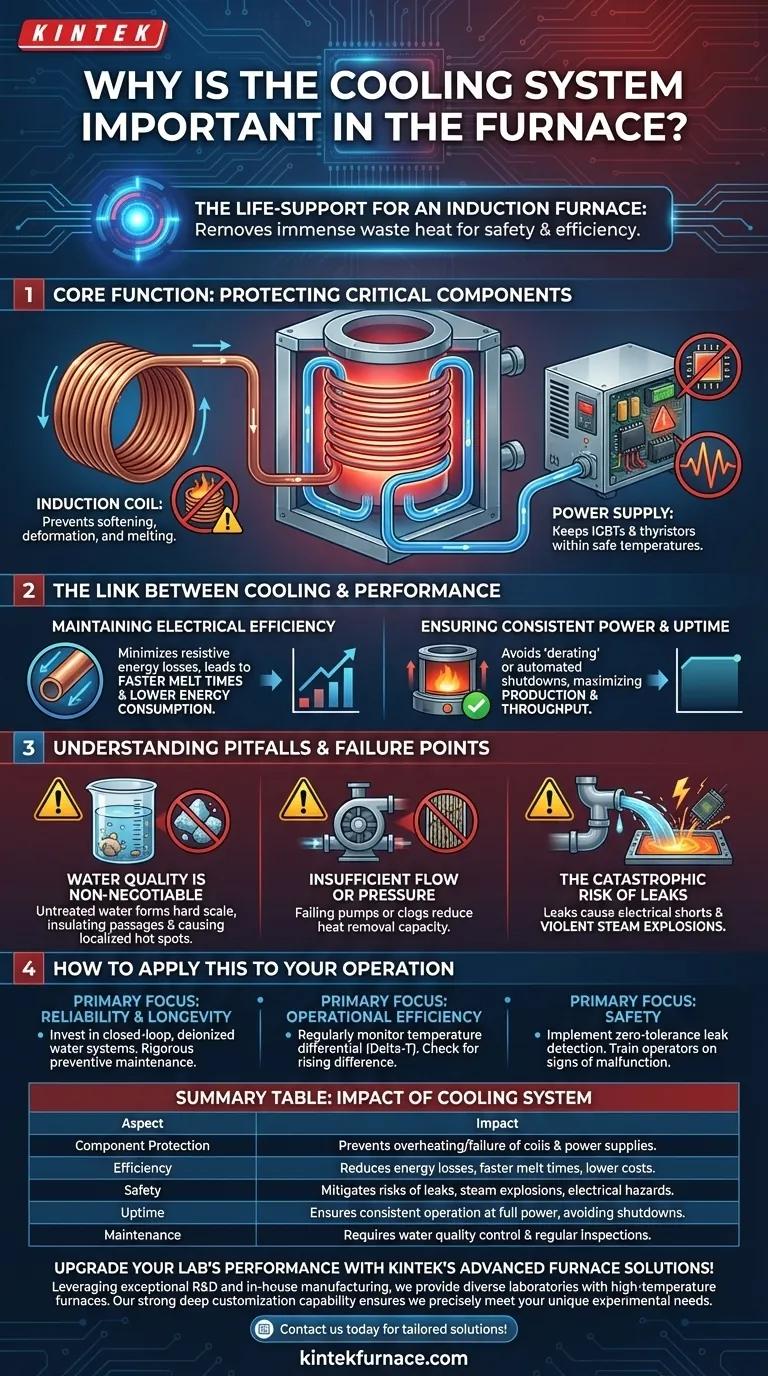
At its core, the cooling system is the life-support for an induction furnace. It continuously removes the immense waste heat generated by high-power electrical components, primarily the induction coil, preventing them from self-destructing and ensuring the furnace can operate both efficiently and safely.
The intense heat you want in the crucible is matched by an intense, unwanted heat in the furnace's own electronics. The cooling system’s primary job is not just to cool, but to protect the most expensive and vital components from catastrophic failure, directly dictating the furnace's lifespan and performance.
