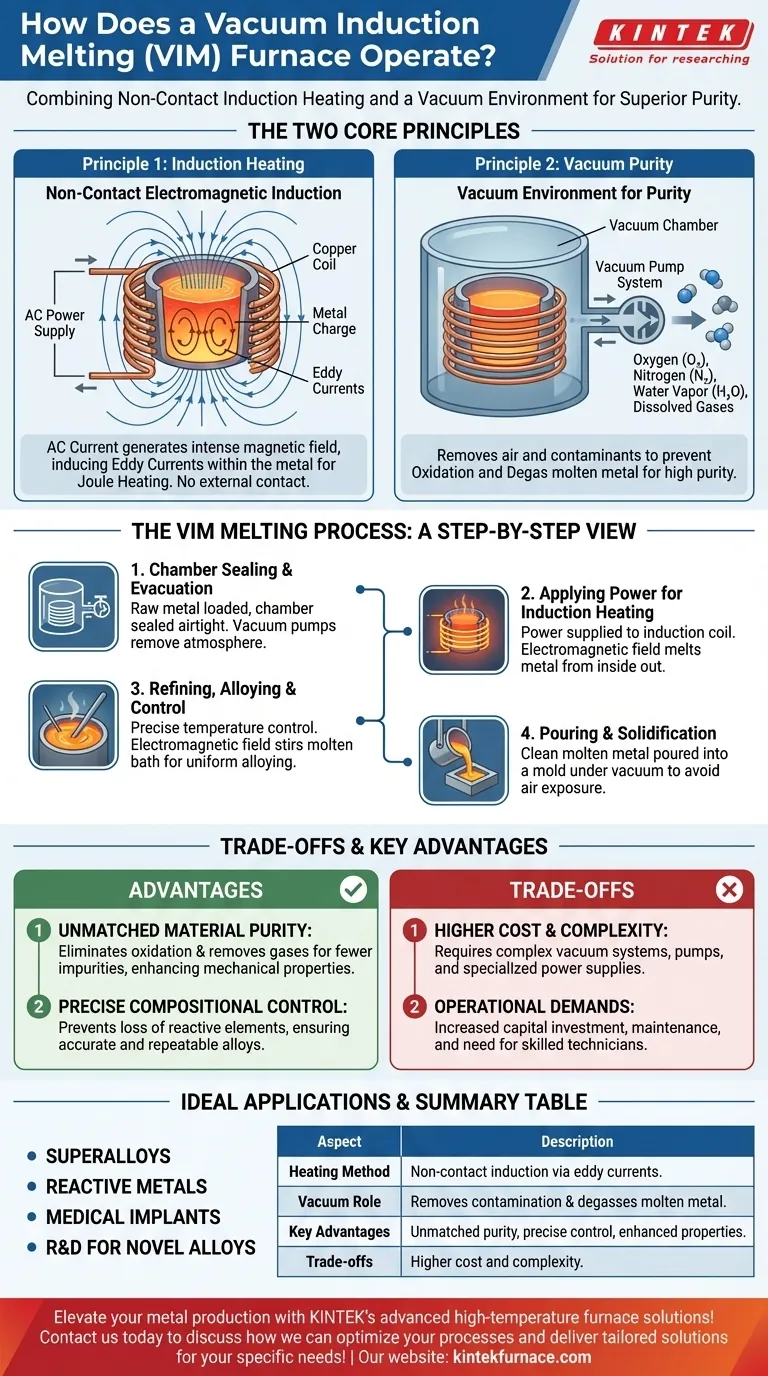
The Two Core Principles of VIM Operation
The power of a VIM furnace comes from the elegant integration of two distinct physical principles: electromagnetic induction for heating and a vacuum for purification.
Principle 1: Non-Contact Heating via Electromagnetic Induction
The heating mechanism does not rely on any external flame or heating element touching the metal. Instead, it generates heat directly within the material itself.
A high-power alternating current (AC) is passed through a copper coil that surrounds the crucible holding the metal.
This current generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field around and through the metal charge.
This magnetic field, in turn, induces strong electrical currents, known as eddy currents, to flow within the conductive metal.
