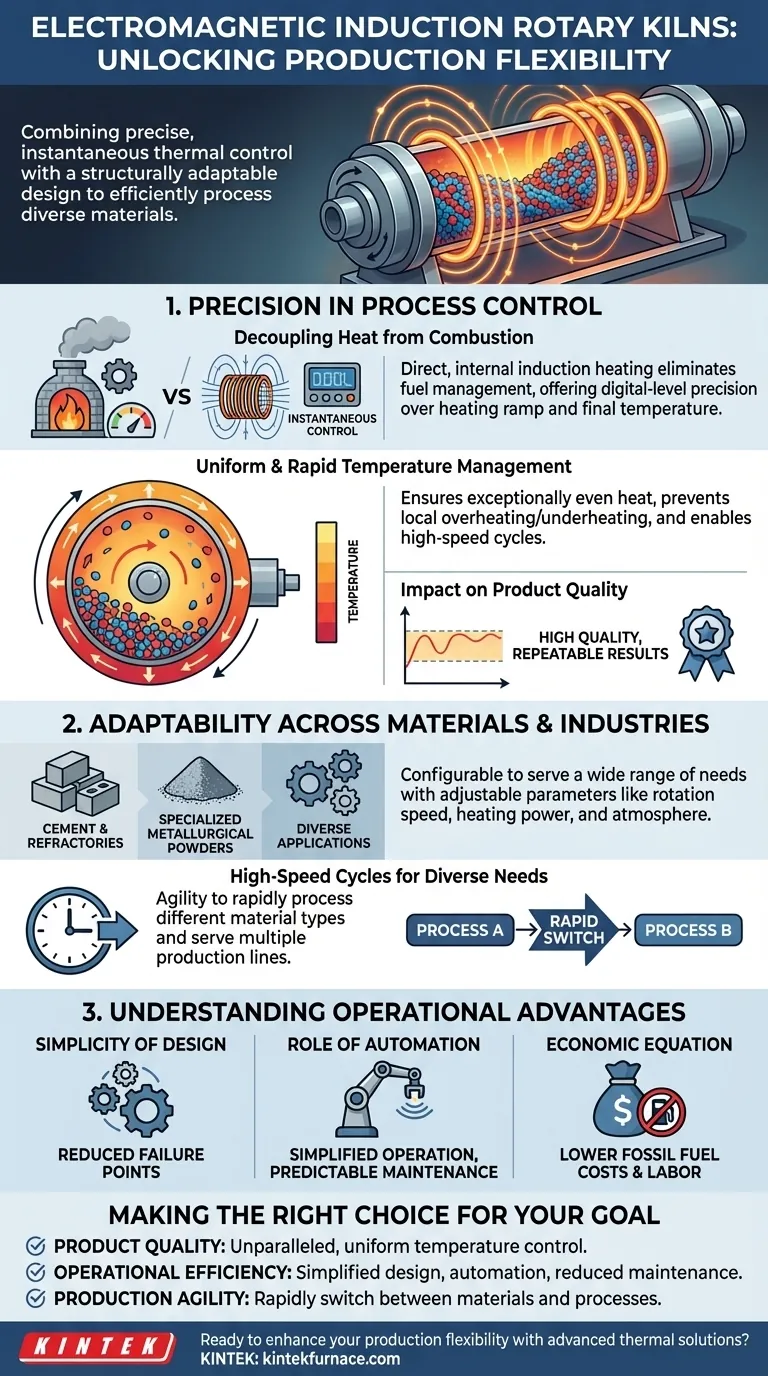
At its core, an electromagnetic induction rotary kiln enhances production flexibility by combining precise, instantaneous thermal control with a structurally adaptable design. This allows it to efficiently process a wide variety of materials and meet diverse production requirements without the operational constraints of traditional fuel-fired systems.
The fundamental advantage is not just a new way to generate heat, but a new level of control over the entire thermal process. By decoupling heat generation from combustion, electromagnetic induction gives operators digital-level precision, which is the foundation of its superior flexibility and product quality.

