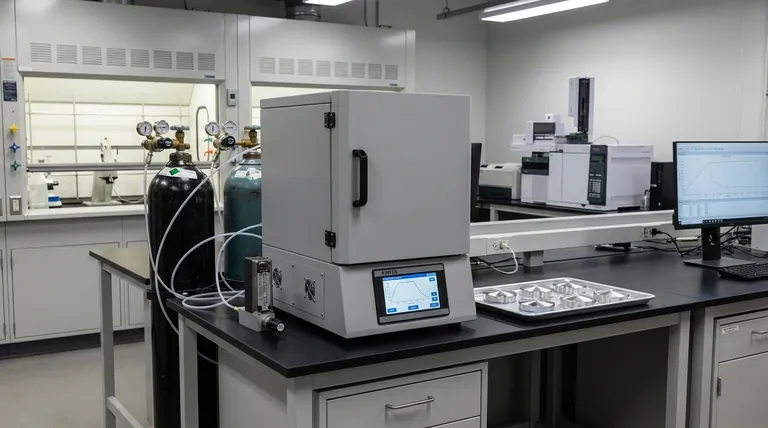
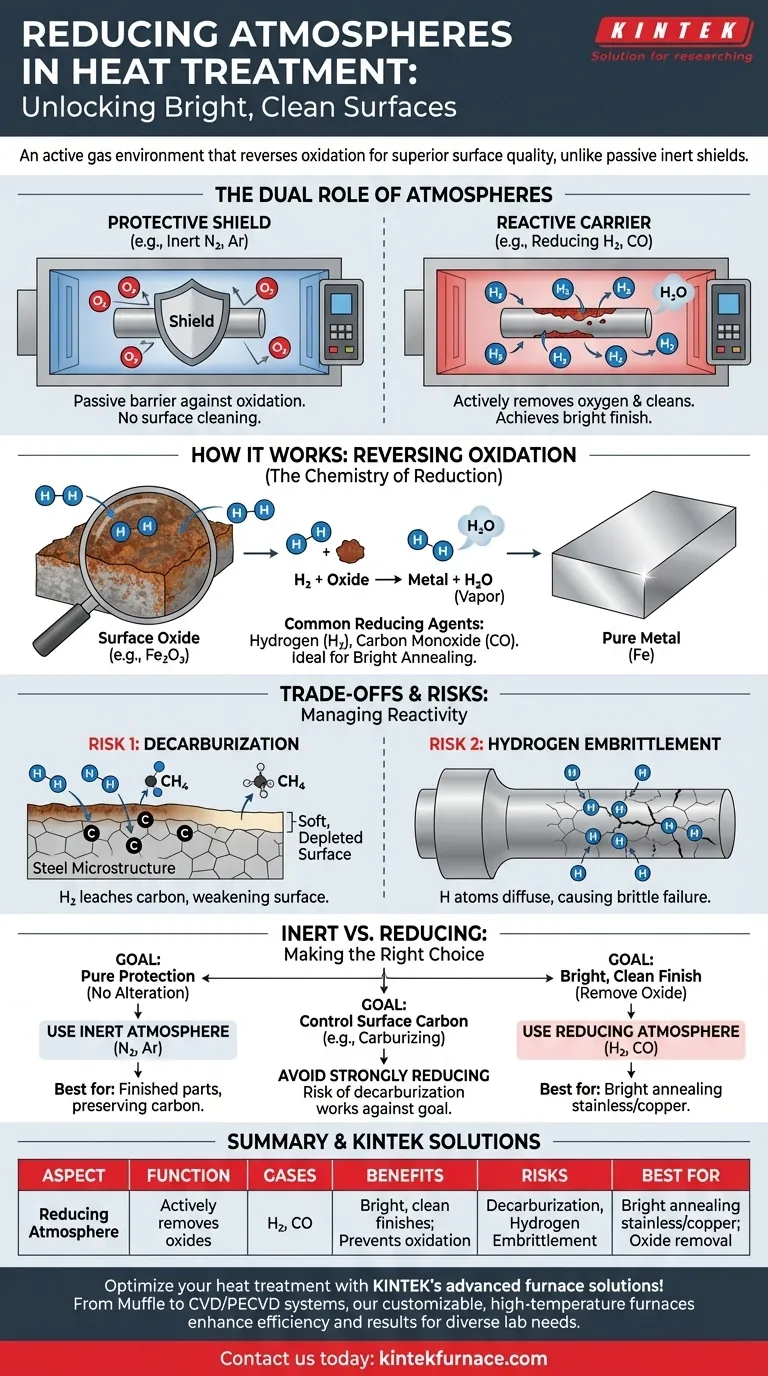
In heat treatment, a reducing atmosphere is a chemically active gas environment that reverses oxidation on a material's surface. Unlike a passive, inert atmosphere that simply shields a part from oxygen, a reducing atmosphere actively removes oxygen from existing oxides, effectively cleaning the material at a microscopic level during the heating process. This is achieved using gases like hydrogen or carbon monoxide that have a strong chemical affinity for oxygen.
