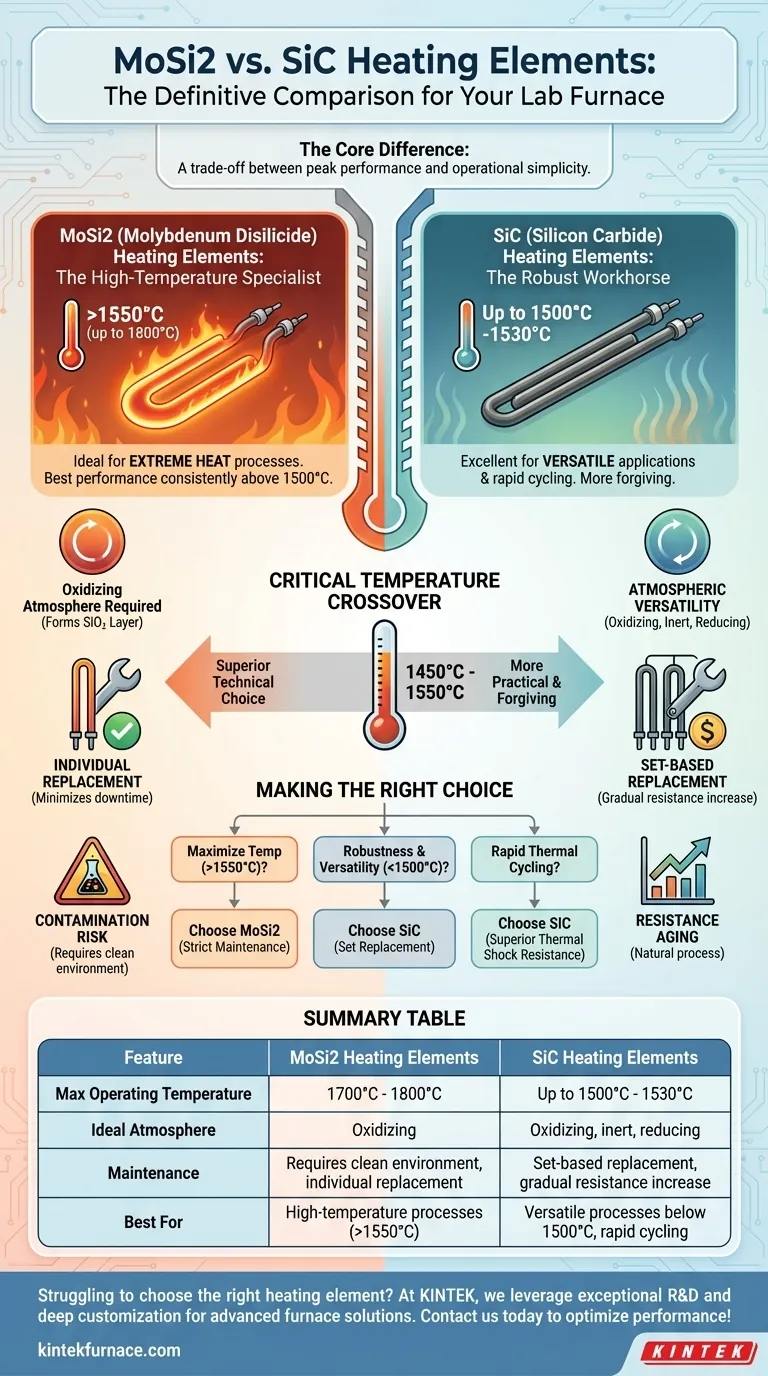
When choosing between Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements, the decision hinges on your furnace's maximum operating temperature and your maintenance philosophy. MoSi2 elements are specialists for the highest temperature ranges (above 1550°C) in oxidizing atmospheres but require careful handling. SiC elements are robust, versatile workhorses for slightly lower temperatures (up to 1500°C) that are more forgiving of process variations but come with unique replacement challenges.
The core difference is a trade-off between peak performance and operational simplicity. MoSi2 offers a higher temperature ceiling at the cost of requiring precise operating conditions, while SiC provides broader versatility and physical toughness at a lower maximum temperature.
The Core Difference: Operating Temperature
The single most important factor in your decision is the required temperature of your process. The materials are engineered for fundamentally different thermal ranges.
