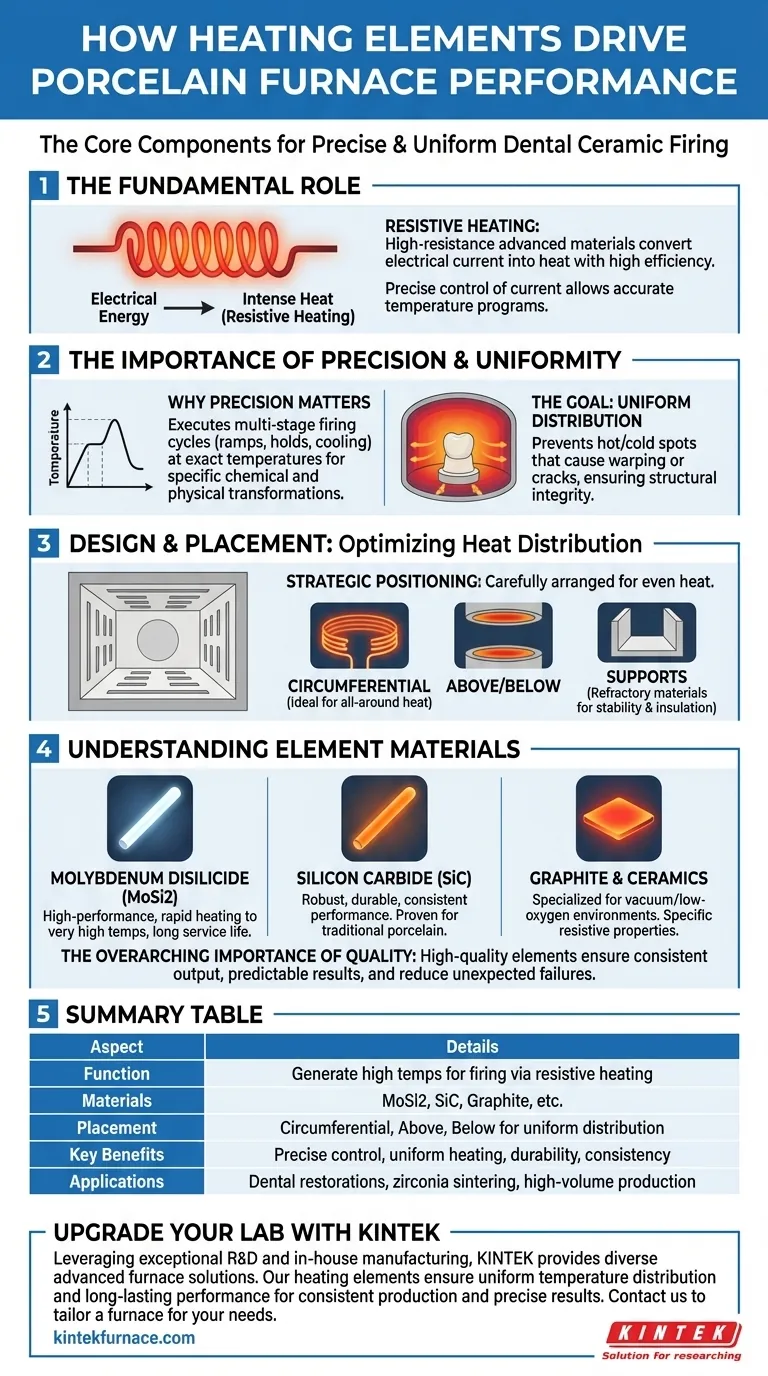
In a porcelain furnace, heating elements are the core components responsible for generating the high temperatures required to fire dental ceramics. These elements, typically made of advanced materials like silicon carbide or molybdenum disilicide, convert electrical energy into intense heat through resistance. They are strategically positioned within the firing chamber to ensure the dental restoration is heated uniformly, which is critical for achieving its final strength, fit, and aesthetic properties.
The function of a heating element goes far beyond simple heat generation. Its material composition, physical placement, and overall quality directly determine the furnace's ability to achieve the precise temperature control and uniform heating essential for creating durable, flawless dental restorations.
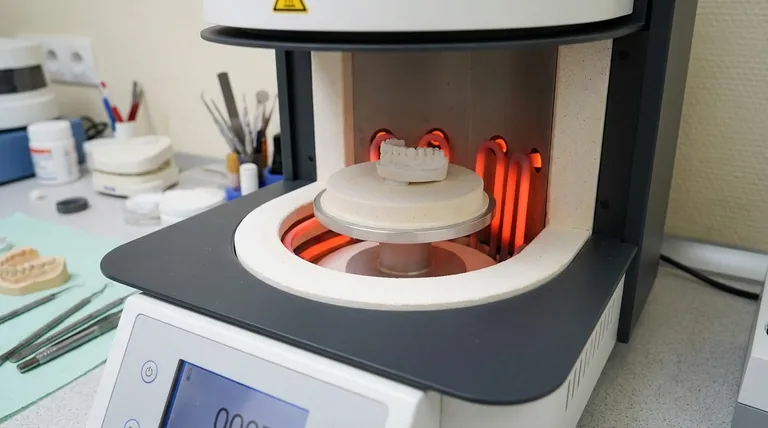

The Fundamental Role of Heating Elements
A porcelain furnace's performance is entirely dependent on its heating system. Understanding how these elements work reveals why some furnaces produce consistently better results than others.
