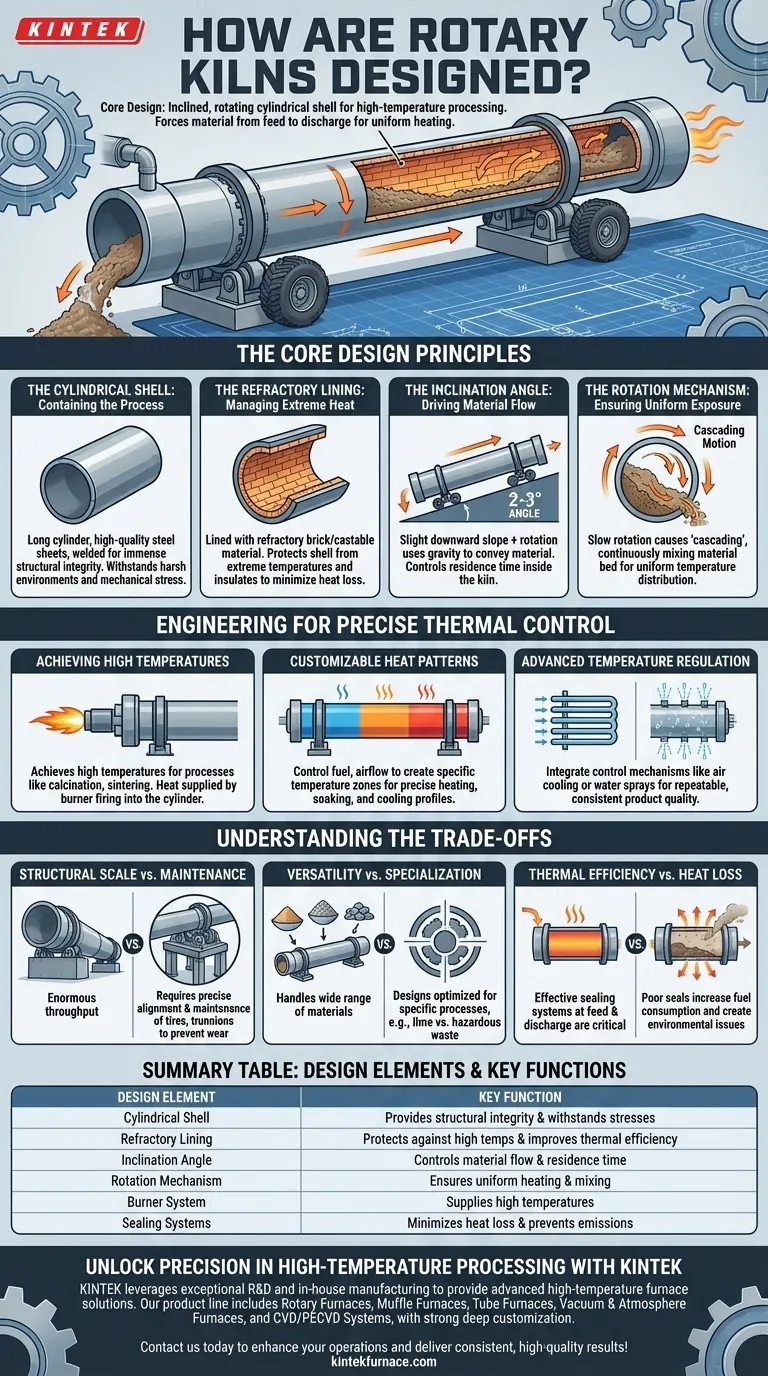
At its core, a rotary kiln is designed as a slightly inclined, rotating cylindrical shell engineered for high-temperature processing. This large steel tube is lined with heat-resistant refractory brick and turns slowly on its axis. The combination of rotation and a slight horizontal angle (typically 2-3%) forces material to move from the feed end to the discharge end, ensuring it is thoroughly and uniformly heated.
The design of a rotary kiln is not just about its components; it's a carefully engineered system where every element—from its inclination angle to its refractory lining—is optimized to control material flow and heat transfer for a specific thermal process.

The Core Design Principles
The effectiveness of a rotary kiln stems from a few fundamental design principles that work in concert to create a controlled processing environment.
The Cylindrical Shell: Containing the Process
The kiln's body is a long cylinder constructed from high-quality steel sheets. These are typically welded automatically to ensure immense structural integrity.
This robust steel shell is built to withstand harsh industrial environments and the immense mechanical stresses of rotation, reducing the need for frequent maintenance.
The Refractory Lining: Managing Extreme Heat
Inside the steel shell is a lining of refractory brick or castable material. This is a critical design feature.
