At their core, silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements reduce operating costs through a combination of high energy efficiency, exceptional longevity, and minimal maintenance needs. Unlike many alternatives, they convert a higher percentage of electricity into usable heat and operate reliably for extended periods, directly cutting expenses related to energy consumption, replacement parts, and labor.
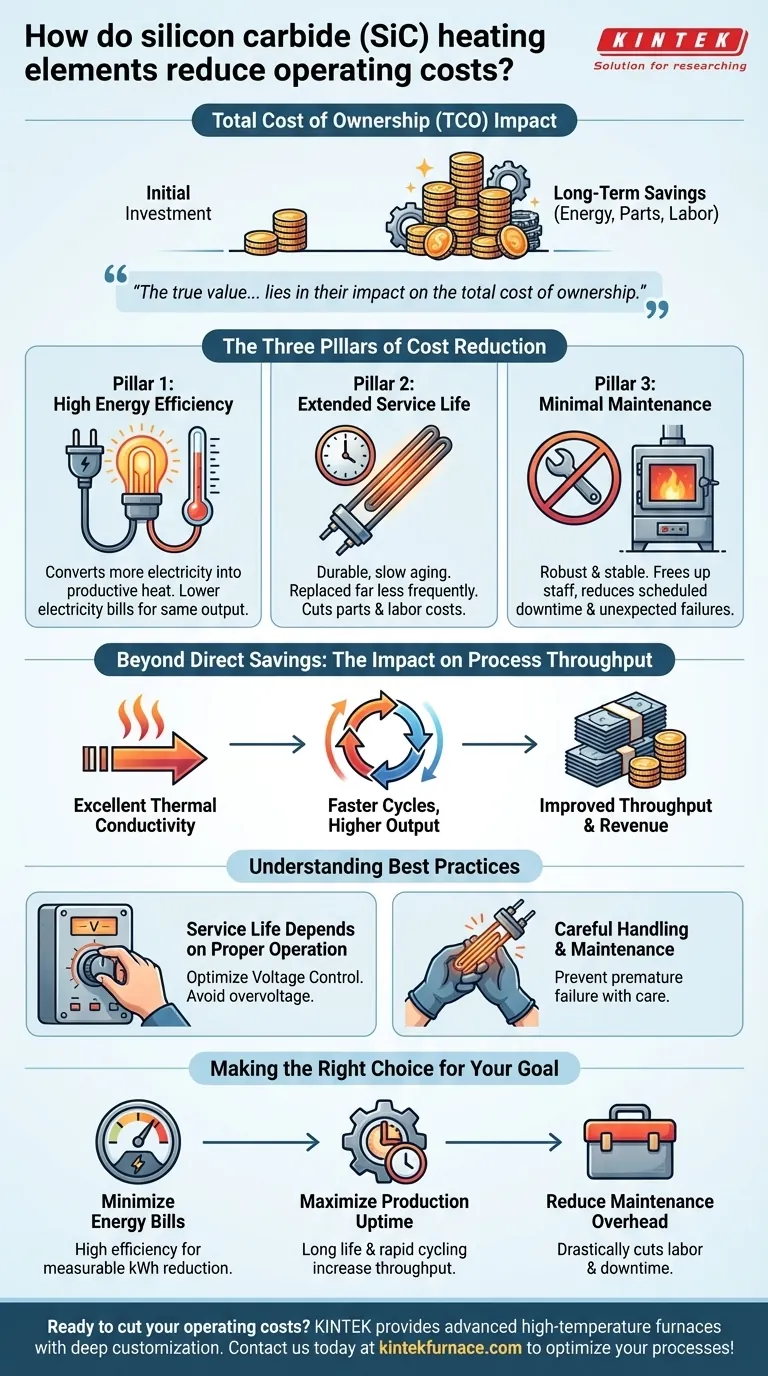
The true value of silicon carbide elements lies in their impact on the total cost of ownership. While initial investment is a factor, the significant long-term savings in energy, maintenance, and production uptime are what make them a strategically sound financial choice for high-temperature processes.
