In short, verifying the presence of argon gas is not possible with the naked eye. Because argon is colorless, odorless, and inert, its existence must be confirmed either through indirect physical evidence on the product or, for definitive proof, with specialized analytical tools that can detect its unique physical or chemical properties.
The only way to be certain that argon is present is through direct measurement with a specialized detector. Indirect clues, such as manufacturing marks or product labels, only indicate the intention to include argon, not its actual presence.

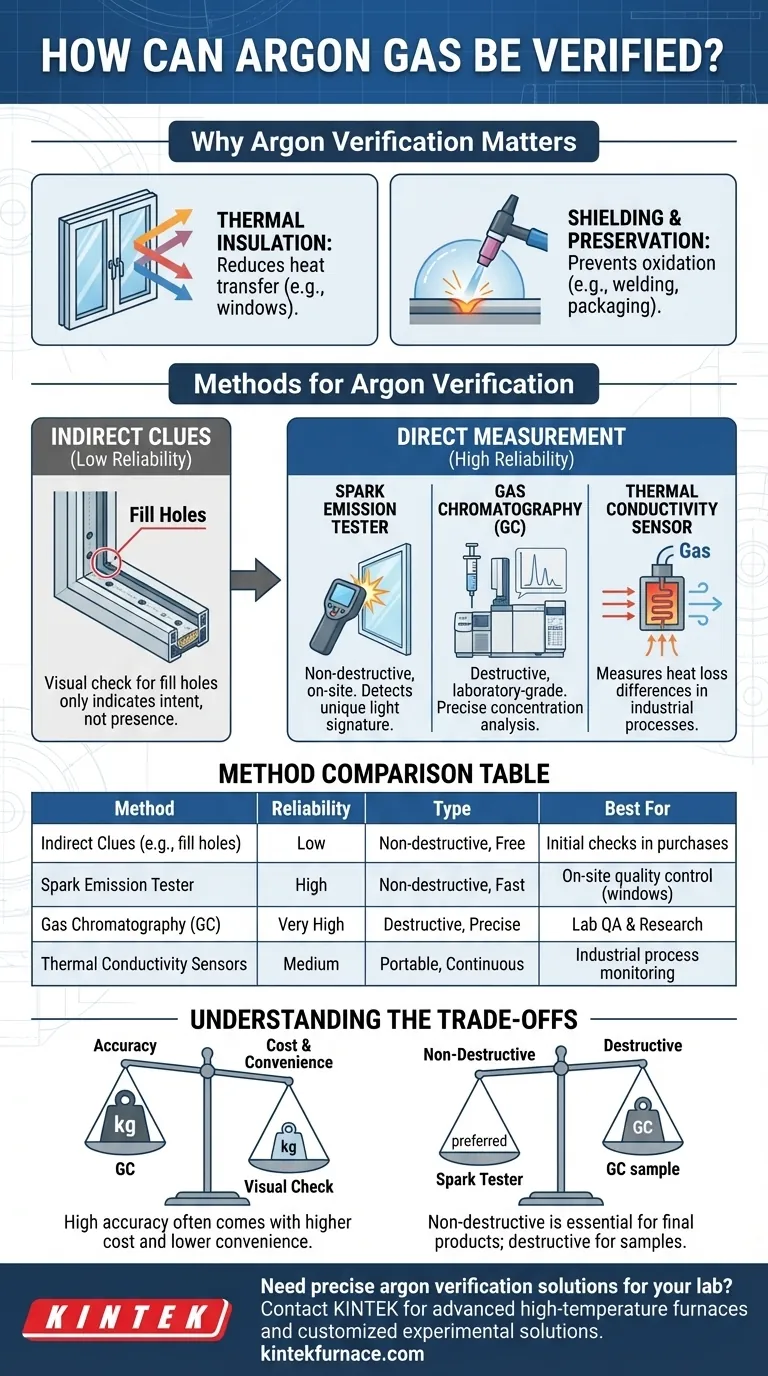
Why Argon Verification Matters
Argon is used in specific applications because it is an inert gas, meaning it does not readily react with other elements. This property makes it highly valuable for creating a protective, non-reactive environment.
For Thermal Insulation
In modern double or triple-pane windows, argon gas is sealed between the panes. Because argon is denser and has lower thermal conductivity than air, it significantly reduces heat transfer, improving the window's energy efficiency and insulation value (R-value). If the argon has leaked out, the window's performance degrades substantially.
For Shielding and Preservation
In applications like TIG or MIG welding, argon creates an oxygen-free shield around the weld point, preventing oxidation and ensuring a strong, clean weld. In food packaging or document preservation, it displaces oxygen to prevent decay and degradation. In these cases, a lack of argon leads to immediate and obvious failure of the process.
Methods for Argon Verification
Verification techniques range from simple observation, which is highly unreliable, to precise instrumental analysis. The right method depends on your need for certainty.
