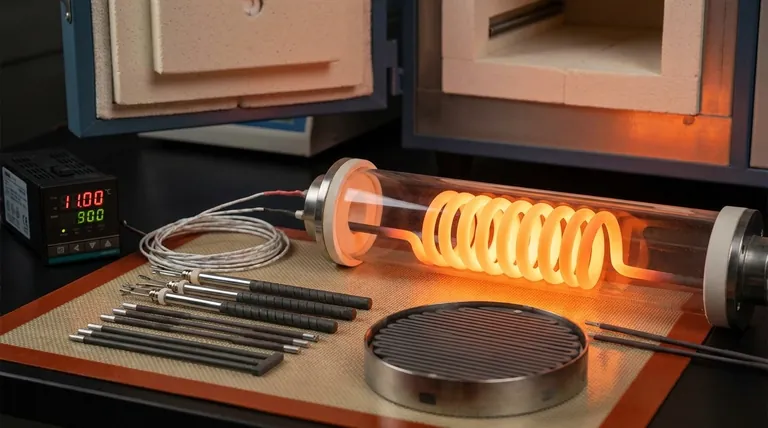
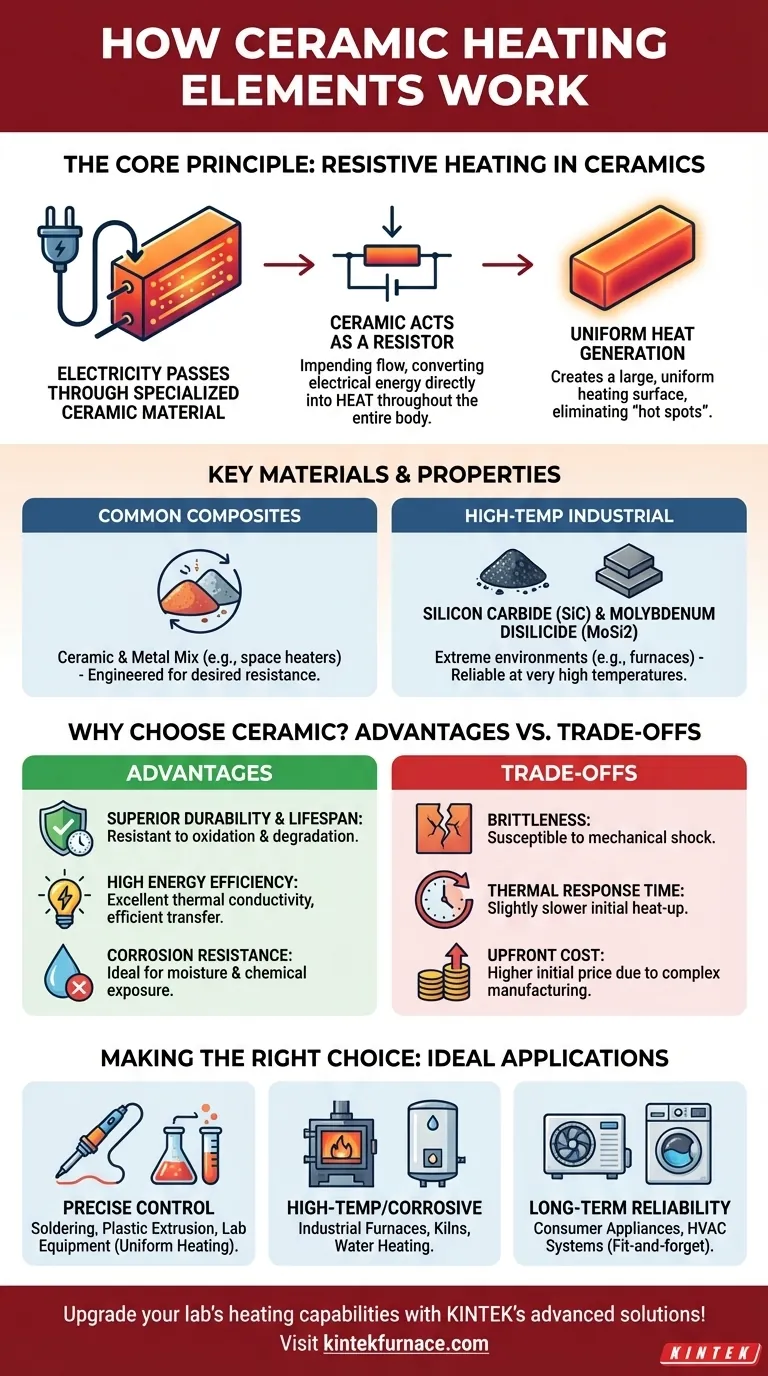
At its core, a ceramic heating element works by passing electricity through a specialized ceramic material. This material acts as a resistor, impeding the flow of electricity and converting the electrical energy directly into heat. Unlike a simple metal wire, the unique properties of the ceramic allow for highly uniform heat generation and efficient transfer, making it a stable and durable heat source.
