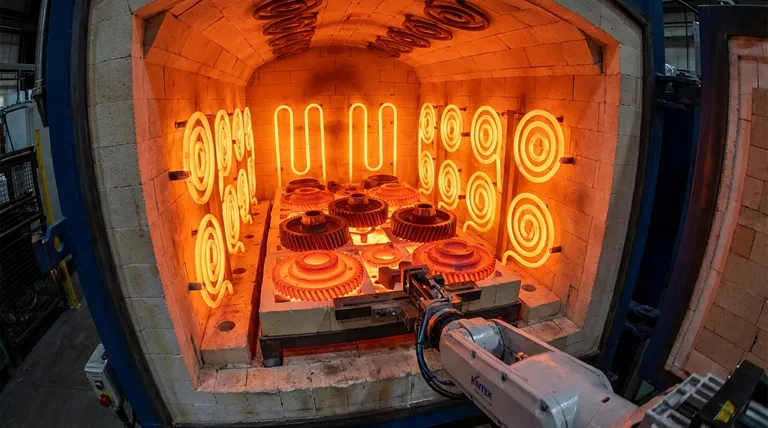
At their core, silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements benefit metal heat treatment by providing exceptionally uniform heat distribution at high temperatures. This consistency is crucial for achieving specific, repeatable metallurgical properties like hardness and strength in processes such as annealing, hardening, and sintering, ensuring every part is treated to the exact same standard.
The true value of a heating element is not just its ability to get hot, but its ability to control heat with precision. For metal heat treatment, silicon carbide provides the thermal uniformity required to transform a raw metal part into a component with predictable, high-performance mechanical properties.

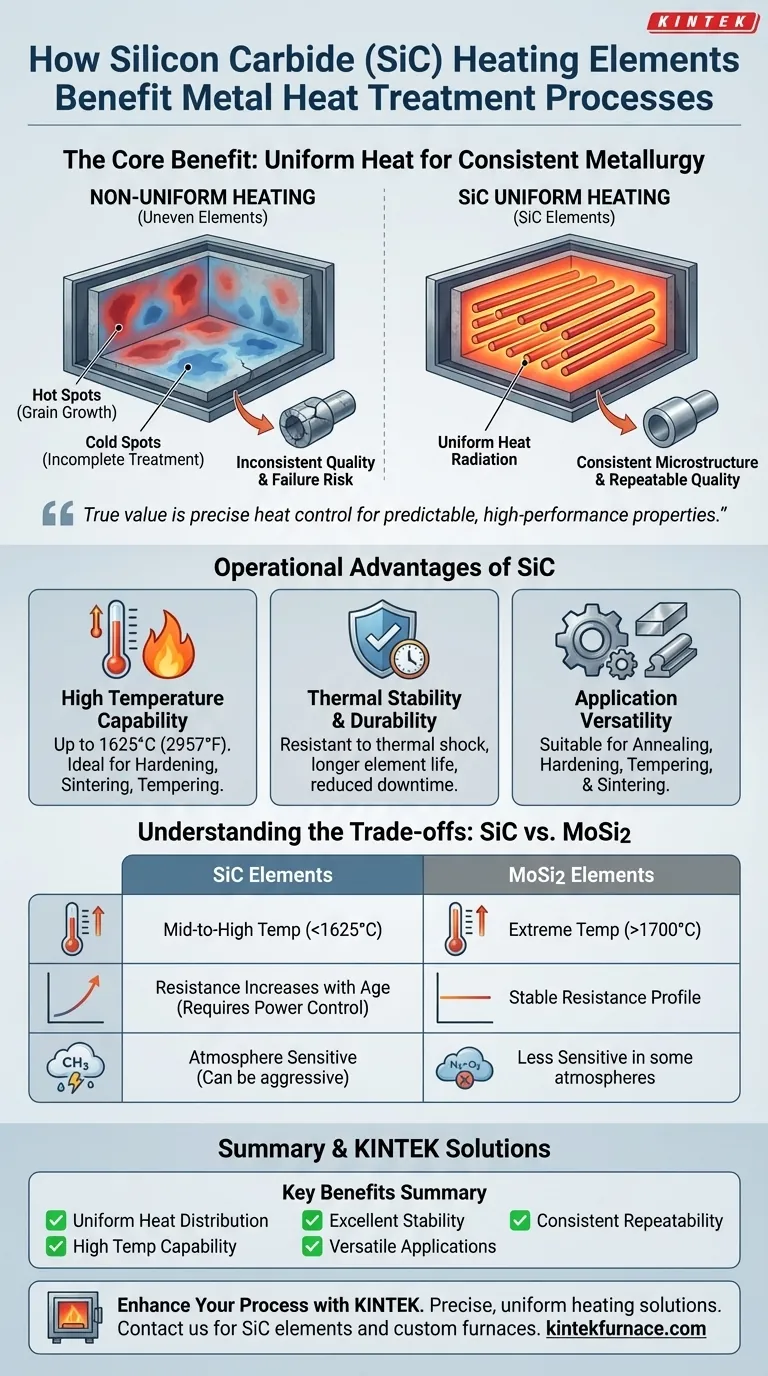
Why Uniform Heating is Non-Negotiable in Metallurgy
The goal of heat treatment is to deliberately alter a metal's internal microstructure. Any deviation in temperature, even in a small section of the furnace, can lead to failed parts and inconsistent product quality.
