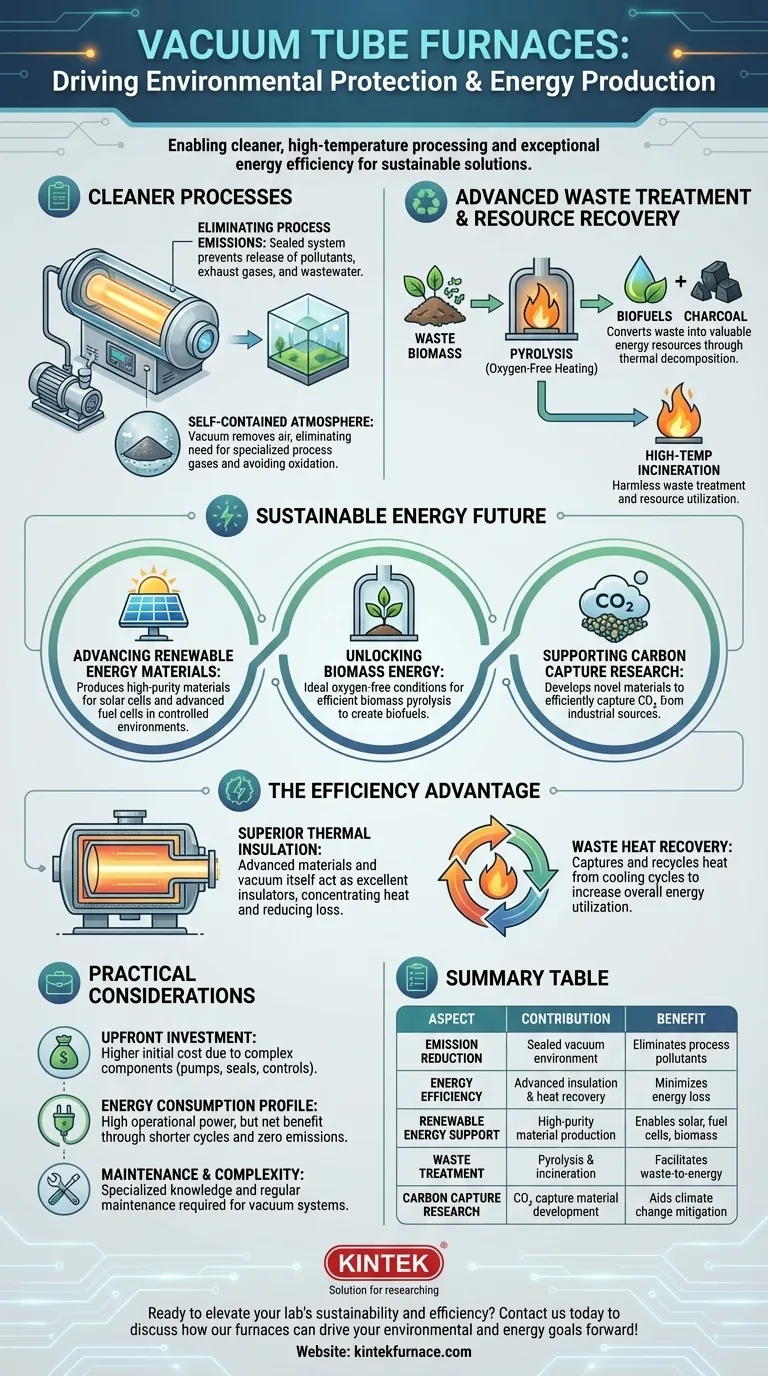
At their core, vacuum tube furnaces contribute to environmental goals in two primary ways: by enabling cleaner, high-temperature processing for waste treatment and advanced materials, and by operating with exceptional energy efficiency. They are instrumental in developing renewable energy technologies and minimizing industrial pollution through their self-contained, low-emission design.
The primary environmental advantage of a vacuum furnace is not a single feature, but its fundamental design. By creating a controlled, emission-free environment, it transforms high-temperature processes from a source of pollution into a tool for creating sustainable solutions.
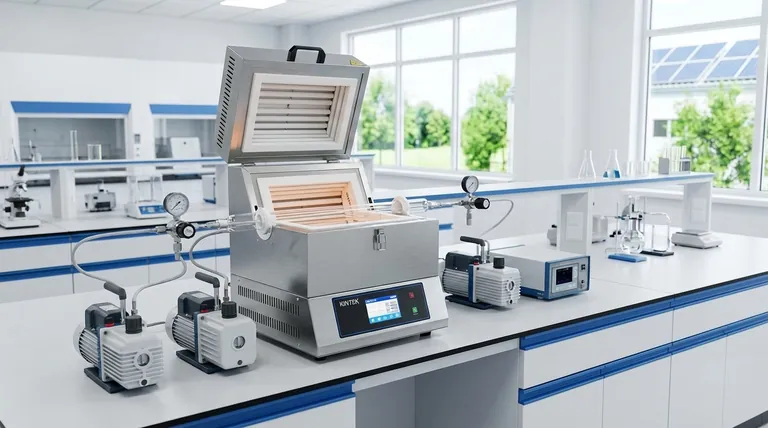

How Vacuum Furnaces Enable Cleaner Processes
A vacuum furnace's main purpose is to heat materials in an environment below atmospheric pressure. This core function has profound environmental benefits, moving high-temperature industry toward a cleaner model.
