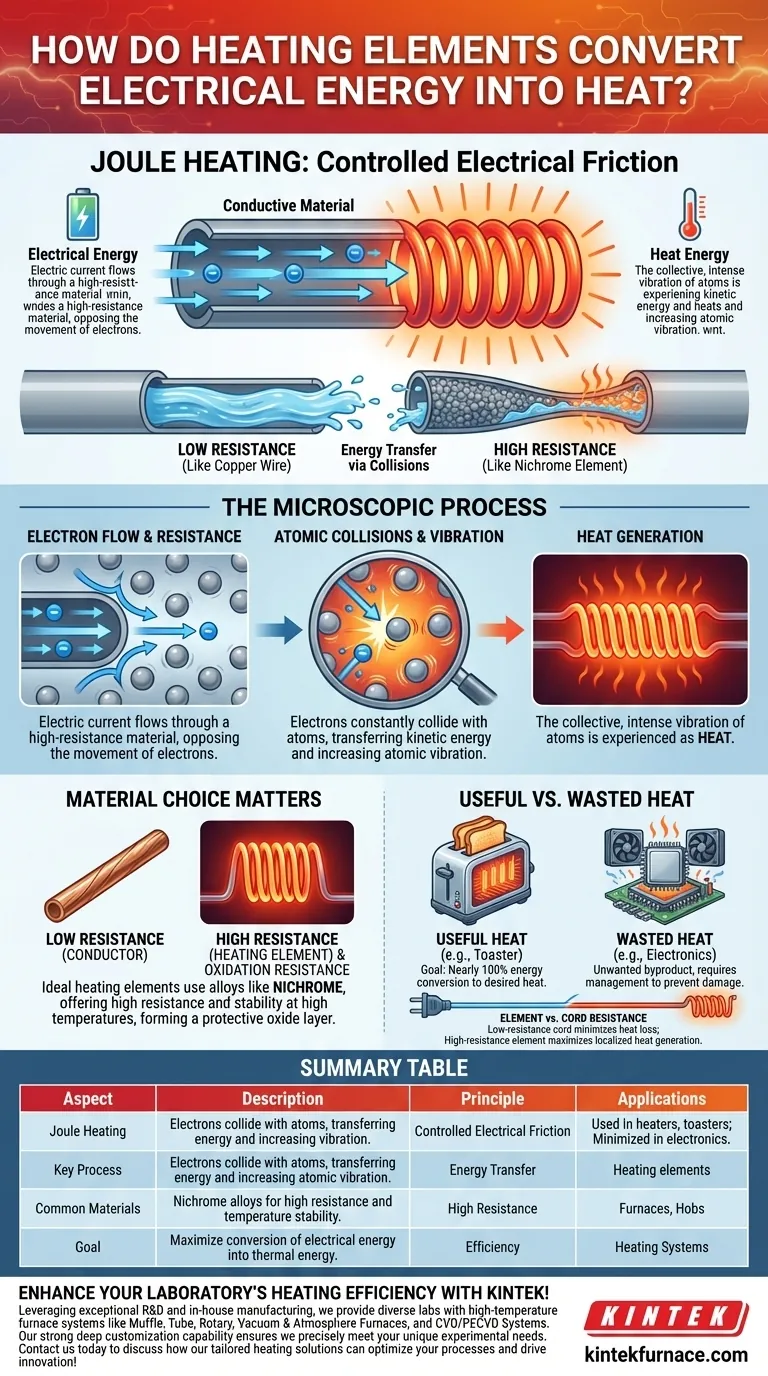
At its core, a heating element converts electrical energy into heat by deliberately resisting the flow of electricity. This process, known as Joule heating, occurs when the electrons carrying the electric current collide with the atoms of the resistive material, transferring their energy and causing the material to heat up.
Think of it as controlled electrical friction. By forcing a current through a material that "pushes back" (resists), the energy that would otherwise move electrons forward is instead converted directly into thermal energy, or heat.
The Physics of Electrical Friction
To understand how this works, we need to look at what's happening at a microscopic level. The principle is surprisingly simple and relies on the interaction between electrons and the atomic structure of a material.
What is Electrical Resistance?
Imagine water flowing through a pipe. A wide, smooth pipe offers little resistance, and water flows easily. A narrow pipe filled with gravel offers high resistance, forcing the water to work harder to get through.
In an electrical circuit, resistance is the opposition to the flow of electric current. Materials like copper have very low resistance, making them excellent conductors for wires. Materials used in heating elements have very high resistance.
From Electron Flow to Atomic Vibration
An electric current is simply a flow of electrons. When these electrons move through a high-resistance material, they constantly collide with the atoms that make up the material's structure.
Each collision transfers kinetic energy from the electron to the atom. This energy causes the atom to vibrate more intensely. This increased, collective vibration of atoms is what we perceive and measure as heat.
The Role of Material Choice
The effectiveness of a heating element depends entirely on the material it's made from. An ideal material has high electrical resistance but can also withstand very high temperatures without melting or oxidizing (rusting).
This is why alloys like nichrome (nickel-chromium) are commonly used. They are designed specifically to have high resistance and to form a protective, stable layer of oxide on their surface when heated, which prevents them from degrading over time.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The principle of Joule heating is fundamental, but its application reveals important trade-offs between desired outcomes and wasted energy.
Useful Heat vs. Wasted Energy
In an electric heater, toaster, or stove, the goal is to generate heat. In this context, the conversion of electricity to heat is nearly 100% efficient; virtually all the electrical energy becomes the desired product.
However, in most other electronic devices, this same effect is a source of waste and potential damage. The heat generated by the processor in your computer or the circuitry in your phone is an unwanted byproduct that must be managed with fans and heat sinks.
Element Resistance vs. Cord Resistance
A critical design choice is the contrast between the heating element and the power cord connected to it. The appliance's cord is made of low-resistance copper to ensure that very little heat is generated as electricity travels to the appliance.
The heating element, in contrast, is made of high-resistance nichrome to ensure maximum heat is generated exactly where it is needed. This stark difference in resistance is what allows the toaster's coils to glow red-hot while its cord remains cool to the touch.
Applying This Principle
Understanding Joule heating helps you see its deliberate application everywhere, whether it's being harnessed for warmth or minimized for performance.
- If your primary focus is generating heat (like in a space heater): The goal is to use a material with high, stable electrical resistance to maximize the conversion of electrical energy into thermal energy.
- If your primary focus is efficient electronics (like in a computer): The goal is to use materials with the lowest possible resistance (like copper or gold) for wiring and connections to minimize energy loss as unwanted heat.
This simple principle of converting electrical flow into atomic vibration is a cornerstone of modern technology, used for everything from providing comfort to enabling computation.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Principle | Joule heating converts electrical energy to heat via resistance in materials. |
| Key Process | Electrons collide with atoms, transferring energy and increasing atomic vibration. |
| Common Materials | Nichrome alloys for high resistance and temperature stability. |
| Applications | Used in heaters, toasters; minimized in electronics to reduce waste. |
Enhance your laboratory's heating efficiency with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored heating solutions can optimize your processes and drive innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control



