Indirect Clues (Low Reliability)
For manufactured goods like insulated glass units (IGUs), you can look for physical artifacts. Check the spacer bar between the glass panes for one or two small fill holes. These are used to pump the argon in and are then sealed.
The presence of these holes suggests the unit was designed to be argon-filled, but it does not confirm the gas is still present or was filled to the correct concentration. Leaks can and do occur.
Direct Measurement (High Reliability)
To definitively confirm argon's presence and concentration, you must use a specialized instrument.
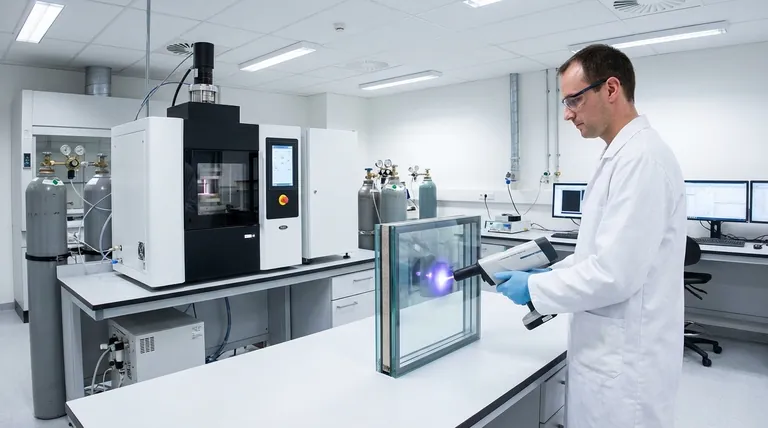
Spark Emission Testers are the most common non-destructive tool for windows. The device applies a high-voltage, low-current field to the glass, causing the gas inside to emit light (a spark). A spectrometer analyzes this light, as argon emits a unique color signature that the sensor can identify.
Gas Chromatography (GC) is a laboratory-grade technique. It involves extracting a small sample of the gas and injecting it into a machine that separates the different components. This method is extremely accurate and can measure the precise concentration of argon, but it is typically a destructive test and is not portable.
Thermal Conductivity (TC) Sensors work by measuring how quickly a heated element loses heat to the surrounding gas. Since argon has a different thermal conductivity than air, these sensors can detect its presence. They are often used in industrial process monitoring.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a verification method requires balancing accuracy, cost, and convenience. There is no single best tool for every situation.
Accuracy vs. Cost and Convenience
A visual inspection for fill holes is free and instant but provides no real assurance. It is the least reliable method.
A handheld spark tester offers a very good balance. It provides definitive, non-destructive confirmation in seconds, making it ideal for on-site quality control for windows. These tools represent a moderate investment.
Gas chromatography provides the highest possible accuracy and quantification but is expensive, slow, and often requires destroying the product's seal to obtain a sample. This is reserved for lab-based quality assurance and research.
Destructive vs. Non-Destructive Testing
For a consumer product like a sealed window, non-destructive testing is essential. You cannot drill a hole to test the gas without ruining the window. This is why spark testers are the industry standard for field verification.
In manufacturing or industrial processes, taking a sample for a destructive test like GC may be an acceptable part of routine quality control on a small percentage of products.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your need determines the right approach. Focus on the level of certainty you require.
- If your primary focus is purchasing a home or new windows: Look for the NFRC label and manufacturer specifications that state the windows are argon-filled. A visual check for fill holes is a secondary, but not definitive, clue.
- If your primary focus is quality control as an installer or inspector: Invest in a handheld, non-destructive spark emission tester. This is the only way to provide your clients with absolute certainty that the product meets specifications.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing or scientific research: Use gas chromatography for precise quantification and process validation, accepting that it is a destructive and complex laboratory test.
Ultimately, choosing the right verification method is about managing risk and ensuring the product or process performs as designed.
Summary Table:
| Method | Reliability | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Indirect Clues (e.g., fill holes) | Low | Non-destructive, free, instant | Initial checks in window purchases |
| Spark Emission Tester | High | Non-destructive, fast, identifies argon via light spectrum | On-site quality control for windows |
| Gas Chromatography (GC) | Very High | Destructive, precise concentration measurement | Laboratory research and manufacturing QA |
| Thermal Conductivity Sensors | Medium | Measures heat loss differences, portable | Industrial process monitoring |
Need precise argon verification solutions for your lab? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can meet your unique experimental needs, enhancing accuracy and efficiency in gas detection and beyond. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can benefit your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering SPS Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
People Also Ask
- What are the process advantages of using SPS for protonic ceramic electrolytes? Achieve Rapid Densification
- What are the advantages of Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS)? Enhance Thermoelectric Performance in Copper Sulfide
- What are the advantages of benchtop SPS/FAST for titanium R&D? Accelerate Your Microstructural Engineering
- Why is Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) preferred for Ba0.95La0.05FeO3-δ ceramics? Achieve High Density Fast
- How does Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) offer technical advantages over traditional sintering? Achieve Rapid Densification


