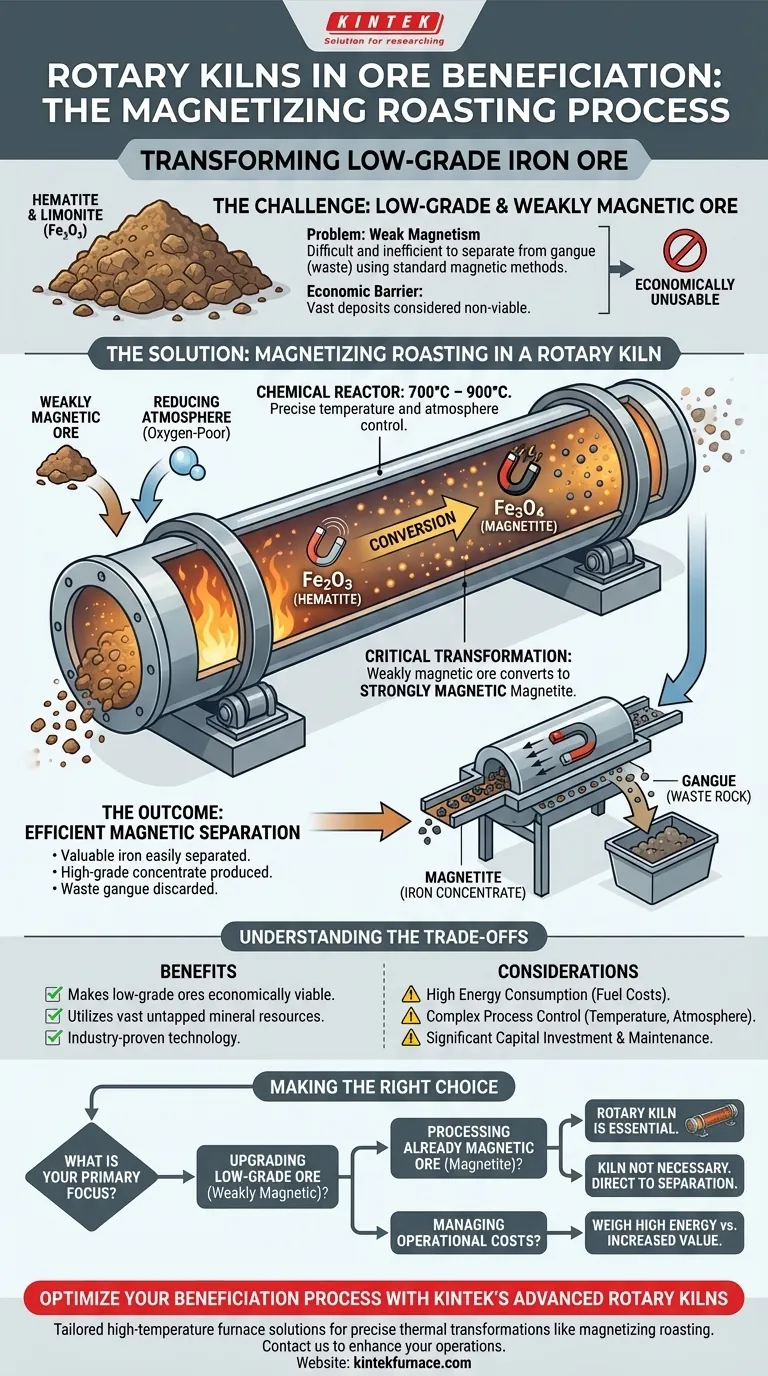
In the context of ore beneficiation, a rotary kiln's primary function is to thermally transform low-grade, weakly magnetic iron ore into a strongly magnetic state. This process, known as magnetizing roasting, makes the valuable iron easily separable from waste rock using standard magnetic separation techniques.
The rotary kiln is not just a heater; it is a chemical reactor. It alters the fundamental magnetic properties of iron ore, making it possible to economically extract iron from deposits that would otherwise be unusable.

