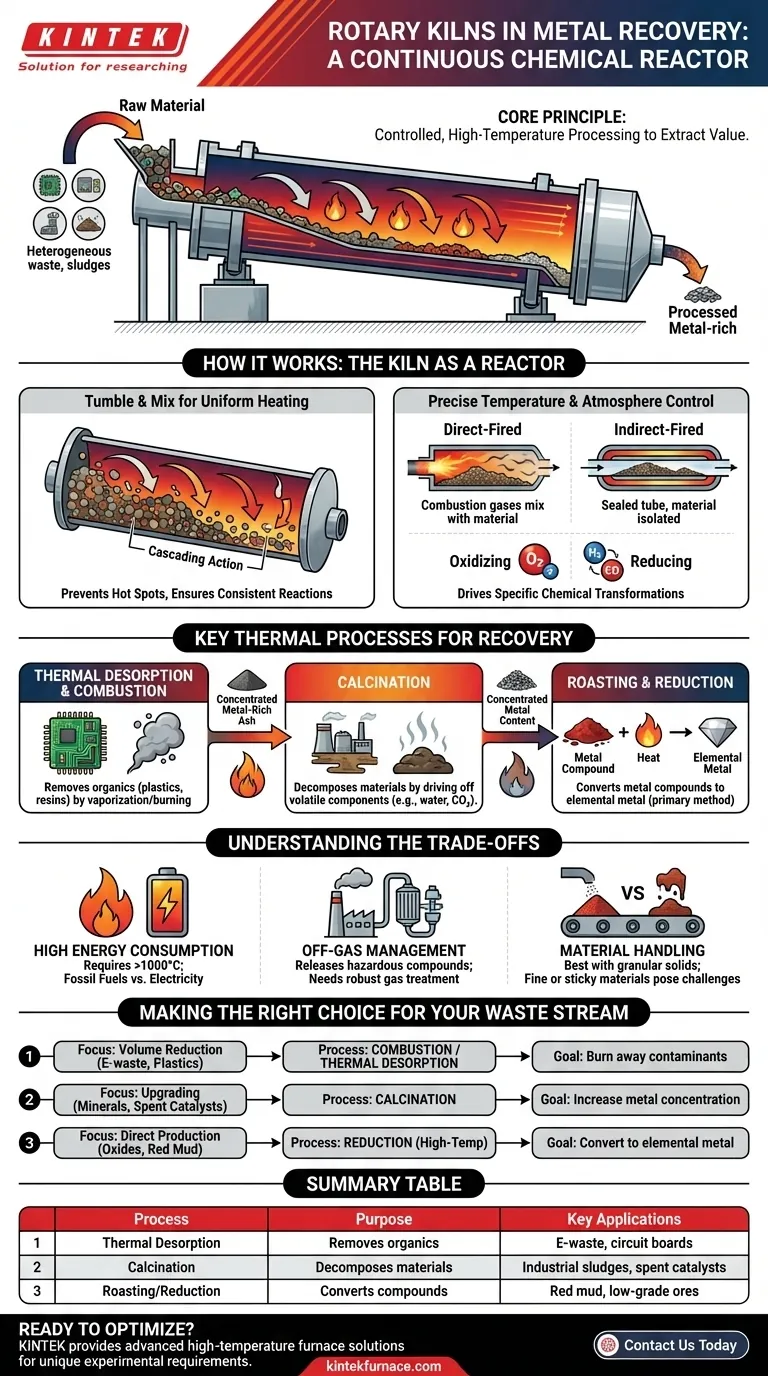
At their core, rotary kilns recover metals by using controlled, high-temperature processing. They function as large, rotating industrial furnaces that subject metal-bearing waste materials to a specific thermal and chemical environment. This precisely managed process is designed to either physically separate contaminants or chemically transform metal compounds into a more easily recoverable form.
The challenge in metal recovery is separating valuable metals from complex, heterogeneous waste streams. A rotary kiln solves this not by simply melting, but by acting as a continuous chemical reactor that uses heat, motion, and a controlled atmosphere to drive specific physical and chemical transformations.

