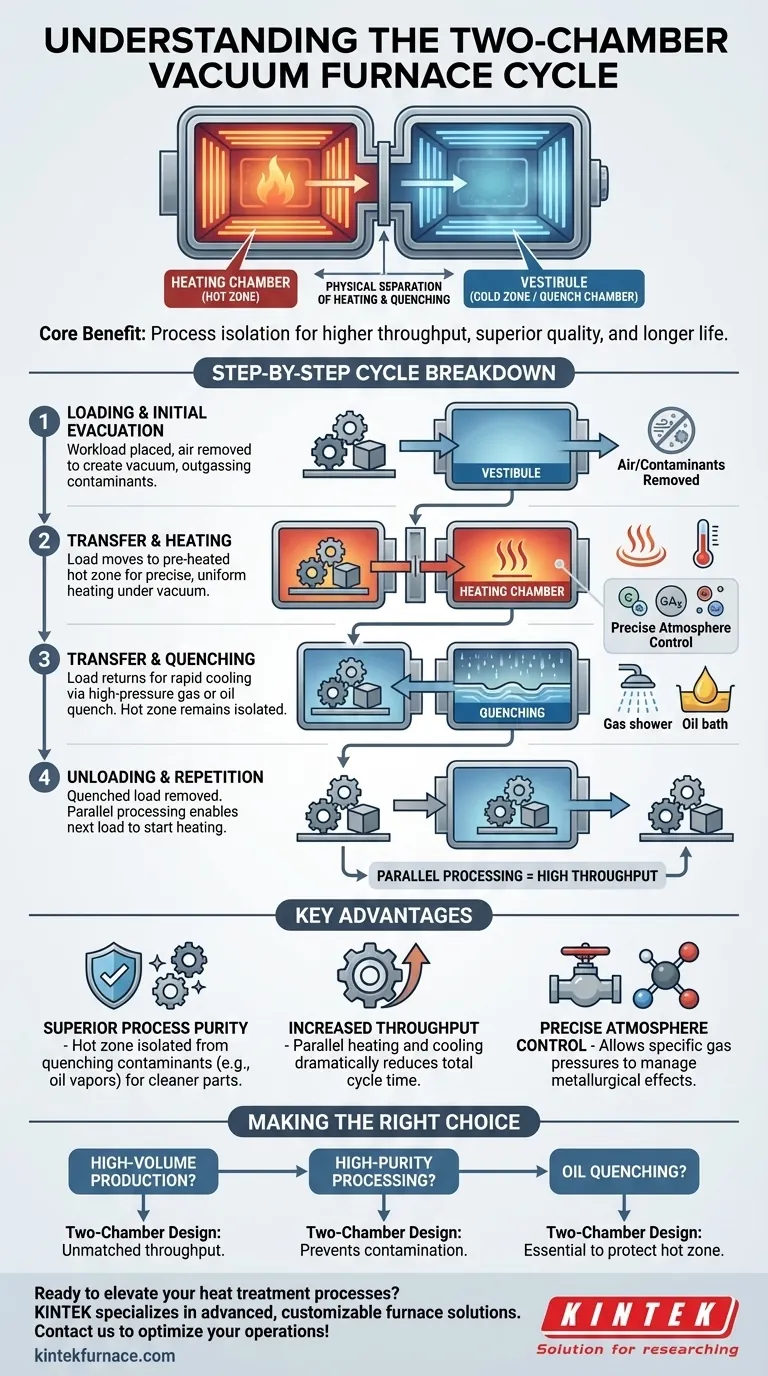
At its core, a two-chamber vacuum furnace operates by physically separating the heating and quenching stages of a heat treatment cycle. A workload is loaded into a vestibule, which is pumped down to a vacuum before an inner door opens, allowing the load to be transferred into the pre-heated hot zone. After the heating cycle, the load is moved back to the vestibule for rapid cooling (quenching) in oil or gas, while the heating chamber remains under vacuum and at temperature, ready for the next load.
The fundamental advantage of the two-chamber design is process isolation. By keeping the clean, high-temperature heating chamber separate from the quenching environment, it achieves higher throughput, superior part quality, and longer furnace life compared to single-chamber designs.

The Purpose of the Dual-Chamber Design
A vacuum furnace heats materials in a low-pressure environment to prevent oxidation and other unwanted chemical reactions. The two-chamber architecture optimizes this process by creating specialized zones for heating and cooling.