The Challenge of Low-Grade Ore
Ore beneficiation is the industrial process of enriching ore by removing the non-valuable material, known as gangue. The goal is to increase the concentration of the desired metal before it moves to the smelting phase.
The Problem with Weak Magnetism
Many significant iron ore deposits, such as hematite (Fe₂O₃) and limonite, are only weakly magnetic. This property makes it difficult and inefficient to separate the iron-bearing particles from the gangue using simple and cost-effective magnetic separators.
The Economic Barrier
Without an effective way to concentrate these ores, they are often considered low-grade and may not be economically viable to process. This leaves vast mineral resources untapped.
How the Rotary Kiln Solves the Problem
The rotary kiln enables a process called magnetizing roasting, which is a form of reduction. It directly addresses the weak magnetism problem by inducing a specific chemical change in the ore.
Creating a Controlled Environment
A rotary kiln is a long, rotating cylindrical furnace. It heats the ore to a precise temperature, typically between 700°C and 900°C, within a carefully controlled, oxygen-poor (reducing) atmosphere.
The Critical Transformation
Inside the kiln, the heat and reducing atmosphere cause the weakly magnetic hematite (Fe₂O₃) to convert into magnetite (Fe₃O₄). Magnetite is a form of iron oxide that is strongly magnetic.
Enabling Magnetic Separation
Once the ore exits the kiln and cools, the newly formed magnetite can be easily and efficiently captured by magnetic separators. The non-magnetic gangue is discarded, resulting in a high-grade iron concentrate ready for further processing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, using a rotary kiln for magnetizing roasting involves significant operational considerations. Understanding these is critical for process design and economic viability.
High Energy Consumption
Heating immense volumes of rock to very high temperatures is an energy-intensive process. Fuel costs represent a major component of the operational expense and must be carefully factored into the project's economics.
Process Control Complexity
The transformation from hematite to magnetite requires precise control over temperature, residence time in the kiln, and the composition of the internal atmosphere. Any deviation can lead to incomplete conversion or the creation of other, less desirable iron compounds.
Capital Investment and Maintenance
Rotary kilns are large, heavy-duty pieces of industrial equipment that represent a significant upfront capital investment. They also require regular maintenance, particularly of the refractory lining that protects the steel shell from extreme heat.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to integrate a rotary kiln into a beneficiation circuit is dictated entirely by the characteristics of the ore deposit.
- If your primary focus is upgrading low-grade, weakly magnetic iron ores: A rotary kiln for magnetizing roasting is an essential and industry-proven technology to make these resources viable.
- If your primary focus is processing ore that is already strongly magnetic (magnetite): A kiln is not necessary for this step, as the ore can proceed directly to magnetic separation.
- If your primary focus is managing operational costs: The high energy requirement of the kiln is a critical variable that must be weighed against the increased value of the final iron concentrate.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln acts as a transformative tool, turning a challenging mineral resource into a valuable industrial asset.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Thermally transform weakly magnetic iron ore (e.g., hematite) into strongly magnetic magnetite via magnetizing roasting. |
| Key Process | Reduction in a controlled, oxygen-poor atmosphere at 700°C–900°C. |
| Benefits | Enables efficient magnetic separation, making low-grade ores economically viable. |
| Challenges | High energy consumption, precise process control required, significant capital investment and maintenance. |
| Ideal Use Case | Upgrading low-grade, weakly magnetic iron ores like hematite and limonite. |
Optimize Your Beneficiation Process with KINTEK's Advanced Rotary Kilns
Struggling with low-grade iron ore that's hard to process? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for your lab's needs. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is designed to handle precise thermal transformations like magnetizing roasting. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure our equipment meets your unique experimental requirements, boosting efficiency and economic viability.
Ready to enhance your ore beneficiation? Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can transform your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions



