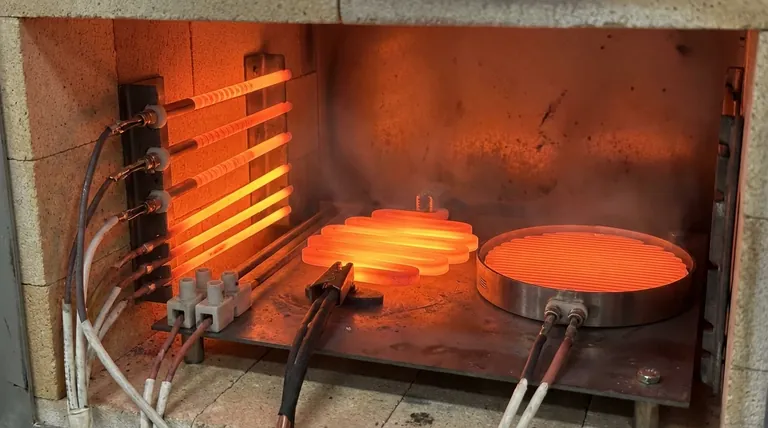

The Three Pillars of Cost Reduction
The financial benefits of SiC elements are not based on a single feature, but on the synergy of three key operational characteristics. Understanding each one provides a clear picture of how savings accumulate over time.
Pillar 1: High Energy Efficiency
Silicon carbide's material properties allow it to operate at very high temperatures with outstanding efficiency. This means more of the electrical energy consumed is converted directly into productive heat, with less being lost. This directly translates to lower electricity bills for the same thermal output compared to less efficient heating methods.
Pillar 2: Extended Service Life
SiC elements are known for their durability and slow aging characteristics. A longer operational lifespan means they need to be replaced far less frequently. This reduces not only the direct cost of purchasing new elements but also the significant indirect costs associated with production downtime and the labor required for replacement.
Pillar 3: Minimal Maintenance Requirements
The robust nature of these elements means they do not require constant adjustment, cleaning, or servicing. This low-maintenance profile frees up technical staff, reduces scheduled downtime for maintenance, and minimizes the risk of unexpected failures, leading to more predictable and cost-effective operations.
Beyond Direct Savings: The Impact on Process Throughput
The cost benefits of SiC extend beyond simple energy and maintenance savings. The physical properties of the material directly enhance the productivity of the entire heating process.
The Role of Thermal Conductivity
Silicon carbide possesses excellent thermal conductivity. In practical terms, this means it can absorb and release heat very quickly and efficiently.
Faster Cycles, Higher Output
This ability to heat up and cool down rapidly shortens the time required for each production cycle. By reducing cycle times, a facility can process more material or products in the same amount of time, effectively improving throughput and increasing revenue potential without investing in additional furnaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Best Practices
While highly cost-effective, realizing the maximum financial benefit from SiC elements requires acknowledging their operational realities. The exceptional service life is not automatic; it depends on proper use and care.
Service Life Depends on Proper Operation
The longevity of a silicon carbide element is directly influenced by its operating environment. To maximize its life and secure the expected cost savings, certain best practices must be followed.
The Impact of Operating Conditions
Factors like voltage control are critical. Running the furnace at the lowest possible voltage that still achieves the target temperature can significantly prolong element life. Likewise, careful mechanical handling during installation and regular furnace maintenance prevent premature failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To decide if SiC elements are the right fit, align their strengths with your primary operational objective.
- If your primary focus is minimizing energy bills: The high electrical-to-thermal efficiency of SiC offers a direct and measurable reduction in kilowatt-hour consumption.
- If your primary focus is maximizing production uptime: The combination of long service life and rapid thermal cycling directly increases throughput and reduces costly downtime.
- If your primary focus is reducing maintenance overhead: The inherent durability and stability of SiC elements drastically cut down on the labor and downtime associated with heater servicing and replacement.
Ultimately, adopting silicon carbide heating elements is an investment in long-term operational efficiency and financial predictability.
Summary Table:
| Cost Reduction Factor | Key Benefit | Impact on Operating Costs |
|---|---|---|
| High Energy Efficiency | Converts more electricity to heat | Lower electricity bills |
| Extended Service Life | Durable with slow aging | Fewer replacements and reduced downtime |
| Minimal Maintenance | Robust and stable operation | Less labor and fewer disruptions |
| Improved Throughput | Fast heating/cooling cycles | Higher output and revenue potential |
Ready to cut your operating costs with reliable heating solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise fit for your unique needs, delivering energy savings, reduced maintenance, and enhanced productivity. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions



















