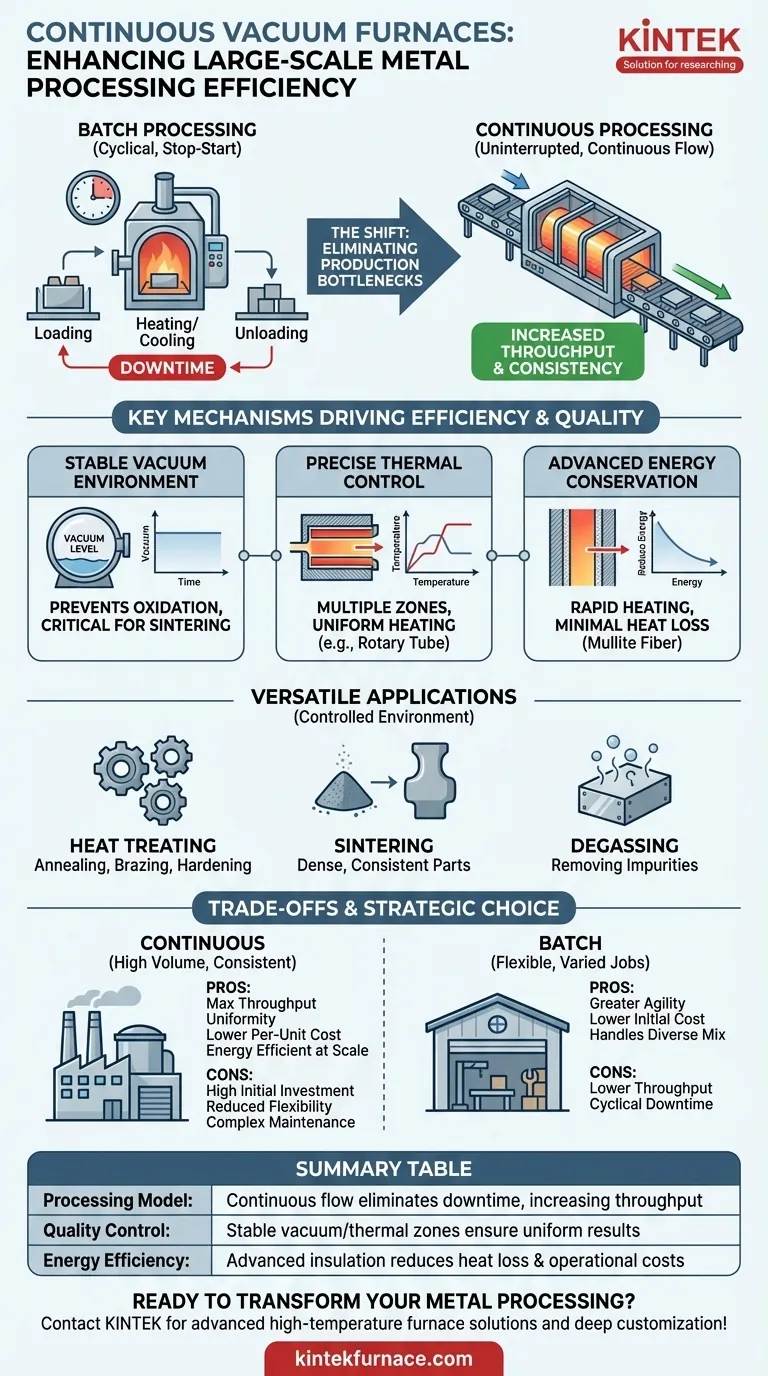
In essence, continuous vacuum furnaces enhance production efficiency by transforming metal processing from a start-and-stop batch model into an uninterrupted, continuous flow. This fundamental shift minimizes downtime between loads, drastically increases throughput, and ensures a higher degree of process consistency, which is critical for large-scale manufacturing environments.
A continuous vacuum furnace isn't just a faster heater; it's a paradigm shift in production methodology. By eliminating the cyclical downtime inherent in batch processing, it unlocks a new level of throughput, quality control, and energy efficiency for high-volume operations.
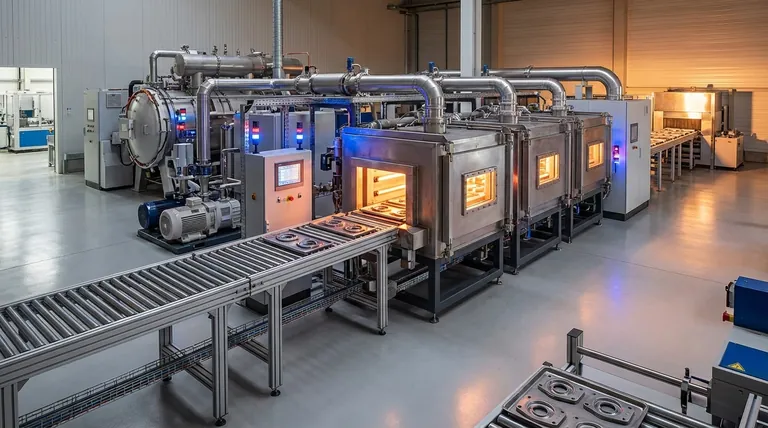

The Shift from Batch to Continuous Processing
The primary efficiency gain from a continuous vacuum furnace comes from its ability to process materials without interruption. Unlike a traditional batch furnace, which must be loaded, heated, cooled, and unloaded for every single run, a continuous system moves parts through various zones simultaneously.