The Principle of Resistive Heating
The core mechanism is resistive heating. When a strong electrical current is passed through the heating elements, the material's natural resistance causes it to heat up significantly. This process converts electrical energy into thermal energy with high efficiency.
The furnace's controller precisely modulates the current sent to these elements, allowing it to follow the complex temperature programs required for modern ceramics.
Why Precision is Non-Negotiable
Dental ceramics do not simply get hot; they undergo specific chemical and physical transformations at exact temperatures. A firing cycle involves multiple stages, including controlled temperature ramps, precise holds (soaks), and managed cooling.
Failure to hit these temperature targets accurately can result in a failed restoration, exhibiting issues like porosity, incorrect shade, or low strength. The heating elements are the tools that execute these precise instructions.
The Goal: Uniform Temperature Distribution
The ultimate goal of the heating system is to create a perfectly uniform thermal environment. If one part of a crown heats faster than another, it can create internal stresses that lead to warping or microscopic cracks, compromising the restoration's integrity.
Design and Placement: The Key to Uniformity
The engineering of a furnace's firing chamber is centered on optimizing heat distribution. The placement and support of the heating elements are a critical part of this design.
Strategic Positioning
To prevent hot or cold spots, elements are carefully arranged within the furnace. Common configurations include placing them circumferentially (around), above, or below the platform where the restoration sits.
A circumferential arrangement is often considered ideal as it surrounds the workpiece with heat, promoting the most even temperature distribution from all sides.
Element Support Structures
Heating elements are held in place by specialized supports made from refractory materials, ceramics, or high-temperature alloys. These hangers, hooks, or form tiles serve two key purposes.
First, they secure the elements to prevent sagging or shifting over thousands of heat cycles. Second, they provide electrical insulation, ensuring the current flows only through the elements themselves.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Element Materials
The material used for the heating element has a major impact on the furnace's maximum temperature, longevity, and performance stability.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2)
These are high-performance elements known for their ability to reach very high temperatures quickly and for their long service life. They are a common choice in modern, high-end furnaces designed for zirconia sintering and other demanding applications.
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Silicon carbide elements are extremely robust and durable, offering excellent performance and a long operational lifespan. They are a proven technology used widely across the industry for reliable and consistent firing of traditional porcelains.
Graphite and Other Ceramics
In some specialized furnaces, particularly vacuum furnaces, elements made of graphite or other advanced ceramics are used. These materials are chosen for their specific resistive properties and performance in low-oxygen environments.
The Overarching Importance of Quality
Regardless of the specific material, the manufacturing quality of the heating element is paramount. High-quality elements deliver more consistent heat output over their lifespan, contributing to predictable firing results and reducing unexpected failures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When assessing a porcelain furnace, focusing on how its heating system aligns with your lab's needs will lead to a better investment.
- If your primary focus is consistency and high-volume production: Look for furnaces with high-quality Molybdenum Disilicide or Silicon Carbide elements known for their long service life and stable performance.
- If your primary focus is achieving precise aesthetic results: Prioritize furnaces that explicitly market their uniform heat distribution, often achieved through circumferential element placement.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: Consider the furnace's specified heating rate and the expected lifespan of the elements, as these directly impact energy consumption and maintenance costs.
Ultimately, understanding the heating elements empowers you to look past marketing and evaluate a furnace based on its core engineering.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Function | Generate high temperatures for firing dental ceramics via resistive heating |
| Materials | Silicon carbide, molybdenum disilicide, graphite, or other ceramics |
| Placement | Circumferential, above, or below the platform for uniform distribution |
| Key Benefits | Precise temperature control, uniform heating, durability, and consistent results |
| Applications | Firing dental restorations, zirconia sintering, high-volume production |
Upgrade Your Dental Lab with KINTEK's Advanced Furnace Solutions
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need consistent high-volume production, precise aesthetic results, or operational efficiency, our heating elements ensure uniform temperature distribution and long-lasting performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a furnace to enhance your dental restoration quality and lab productivity!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What aspects of a dental restoration are directly impacted by the choice of a dental sintering furnace? Ensure Fit, Strength & Longevity
- Why is temperature range important when selecting a dental furnace? Unlock Material Compatibility and Precision
- What is the working principle of a dental furnace? Mastering Precision Sintering & Firing for Crowns
- Why is using a universal setting for all materials in a dental furnace a mistake? Master Precision Sintering for Perfect Restorations
- What role does temperature range and accuracy play in dental furnace performance? Ensure Precision for Superior Dental Restorations



