The Core Principle: A Continuous Chemical Reactor
A rotary kiln is far more than a simple furnace. Its unique design creates an ideal environment for the difficult task of extracting value from industrial by-products, e-waste, and spent materials.
Tumble and Mix for Uniform Heating
The gentle slope and constant rotation of the kiln cause the material to tumble and mix as it travels through the chamber. This tumbling action, known as cascading, ensures every particle is exposed to the heat source uniformly.
This continuous agitation prevents hot spots and guarantees that the desired chemical reactions occur consistently throughout the entire batch of material.
Precise Temperature and Atmosphere Control
The long cylindrical body of a kiln allows for the creation of distinct temperature zones. This enables multi-stage processes to occur within a single piece of equipment.
Furthermore, kilns can be direct-fired (where combustion gases mix with the material) or indirect-fired (where the material is isolated in a sealed tube). This control is critical for managing the chemical atmosphere, allowing operators to create an oxidizing or reducing environment to drive specific reactions.
Key Thermal Processes for Metal Recovery
Different waste streams require different thermal treatments. Rotary kilns are versatile enough to perform several key processes necessary for metal recovery.
Thermal Desorption and Combustion
For waste like e-waste or shredded circuit boards, the first step is often removing organic components like plastics and resins.
A kiln heats the material to a temperature high enough to vaporize (desorb) or burn off (combust) these organic fractions, leaving behind a concentrated, metal-rich ash for further processing.
Calcination
Calcination is a process that uses heat to decompose a material by driving off volatile components, such as carbon dioxide or water.
In metal recovery, this is used on materials like industrial sludges or spent catalysts to remove bound water or carbonates. This concentrates the metal content and prepares it for subsequent recovery steps.
Roasting and Reduction
This is often the most critical chemical step. Roasting uses heat and a specific atmosphere to convert metal compounds (like sulfides) into a more reactive form (like oxides).
Reduction then uses high temperatures and a reducing atmosphere (low in oxygen) to strip oxygen atoms from metal oxides, converting them back into their elemental metallic form. This is a primary method for processing materials like red mud or certain low-grade ores.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, using a rotary kiln involves important considerations that impact operational efficiency and environmental compliance.
High Energy Consumption
Achieving temperatures needed for calcination or reduction (often over 1000°C) is energy-intensive. The choice between fossil fuels and electricity for heating the kiln is a major factor in both operational cost and environmental footprint.
Off-Gas Management
Heating complex waste materials, especially e-waste or batteries, can release hazardous volatile compounds and create toxic off-gases. An effective kiln system must include a robust gas handling and treatment system to capture and neutralize these emissions before they are released into the atmosphere.
Material Handling and Suitability
Rotary kilns perform best with granular, relatively free-flowing solids. Materials that are very fine, sticky, or prone to agglomeration can pose significant handling challenges, potentially reducing the efficiency of the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Waste Stream
The optimal kiln process depends entirely on the material you are processing and the metal you intend to recover.
- If your primary focus is volume reduction of organic-rich waste (e-waste, plastics): Your key process will be combustion and thermal desorption to burn away contaminants and concentrate the inorganic metal fraction.
- If your primary focus is upgrading minerals or spent catalysts: Your key process will be calcination to drive off water or CO2, increasing the concentration of the target metal oxide.
- If your primary focus is direct metal production from oxides (e.g., red mud, zinc oxides): Your key process will be high-temperature reduction in a carefully controlled, oxygen-poor atmosphere to convert the oxides into elemental metal.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln is a uniquely versatile tool that enables the crucial chemical transformations required to turn complex industrial waste back into valuable resources.
Summary Table:
| Process | Purpose | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Desorption | Removes organic components | E-waste, circuit boards |
| Calcination | Decomposes materials to concentrate metals | Industrial sludges, spent catalysts |
| Roasting/Reduction | Converts compounds to elemental metals | Red mud, low-grade ores |
Ready to optimize your metal recovery process? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance efficiency and yield for your specific waste streams!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing



