Eliminating Production Bottlenecks
In a batch system, the entire furnace is a single point of failure and a significant bottleneck. The time spent cooling, unloading, and reloading is non-productive downtime.
A continuous furnace eliminates this entirely. New material is constantly fed into an entrance chamber while processed material is removed from an exit chamber, allowing the central heating and processing zones to operate without interruption.
Ensuring Process Consistency
By maintaining constant temperature profiles and stable vacuum levels across dedicated zones, continuous furnaces deliver exceptional product uniformity. Every part is exposed to the exact same conditions for the exact same duration.
This level of control is difficult to replicate in batch furnaces, where conditions can fluctuate slightly from one load to the next, impacting the final quality and consistency of the parts.
Key Mechanisms Driving Efficiency and Quality
Several core design principles enable the high efficiency and quality output of continuous vacuum furnaces. These features work in concert to create a stable, optimized processing environment.
Maintaining a Stable Vacuum Environment
A continuous vacuum is critical for preventing oxidation and other unwanted atmospheric reactions, which is paramount for high-quality metal processing.
This is especially significant for processes like vacuum sintering, where maintaining the purity, density, and consistency of metal powders and alloy materials is the primary goal.
Precise Thermal Control and Uniform Heating
Modern furnaces utilize multiple, independently controlled thermal zones. This allows for a precise heating, soaking, and cooling profile as materials move through the furnace.
Designs like rotary tube furnaces further enhance this by tumbling the material, ensuring every surface is heated uniformly. This indirect-fired design enables optimal processing conditions, driving both quality and productivity.
Advanced Energy Conservation
Efficiency is also measured in energy consumption. These furnaces often incorporate high-quality polycrystalline mullite fiber insulation, which enables rapid heating while minimizing heat loss.
Features like double-layer furnace shells and advanced air insulation technology further reduce energy usage, lowering operational costs per unit produced.
The Versatility of Continuous Vacuum Processing
While boosting throughput is a key benefit, the controlled environment of a continuous vacuum furnace makes it suitable for a wide array of sensitive thermal processes.
Heat Treating and Surface Hardening
The stable, oxygen-free environment is ideal for numerous heat treatments. This includes annealing, brazing, stress relief, and tempering.
It also excels at case hardening processes like carburizing, nitriding, and carbonitriding, where precise control over the atmosphere is essential for achieving specific surface properties.
Sintering and Degassing
For powder metallurgy, continuous vacuum sintering provides a consistent environment for creating dense, high-quality final parts.
The vacuum is also highly effective for degassing and homogenizing, removing trapped gases and impurities from metals to improve their structural integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly efficient for their intended purpose, continuous vacuum furnaces are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to making a sound investment decision.
High Initial Investment
Continuous systems are complex machines that represent a significant capital expenditure compared to smaller, simpler batch furnaces. Their economic benefit is only realized in high-volume production scenarios.
Reduced Flexibility for Varied Batches
These systems are optimized for long runs of a single product or process. They lack the flexibility of a batch furnace for operations that frequently switch between different processes, temperatures, or part types.
Maintenance and Operational Complexity
The interconnected nature of a continuous system, with its multiple zones, seals, and material handling mechanisms, can introduce more complex maintenance requirements than a standalone batch unit.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Choosing between a continuous and a batch system depends entirely on your production goals and operational scale.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, consistent production: A continuous vacuum furnace is the superior choice for maximizing throughput, ensuring uniformity, and lowering per-unit costs.
- If your primary focus is process flexibility and small, varied jobs: A traditional batch furnace offers greater agility and a lower initial investment for handling a diverse product mix.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency at scale: The advanced insulation and uninterrupted operation of a continuous furnace will deliver significant long-term energy savings in a 24/7 production environment.
Ultimately, adopting a continuous vacuum furnace is a strategic decision to optimize production flow for scale and consistency.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Processing Model | Continuous flow eliminates downtime, increasing throughput |
| Quality Control | Stable vacuum and thermal zones ensure uniform results |
| Energy Efficiency | Advanced insulation reduces heat loss and operational costs |
| Applications | Ideal for sintering, heat treating, and degassing in high-volume settings |
Ready to transform your metal processing with high-efficiency solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our continuous vacuum furnaces can boost your production efficiency and deliver superior quality for your large-scale operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- Why is a high-precision vacuum tube furnace essential for CVD graphene? Master Growth Control & Purity
- What is the working principle of a vacuum tube furnace? Master Precise High-Temperature Processing
- What is the primary function of high-purity quartz sealed tubes? Master Sb-Te Alloy Synthesis with Precision Isolation
- What role do tube furnaces play in semiconductor and battery production? Unlock Precision in High-Temp Processing



