The Heating Chamber (The "Hot Zone")
This is the inner chamber, maintained at a stable vacuum and high temperature. Its sole purpose is to apply heat to the material with extreme precision and uniformity.
By never being exposed to air or quenching media, this chamber stays exceptionally clean, preventing contamination of the workload.
The Vestibule (The "Cold Zone" or "Quench Chamber")
This outer chamber serves a dual role. First, it acts as a vacuum airlock for loading and unloading parts without breaking vacuum in the hot zone.
Second, it contains the quenching system. After heating, the workload returns here for rapid cooling using either a high-pressure gas quench or by being lowered into an integrated oil tank.
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Cycle
The entire process is automated, ensuring perfect repeatability from one load to the next. The journey of a workload follows four distinct steps.
Step 1: Loading and Initial Evacuation
The workload is placed into the vestibule. The outer door is sealed, and a vacuum pumping system removes the air from this chamber. This step also serves to outgas the workload, removing volatile contaminants before they enter the pristine hot zone.
Step 2: Transfer and Heating
Once the vestibule reaches the target vacuum level, the inner door separating the two chambers opens. A transfer mechanism moves the workload from the vestibule into the heating chamber.
The inner door closes, and the material is heated to a precise temperature for a specified duration, allowing for processes like hardening, annealing, or vacuum carburizing.
Step 3: Transfer and Quenching
After the heating cycle is complete, the inner door opens again. The workload is rapidly transferred back into the vestibule.
The inner door immediately closes, isolating the hot zone. The quenching process begins in the vestibule, where high-pressure inert gas is circulated or the load is submerged in oil to achieve the desired material properties.
Step 4: Unloading and Repetition
While the first load is quenching, the hot zone is already prepared to accept the next load, which can be in the process of being evacuated in the vestibule. This parallel processing is the key to the system's high throughput.
Once the quenched load has cooled to a safe temperature, the vestibule is vented back to atmospheric pressure, and the finished parts are removed.
Understanding the Key Advantages
The two-chamber design is a solution to the inherent limitations of single-chamber furnaces, but it involves its own set of considerations.
Advantage: Superior Process Purity
The most significant benefit is isolating the hot zone from quenching contaminants. In oil quenching, oil vapors are contained within the vestibule and never enter the heating chamber, preventing carbon buildup on heating elements and insulation. This leads to cleaner parts and reduced furnace maintenance.
Advantage: Increased Throughput
Because the heating and quenching processes occur in parallel, the furnace is almost always productive. As one load is being cooled and unloaded, the next is already being heated. This dramatically reduces the total cycle time per load compared to a single-chamber furnace that must cool completely before unloading.
Advantage: Precise Atmosphere Control
The isolated hot zone allows for precise control of the atmosphere during heating. This includes using specific partial pressures of gases to manage metallurgical effects, such as suppressing the vaporization of chromium from the surface of tool steels at high temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Deciding on a furnace architecture depends entirely on your operational goals for quality, volume, and process type.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: The parallel processing capability of a two-chamber furnace offers unmatched throughput for hardening, carburizing, and other common heat treatments.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing (e.g., medical or aerospace): The isolated hot zone prevents contamination from quench media, ensuring the cleanest possible parts and process repeatability.
- If your primary focus is oil quenching: A two-chamber design is almost always required to protect the hot zone from the significant contamination caused by oil vapors.
Ultimately, the two-chamber vacuum furnace is an engineered solution to deliver both processing speed and metallurgical precision without compromise.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Description | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Loading and Initial Evacuation | Workload enters vestibule; air is removed to create vacuum, outgassing contaminants. | Prepares load, prevents contamination in hot zone. |
| Transfer and Heating | Load moves to pre-heated hot zone for precise heating under vacuum. | Ensures uniform heating, process purity, and repeatability. |
| Transfer and Quenching | Load returns to vestibule for rapid cooling with gas or oil quench. | Isolates hot zone, allows fast cooling without contamination. |
| Unloading and Repetition | Quenched load is removed; next load can be processed in parallel. | Increases throughput, reduces cycle time per load. |
Ready to elevate your heat treatment processes? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs, ensuring higher throughput, superior part quality, and longer furnace life. Contact us today to discuss how our two-chamber vacuum furnaces can optimize your operations for efficiency and purity!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today



