The true advantage of ceramic heaters lies not just in creating heat, but in controlling it. Their advanced ceramic composition ensures uniform temperature, high efficiency, and exceptional resilience in demanding environments where traditional metal elements might fail.

The Core Principle: Resistive Heating in Ceramics
To understand why ceramic heaters are so effective, we must look at how the material itself functions. The process is more sophisticated than simply getting a wire hot.
The Foundation: Electrical Resistance
All resistive heaters operate on a simple principle: when an electric current flows through a material that resists it, the electrical energy is converted into thermal energy (heat). This is the fundamental mechanism at play.
The Role of Advanced Ceramics
Ceramic heating elements use semi-conductive ceramic materials, often composites. These materials are engineered to have specific levels of electrical resistance. When current is applied, heat is generated throughout the body of the ceramic component itself, not just in a thin wire.
Uniform Heat Distribution
Because the entire ceramic component heats up, it creates a large, uniform heating surface. This eliminates the "hot spots" common with wire-based elements, providing consistent and predictable thermal output, which is critical for sensitive applications.
Key Materials and Their Properties
The term "ceramic" covers a range of advanced materials, each chosen for specific performance characteristics.
Common Ceramic Composites
Many elements, particularly for consumer and light industrial use, are made from a composite of ceramic and metal. This blend is engineered to achieve the desired resistance and durability for applications like space heaters and soldering equipment.
High-Temperature Industrial Materials
For extreme environments like industrial furnaces, specialized ceramics are required. Materials like silicon carbide (SiC) and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) are used for their ability to operate reliably at very high temperatures for long periods.
Why Choose Ceramic? Key Advantages
Ceramic elements are chosen over traditional metallic ones for several distinct benefits that solve common engineering challenges.
Superior Durability and Lifespan
Ceramics are inherently resistant to oxidation and degradation at high temperatures. This gives them a significantly longer service life compared to metal elements, which can become brittle and fail over time.
High Energy Efficiency
Advanced ceramics have excellent thermal conductivity. This means the heat they generate is transferred to the target area very efficiently, with less energy wasted heating the surrounding air or internal components.
Corrosion Resistance
Unlike metals, ceramics do not rust or corrode. This makes them the ideal choice for applications involving moisture or chemical exposure, such as in water heaters or certain industrial processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is without its limitations. Being aware of the trade-offs is crucial for making an informed decision.
Brittleness and Mechanical Shock
While very hard and durable against heat, ceramics can be brittle. They are more susceptible to cracking or breaking from a sharp impact or significant mechanical vibration than a flexible metal wire element.
Thermal Response Time
Because the entire mass of the ceramic element must heat up to reach its operating temperature, its initial heat-up time can be slightly slower than an exposed, low-mass metal wire that glows hot almost instantly.
Upfront Cost
The manufacturing process for high-purity, engineered ceramic components is more complex than that for simple resistance wire. This can lead to a higher initial purchase price, though it is often offset by longer life and lower maintenance costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a ceramic heater should be based on the primary requirement of your application.
- If your primary focus is precise and stable temperature control: Ceramic is the superior choice for applications like soldering, plastic extrusion, and laboratory equipment due to its uniform heating.
- If your primary focus is operation in high-temperature or corrosive environments: Specialized ceramics are essential for industrial furnaces, kilns, and applications like water heating where metal elements would quickly degrade.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability and low maintenance: The inherent durability of ceramic elements makes them a fit-and-forget solution for consumer appliances and HVAC systems.
By leveraging the unique properties of advanced ceramics, you can achieve a level of performance, efficiency, and longevity that traditional heating elements cannot match.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Resistive heating in semi-conductive ceramics converts electricity to heat uniformly. |
| Key Materials | Composites, silicon carbide (SiC), molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) for high-temperature use. |
| Advantages | Superior durability, high energy efficiency, corrosion resistance, uniform heat distribution. |
| Trade-offs | Brittleness, slower thermal response, higher upfront cost. |
| Ideal Applications | Soldering, industrial furnaces, water heaters, laboratory equipment, HVAC systems. |
Upgrade your lab's heating capabilities with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs for enhanced efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific requirements and drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions



