MoSi2: The High-Temperature Specialist
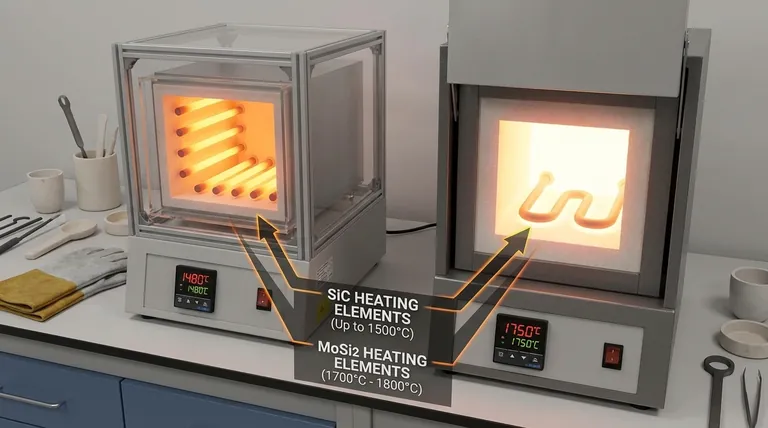
Molybdenum Disilicide elements are the definitive choice for processes requiring extreme heat, capable of operating in furnaces up to 1700°C-1800°C.
They perform best and achieve the longest lifespan when run consistently at very high temperatures, typically above 1500°C.
SiC: The Robust Workhorse
Silicon Carbide elements are ideal for a wide range of applications with a maximum furnace temperature of around 1500°C-1530°C.
They are an excellent, reliable choice for the vast majority of sintering, heat treating, and melting processes that do not require the extreme temperatures of MoSi2.
The Critical Temperature Crossover
The decision is clearest at the extremes. For processes running consistently above 1550°C, MoSi2 is the superior technical choice. For those running below 1450°C, SiC is more practical and forgiving.
The range between 1450°C and 1550°C is a grey area where factors like atmosphere and maintenance become decisive.
Performance in Your Furnace Atmosphere
How an element behaves is directly tied to the chemical environment inside the furnace.
MoSi2's Reliance on Oxidation
MoSi2 elements achieve their remarkable high-temperature stability by forming a thin, protective layer of glassy silicon dioxide (SiO₂) on their surface.
This layer requires an oxidizing atmosphere (one containing oxygen) to form and regenerate. Using MoSi2 in a reducing atmosphere can lead to rapid degradation.
SiC's Atmospheric Versatility
SiC elements are more versatile and perform well across a broader range of environments, including oxidizing, inert, and reducing atmospheres.
This makes SiC a more flexible option if your processes involve different atmospheric conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Maintenance and Lifespan
The long-term cost and reliability of your furnace depend heavily on how these elements age and how they are replaced.
Element Aging: The SiC Challenge
The electrical resistance of SiC elements increases gradually over their lifespan. This is a natural aging process.
Because of this change, a new element will have a different resistance than the older ones. To maintain a balanced electrical load, SiC elements must be replaced in complete sets or matched pairs, which can increase replacement costs.
Contamination Risk: The MoSi2 Vulnerability
MoSi2 elements do not experience the same resistance shift as SiC, but they are highly susceptible to chemical contamination.
Poor furnace maintenance, outgassing from products, or contact with certain materials can attack the element and cause premature failure. They demand a clean operating environment.
Replacement Strategy: Individual vs. Sets
This is a critical operational difference. A failed MoSi2 element can be replaced individually, minimizing material cost and downtime.
A failed SiC element requires replacing the entire set (or a balanced bank), representing a more significant maintenance event and higher upfront cost for parts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your selection should be a deliberate decision based on your specific operational goals, not just on a datasheet.
- If your primary focus is maximizing temperature (>1550°C): Choose MoSi2, but ensure your team commits to a strict protocol for furnace cleanliness and maintenance.
- If your primary focus is process robustness below 1500°C: Choose SiC for its durability and forgiveness, but budget and plan for set-based replacements as part of your maintenance cycle.
- If your process involves rapid thermal cycling: Lean towards SiC, as its superior mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance make it better suited to handle rapid temperature changes.
- If your process requires absolute atmospheric flexibility: SiC is the safer choice due to its reliable performance in oxidizing, inert, or reducing environments.
Ultimately, aligning the element's material science with your specific operating temperature and maintenance culture is the key to a reliable high-temperature process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | MoSi2 Heating Elements | SiC Heating Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Max Operating Temperature | 1700°C - 1800°C | Up to 1500°C - 1530°C |
| Ideal Atmosphere | Oxidizing | Oxidizing, inert, reducing |
| Maintenance | Requires clean environment, individual replacement | Set-based replacement, gradual resistance increase |
| Best For | High-temperature processes (>1550°C) | Versatile processes below 1500°C, rapid cycling |
Struggling to choose the right heating element for your lab furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, whether you need MoSi2 for extreme heat or SiC for versatility. Contact us today to optimize your furnace performance and enhance efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions



