The metal's natural electrical resistance opposes these eddy currents, generating immense heat through a process called Joule heating, which quickly melts the material. For magnetic materials like iron and nickel, additional heat is generated as their internal magnetic domains rapidly realign with the changing field.
Principle 2: Purity via the Vacuum Environment
The second critical component is the vacuum chamber that encloses the entire melting assembly.
Before heating begins, powerful vacuum pumps remove the air from the chamber, primarily oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor.
Removing oxygen is critical as it prevents the formation of oxides (a type of contamination) on the surface of the molten metal, which can become trapped in the final product as defects.
The vacuum also helps pull dissolved gases, such as hydrogen and nitrogen, out of the molten metal, a process known as degassing. This prevents porosity (gas bubbles) from forming as the metal solidifies, which would otherwise compromise its structural integrity.
The VIM Melting Process: A Step-by-Step View
Understanding the operational sequence clarifies how these principles work together to achieve a superior result.
1. Chamber Sealing and Evacuation
First, the raw metal charge is loaded into a crucible inside the furnace chamber. The chamber is then sealed airtight. The vacuum pump system is activated to remove the atmosphere inside, creating a high-vacuum environment.
2. Applying Power for Induction Heating
Once the desired vacuum level is reached, power is supplied to the induction coil. The electromagnetic field begins generating heat within the metal, which melts from the inside out. This process is clean, contained, and highly efficient.
3. Refining, Alloying, and Temperature Control
Operators have precise control over the melting process by adjusting the power supplied to the coil. This allows them to maintain a specific temperature with high accuracy. The electromagnetic field also naturally stirs the molten bath, ensuring any added alloying elements are mixed in uniformly.
4. Pouring and Solidification
After the metal is fully melted, refined, and meets compositional specifications, it is poured into a mold. This is often done by tilting the entire crucible assembly within the vacuum chamber, ensuring the molten metal is never exposed to air before it solidifies.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Advantages
While VIM technology is powerful, its use is dictated by a clear trade-off between performance requirements and operational complexity.
Advantage: Unmatched Material Purity
The primary benefit of VIM is the production of extremely clean metals. By eliminating reactions with air and removing dissolved gases, the final product has far fewer impurities and defects. This leads directly to enhanced mechanical properties like fatigue life, ductility, and fracture toughness.
Advantage: Precise Compositional Control
The controlled vacuum environment prevents the loss of reactive alloying elements (like titanium or aluminum) to oxidation. This allows metallurgists to formulate alloys with exceptionally precise and repeatable chemical compositions, which is impossible in an air-melt furnace.
The Trade-off: Cost and Complexity
VIM furnaces are significantly more complex and expensive than their atmospheric counterparts. The need for robust vacuum chambers, high-capacity pumping systems, and sophisticated power supplies increases both the initial capital investment and ongoing maintenance costs. Their operation requires more highly skilled technicians.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a VIM furnace depends entirely on the performance demands of the final application.
- If your primary focus is producing superalloys, reactive metals, or medical implants: VIM is the essential industry standard, as the required material purity and properties cannot be achieved otherwise.
- If your primary focus is high-volume casting of common steels or aluminum alloys: A conventional induction or arc furnace is far more cost-effective and sufficient for the task.
- If your primary focus is research and development of novel alloys: VIM provides the ultimate controlled environment for creating and testing new materials with precise, repeatable chemistry.
By understanding the VIM process, you can align your manufacturing method with the uncompromising specifications demanded by today's most advanced technologies.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Heating Method | Non-contact electromagnetic induction generates heat via eddy currents in the metal. |
| Vacuum Role | Removes oxygen and gases to prevent contamination and degas the molten metal. |
| Key Advantages | Unmatched purity, precise compositional control, and enhanced mechanical properties. |
| Ideal Applications | Superalloys, reactive metals, medical implants, and R&D for novel alloys. |
| Trade-offs | Higher cost and complexity compared to atmospheric furnaces. |
Elevate your metal production with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with cutting-edge options like Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for superior purity and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your processes and deliver tailored solutions for your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency



