Achieving a Consistent Microstructure
Heat treatment processes like annealing or hardening work by forcing phase transformations within the metal's crystal structure. Non-uniform heating results in an inconsistent microstructure, creating parts with unpredictable internal stresses, variable hardness, and a higher risk of failure.
Eliminating Hot and Cold Spots
Hot spots can cause localized overheating, leading to undesirable grain growth that weakens the metal. Cold spots result in incomplete heat treatment, leaving soft spots in a supposedly hardened component. The excellent thermal conductivity of SiC elements radiates heat evenly, minimizing these critical flaws.
Ensuring Repeatability Across Batches
In an industrial setting, the first part and the thousandth part must have identical properties. SiC elements' stable and predictable performance ensures that the thermal profile of the furnace remains consistent from one batch to the next, which is fundamental to quality control.
The Operational Advantages of Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Beyond uniformity, SiC elements offer a combination of features that make them a workhorse in thermal processing industries.
High Temperature Capability
SiC elements can operate effectively at temperatures up to 1625°C (2957°F). This range makes them perfectly suited for demanding applications like the hardening of steel, tempering of alloys, and the sintering of powdered metals.
Excellent Thermal Stability and Durability
These elements are mechanically robust and highly resistant to thermal shock, allowing for faster furnace cycle times. This durability translates directly to longer element life, reduced maintenance, and less unscheduled downtime.
Application Versatility
SiC's reliability across a wide temperature band makes it suitable for numerous heat treatment processes:
- Annealing: Softening metal to improve ductility.
- Hardening: Heating and rapidly cooling steel to increase its hardness.
- Tempering: Reducing the brittleness of a hardened part.
- Sintering: Fusing metal powders together under high heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs: SiC vs. Other Elements
While powerful, SiC is not the only option. Understanding its characteristics in comparison to other common elements, like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2), is key to making an informed decision.
The Operating Temperature Window
SiC elements excel in the mid-to-high temperature range. For processes requiring extreme temperatures, typically above 1700°C (3092°F), MoSi2 elements are often the superior choice as they can reach temperatures of 1800°C (3272°F) or more.
Resistance and Aging
A defining characteristic of SiC is that its electrical resistance increases gradually over its service life. This "aging" requires a power control system (like a multi-tap transformer or an SCR) that can increase the voltage over time to maintain a constant power output. In contrast, MoSi2 elements have a more stable resistance profile at operating temperature.
Atmospheric Sensitivity
The atmosphere inside a furnace can impact element lifespan. While SiC is highly versatile, certain chemical environments or atmospheres can be aggressive. The choice between SiC and MoSi2 can sometimes depend on the specific gasses used in the heat treatment process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct heating element is a foundational engineering decision that directly impacts product quality and operational efficiency. Base your choice on the specific demands of your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is process versatility and temperatures up to 1600°C: SiC is an excellent, robust, and reliable choice for a wide range of common heat treatments like annealing, tempering, and hardening.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperatures above 1600°C: MoSi2 elements are generally required for specialized high-temperature sintering or the heat treatment of advanced alloys.
- If your primary focus is integrating with control systems: Be prepared to manage the aging characteristic of SiC with an appropriate power supply that can adjust voltage over the element's life.
Ultimately, choosing the right heating element is the first step toward achieving absolute control over your metallurgical outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Uniform Heat Distribution | Ensures consistent temperature for predictable metallurgical properties like hardness and strength. |
| High Temperature Capability | Operates effectively up to 1625°C, ideal for demanding processes such as steel hardening and sintering. |
| Excellent Thermal Stability | Resistant to thermal shock, enabling faster cycles, longer life, and reduced downtime. |
| Application Versatility | Suitable for annealing, hardening, tempering, and sintering across various metals. |
| Consistent Repeatability | Maintains stable thermal profiles for identical results across production batches. |
Ready to enhance your metal heat treatment with precise, uniform heating? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our SiC heating elements can optimize your processes for superior quality and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability



