This lining serves two purposes: it protects the steel shell from the extremely high process temperatures and it insulates the kiln, minimizing heat loss and improving thermal efficiency. The choice of refractory material depends on the specific chemical and thermal demands of the process.
The Inclination Angle: Driving Material Flow
Rotary kilns are never perfectly horizontal. They are installed at a slight angle, usually between two and three degrees.
This slight downward slope, combined with the kiln's rotation, uses gravity to convey material through the cylinder. The precise angle is a key design parameter that helps determine the residence time—how long the material spends inside the kiln.
The Rotation Mechanism: Ensuring Uniform Exposure
The kiln rotates slowly on its axis, a motion that is fundamental to its function. This constant tumbling action is called cascading.
This motion continuously mixes the material bed, ensuring every particle is exposed to the heat source. This is the primary reason rotary kilns achieve such a uniform temperature distribution and consistent product quality.
Engineering for Precise Thermal Control
A kiln's mechanical design is only half the story. Its ability to manage and deliver heat with precision is what makes it an indispensable industrial tool.
Achieving High Temperatures
Rotary kilns are designed to achieve the extremely high temperatures required for processes like calcination, sintering, and reduction.
This heat is typically supplied by a burner located at the discharge end of the kiln, firing a flame into the cylinder. The design must accommodate the intense thermal radiation and convective heat transfer from this source.
Customizable Heat Patterns
Modern kiln systems allow for customizable heat patterns along the length of the cylinder.
By controlling the fuel, airflow, and other parameters, operators can create specific temperature zones. This is crucial for complex processes that require a precise heating, soaking, and cooling profile to achieve the desired chemical or physical transformation.
Advanced Temperature Regulation
To ensure repeatable results, kilns integrate advanced temperature control mechanisms. Systems like air cooling tubes or water sprays on the outer shell can be used to regulate temperature precisely.
This stability is vital for producing consistent, high-quality products and is a hallmark of a well-designed kiln system.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the design of a rotary kiln involves balancing competing factors. Understanding these trade-offs is key to selecting or specifying the right equipment.
Structural Scale vs. Maintenance
Kilns can be massive, with some reaching over 700 feet long. This scale allows for enormous throughput, which is essential for industries like cement manufacturing.
However, this size creates significant engineering challenges. The support structures, including large steel rings (tires) and roller assemblies (trunnions), must be perfectly aligned and maintained to prevent excessive wear and mechanical failure.
Versatility vs. Specialization
A key advantage of the rotary kiln is its versatility in handling a wide range of materials, from fine powders to large stones.
However, a design optimized for one specific process (e.g., lime calcination) may not be perfectly efficient for another (e.g., hazardous waste incineration). The diameter-to-length ratio, refractory type, and sealing systems are often tailored to the specific application.
Thermal Efficiency vs. Heat Loss
The refractory lining is the first line of defense against heat loss, but it's not the only consideration. Air leaking into the kiln is a major source of inefficiency.
Effective sealing systems at both the feed and discharge ends are critical. A poor seal allows cold air to enter, increasing fuel consumption, and can allow dust or harmful gases to escape, creating environmental and safety issues.
Designing for a Specific Application
The optimal design of a rotary kiln is dictated entirely by its intended process and the material being processed.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production like cement: Your design will prioritize a large diameter and length for maximum throughput and specific refractory materials to withstand the highly alkaline environment.
- If your primary focus is hazardous waste incineration: Your design must emphasize gas-tight sealing systems to prevent emissions and a robust control system to ensure complete destruction of contaminants at a specific temperature.
- If your primary focus is mineral roasting or reduction: The design will concentrate on precise atmosphere and temperature control, possibly requiring specialized seals and gas injection ports to manage the chemical reactions.
Ultimately, a successful rotary kiln design is a masterful integration of mechanical engineering, material science, and thermal dynamics to achieve a specific process goal.
Summary Table:
| Design Element | Key Function |
|---|---|
| Cylindrical Shell | Provides structural integrity and withstands mechanical stresses |
| Refractory Lining | Protects against high temperatures and improves thermal efficiency |
| Inclination Angle | Controls material flow and residence time |
| Rotation Mechanism | Ensures uniform heating and mixing of materials |
| Burner System | Supplies high temperatures for processes like calcination |
| Sealing Systems | Minimizes heat loss and prevents emissions |
Unlock Precision in High-Temperature Processing with KINTEK
Are you looking to optimize your industrial processes with a custom rotary kiln? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet unique experimental and production requirements.
Whether you're in cement production, hazardous waste incineration, or mineral processing, we ensure precise thermal control, durability, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your operations and deliver consistent, high-quality results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency



