The core function of a reducing atmosphere is to not only prevent oxidation but to actively remove it. This makes it a powerful tool for achieving a bright, clean surface finish, but its chemical reactivity also introduces risks, such as altering the carbon content of steel.

The Dual Role of Furnace Atmospheres
To understand the specific function of a reducing atmosphere, it's essential to first recognize the two primary roles any controlled atmosphere plays in a furnace.
The Protective Shield
At the high temperatures required for heat treatment, metals are highly susceptible to reacting with ambient air. The most common reaction is oxidation, which creates scale and discoloration on the part's surface. The first job of any controlled atmosphere is to act as a protective shield, displacing the oxygen and moisture to prevent these unwanted reactions.
The Reactive Carrier
In some processes, the atmosphere is intended to do more than just protect the part; it's meant to intentionally change its surface. The atmosphere acts as a carrier, delivering elements to the surface (like in carburizing) or removing them (like in decarburizing). A reducing atmosphere falls into this reactive category.
How a Reducing Atmosphere Works
A reducing atmosphere achieves its effect through specific chemical reactions driven by its constituent gases.
The Chemistry of Reduction
The term "reducing" is the chemical opposite of "oxidizing." While oxidation involves a material losing electrons (typically by bonding with oxygen), reduction involves a material gaining electrons. A reducing atmosphere facilitates this by introducing gases that readily bond with oxygen.
Common Reducing Agents
The most common and powerful reducing agent used in heat treatment is hydrogen (H₂). Another is carbon monoxide (CO). These gases are often part of a mixture known as an endothermic or exothermic gas.
Reversing Oxidation
When a part with surface oxide (like rust on steel, which is iron oxide) is heated in a hydrogen atmosphere, the hydrogen molecules will strip the oxygen atoms from the iron oxide. This reaction converts the oxide back into pure iron and creates water vapor, which is then carried away. This is why the process is often used for "bright annealing"—it produces a clean, bright metallic surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Side Effects
The same chemical reactivity that makes a reducing atmosphere so useful also creates potential downsides that must be carefully managed.
The Risk of Decarburization
For steels, the most significant risk is decarburization. The same hydrogen that removes oxygen can also react with the carbon in the steel's surface, forming methane (CH₄). This process leaches carbon from the surface, leaving it softer and weaker than the core material, which is often a critical failure point.
The Challenge of Hydrogen Embrittlement
Certain high-strength steels are susceptible to hydrogen embrittlement. In this phenomenon, individual hydrogen atoms can diffuse into the metal's grain structure, causing a significant loss of ductility and leading to premature, catastrophic failure under stress.
Inert vs. Reducing Atmospheres
The primary alternative is an inert atmosphere, typically using nitrogen (N₂) or argon (Ar). These gases are non-reactive. They excel at protecting the part from oxygen but will not remove any existing oxides. The choice between them depends entirely on the goal of the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct atmosphere is critical for achieving the desired material properties without introducing unintended defects.
- If your primary focus is pure protection without surface alteration: An inert atmosphere (nitrogen or argon) is the safest and most predictable choice, especially for finished parts where surface carbon must be preserved.
- If your primary focus is achieving a bright, clean finish on a part with light surface oxide: A reducing atmosphere is ideal, as it will actively clean the surface during the heat treat cycle (e.g., bright annealing stainless steel or copper).
- If your primary focus is controlling surface carbon (e.g., carburizing or neutral hardening): You must use an atmosphere with a precisely controlled carbon potential. A strongly reducing atmosphere is often unsuitable here, as its decarburizing effect would work against your goal.
Ultimately, a reducing atmosphere is a specialized tool used when its active cleaning properties are necessary to achieve the final product specification.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | Actively removes surface oxides to clean materials during heating. |
| Common Gases | Hydrogen (H₂), Carbon Monoxide (CO). |
| Benefits | Achieves bright, clean surface finishes; prevents oxidation. |
| Risks | Can cause decarburization or hydrogen embrittlement in steels. |
| Best For | Bright annealing of stainless steel or copper; processes needing oxide removal. |
Optimize your heat treatment processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.



