The Foundation: Precision in Process Control
The primary source of an induction kiln's flexibility is its unique heating method. Unlike traditional kilns that rely on the slow, indirect heat of burning fuel, induction heating is direct, internal, and instantly adjustable.
Decoupling Heat from Combustion
Traditional kilns burn gas or oil, a chemical process that is difficult to fine-tune. Electromagnetic induction uses a magnetic field to generate heat directly within the material or a susceptor, functioning more like a precise digital tool than a blunt furnace.
This eliminates the need for fuel management and allows for exact power modulation, giving operators unparalleled control over the heating ramp and final temperature.
Uniform and Rapid Temperature Management
The kiln's rotating mechanism ensures the material tumbles and exposes all surfaces to the heat source. When combined with the precision of induction, this guarantees exceptionally even temperature distribution.
This prevents local overheating or underheating, common issues in conventional kilns that lead to inconsistent product quality. The system can also achieve high-speed heating and cooling cycles, drastically reducing processing time.
The Impact on Product Quality
This level of control directly translates to repeatable, high-quality results. For processes with very narrow temperature windows, induction heating ensures the material stays within specification from batch to batch, which is critical for advanced materials and metallurgical applications.
Adaptability Across Materials and Industries
The inherent control and design simplicity make these kilns remarkably versatile. They are not built for a single purpose but can be configured to serve a wide range of industrial needs.
Structural and Process Adjustments
The core technology can be integrated into kiln structures of varying sizes and configurations. This allows them to be tailored for different materials, from cement and refractories to specialized metallurgical powders.
Process parameters, such as rotation speed, heating power, and atmosphere, can be adjusted on the fly to match the specific requirements of the material being processed.
High-Speed Cycles for Diverse Needs
The ability to perform high-speed cycles, often paired with high-pressure gas quenching, allows for the rapid processing of different material types. This agility means a single kiln can potentially serve multiple production lines, maximizing its utilization and return on investment.
Understanding the Operational Advantages
Flexibility isn't just about what you can produce; it's also about how easily and economically you can do it. Induction kilns present a significant shift in operational reality.
Simplicity of Design
By eliminating the entire fuel train—burners, pipes, storage tanks, and exhaust systems—the kiln's design becomes much simpler. This inherently reduces the number of potential failure points, leading to higher uptime and lower malfunction rates.
The Role of Automation
These kilns are built for modern automation. Advanced sensors continuously monitor key parameters, allowing the control system to make automatic adjustments. This simplifies operation, reduces the need for constant manual oversight, and makes maintenance tasks more predictable and manageable.
The Economic Equation
While the initial capital investment may differ from traditional systems, the operational economics are often more favorable. The primary savings come from eliminating fossil fuel costs and reducing the labor required for operation and maintenance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if this technology fits your needs, evaluate it against your primary production driver.
- If your primary focus is product quality and consistency: The unparalleled, uniform temperature control of an induction kiln is its single greatest advantage.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: The simplified design, reduced maintenance, and automation capabilities will deliver the most significant impact.
- If your primary focus is production agility: The ability to rapidly switch between different materials and process parameters makes this an ideal choice for multi-product environments.
Ultimately, adopting an electromagnetic induction rotary kiln is a strategic move toward a more precise, responsive, and efficient manufacturing process.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Precision Control | Direct, instantaneous heating with digital-level accuracy for uniform temperature distribution. |
| Material Adaptability | Processes diverse materials (e.g., cement, refractories, powders) with adjustable parameters. |
| Operational Efficiency | Simplified design reduces failure points, lowers maintenance, and eliminates fuel costs. |
| Production Agility | Enables rapid switching between processes and high-speed cycles for multi-product use. |
Ready to enhance your production flexibility with advanced thermal solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our induction kilns can boost your efficiency and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes



