Eliminating Process Emissions
Traditional furnaces often release exhaust gases, wastewater, and other residues. A vacuum furnace, by design, is a sealed system.
This closed environment inherently prevents the release of pollutants. Because processing occurs in a vacuum, there are no waste gases to treat or wastewater to manage, directly meeting environmental standards and reducing secondary treatment costs.
A Self-Contained Atmosphere
Many industrial heating processes require a specific atmosphere to prevent the material from reacting with air, which causes oxidation and contamination.
A vacuum furnace elegantly solves this by removing the air entirely. The vacuum itself serves as the perfect, non-reactive atmosphere, eliminating the need to procure, manage, and dispose of specialized process gases.
Advanced Waste Treatment
Vacuum furnaces are critical tools for high-temperature waste disposal methods like pyrolysis and incineration.
Pyrolysis, the thermal decomposition of materials at high temperatures in the absence of oxygen, can convert waste biomass into valuable biofuels. This process achieves harmless treatment of waste while simultaneously enabling resource utilization.
Driving a Sustainable Energy Future
Beyond cleaning up existing processes, vacuum furnaces are indispensable in the research and production of next-generation energy technologies.
Advancing Renewable Energy Materials
The production of high-purity materials for solar cells and the preparation of components for advanced fuel cells require extremely clean, controlled high-temperature environments.
Vacuum furnaces provide these exact conditions, preventing impurities that would otherwise degrade the performance and efficiency of these renewable energy systems.
Unlocking Biomass Energy
Biomass pyrolysis is a key process for creating renewable energy. It requires heating organic matter (like agricultural waste) without oxygen to produce biofuels and charcoal.
The oxygen-free environment of a vacuum furnace is ideal for this application, making it a cornerstone technology in the waste-to-energy sector.
Supporting Carbon Capture Research
The development of materials and technologies for carbon capture and storage (CCS) is a critical frontier in climate science.
Researchers use vacuum furnaces to test and create novel materials that can efficiently capture CO₂ from industrial sources, directly contributing to efforts to mitigate climate change.
Understanding the Efficiency Advantage
While they perform energy-intensive work, vacuum furnaces are engineered for maximum thermal efficiency, minimizing waste.
Superior Thermal Insulation
These furnaces use advanced insulation materials and often feature a water-jacketed "cold wall" design. This concentrates heat directly on the material being processed and prevents it from escaping into the surrounding environment.
The vacuum itself also acts as an excellent insulator, further reducing heat loss and overall energy consumption.
Waste Heat Recovery
To further improve their energy footprint, some advanced vacuum furnace models incorporate waste heat recovery systems.
This technology captures heat that would otherwise be lost during the cooling cycle and recycles it, significantly increasing the overall energy utilization rate of the equipment.
Acknowledging the Practical Considerations
While highly beneficial, this technology comes with its own set of trade-offs that are important for any technical evaluation.
The Upfront Investment
Vacuum furnaces are complex, precision-engineered systems. Their initial acquisition cost is typically higher than that of simpler atmospheric furnaces due to the need for vacuum pumps, robust seals, and sophisticated controls.
Energy Consumption Profile
While highly efficient, they are still high-temperature devices that consume significant electrical power during operation. The net environmental benefit comes from shorter cycle times, higher product quality with fewer rejects, and zero process emissions, not from using minimal energy.
Maintenance and Complexity
The components that create the vacuum—pumps, seals, and gauges—require specialized knowledge and regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. This represents a different operational skill set compared to conventional furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a vacuum furnace should be aligned with your specific technical and environmental objectives.
- If your primary focus is waste-to-energy or resource recovery: The pyrolysis and high-temperature incineration capabilities in a controlled, emission-free environment are your most valuable assets.
- If your primary focus is R&D for next-gen energy: A vacuum furnace is an essential, non-negotiable tool for developing high-purity materials for fuel cells, solar panels, and carbon capture.
- If your primary focus is maximizing process efficiency and product quality: The energy savings and pollution prevention are significant co-benefits of achieving the pure, contamination-free processing environment that only a vacuum can provide.
Ultimately, adopting vacuum furnace technology is a strategic investment in process quality, operational efficiency, and environmental responsibility.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Contribution |
|---|---|
| Emission Reduction | Sealed vacuum environment eliminates process emissions and waste gases, reducing pollution. |
| Energy Efficiency | Advanced insulation and waste heat recovery systems minimize energy loss and consumption. |
| Renewable Energy Support | Enables production of high-purity materials for solar cells, fuel cells, and biomass pyrolysis. |
| Waste Treatment | Facilitates pyrolysis for converting waste to biofuels, promoting resource recovery. |
| Carbon Capture Research | Aids in developing materials for CO₂ capture, supporting climate change mitigation efforts. |
Ready to elevate your lab's sustainability and efficiency? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're focused on waste-to-energy, renewable energy R&D, or maximizing process quality, we deliver tailored solutions that reduce emissions and enhance performance. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can drive your environmental and energy goals forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety



