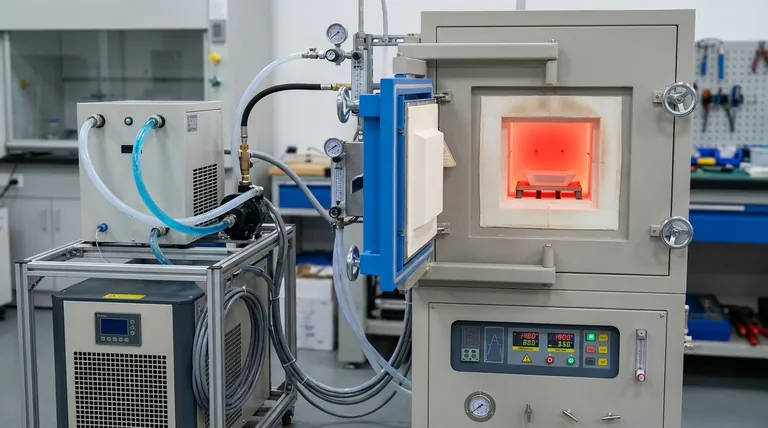

The Core Function: Protecting Critical Components
A furnace's cooling system is an active defense mechanism. It circulates a coolant—typically treated water—through a network of passages in and around the most vulnerable parts of the equipment.
The Induction Coil
The induction coil is essentially a large copper tube that carries immense electrical current to generate the magnetic field for heating. This current also creates significant resistive heat within the copper itself.
Without constant cooling, this heat would rapidly accumulate, causing the copper to soften, deform, and ultimately melt. A coil failure is a catastrophic event that results in complete furnace shutdown and an extremely expensive repair.
The Power Supply
The power supply, which converts mains electricity into the high-frequency power needed for induction, is packed with sensitive electronics like IGBTs or thyristors. These components generate their own heat during operation.
Effective cooling is essential to keep these solid-state devices within their safe operating temperature. Overheating leads to premature failure, erratic performance, and costly power supply repairs.
The Link Between Cooling and Furnace Performance
Beyond simply preventing failure, the quality of the cooling system has a direct and measurable impact on the furnace's day-to-day operational efficiency.
Maintaining Electrical Efficiency
The electrical resistance of copper increases with its temperature. A hotter induction coil is a less efficient one.
By keeping the coil cool, the cooling system minimizes these resistive energy losses. This means more of the electrical power you pay for is delivered to the metal charge, and less is wasted as excess heat, leading to faster melt times and lower energy consumption.
Ensuring Consistent Power and Uptime
An inadequate cooling system can force a furnace to be "derated"—operated at a lower power level to prevent overheating. This directly slows down production.
In a worst-case scenario, automated trips will shut the furnace down completely if cooling parameters are not met. A robust and well-maintained cooling system is the key to running consistently at full power and maximizing throughput.
Understanding the Pitfalls and Failure Points
Treating the cooling system as an afterthought is one of the most common and costly mistakes in furnace operation. Its reliability is dependent on several critical factors.
Water Quality is Non-Negotiable
Using untreated tap or well water is a recipe for disaster. Minerals like calcium and magnesium will precipitate out of the water as it heats up, forming a hard scale on the inside of the cooling passages.
This scale acts as an insulator, drastically impeding heat transfer. This can create localized hot spots on the coil that lead to failure, even if the overall water flow seems adequate. A closed-loop system using distilled or deionized water is the industry standard for a reason.
Insufficient Flow or Pressure
Low coolant flow, whether from a failing pump, a clogged filter, or a kinked hose, is just as dangerous as poor water quality. The system relies on a specific flow rate to carry away the required amount of thermal energy.
Modern furnaces have sensors to monitor flow and pressure, but these systems require regular calibration and inspection to be effective.
The Catastrophic Risk of Leaks
A coolant leak is arguably the most dangerous failure mode. A leak onto high-voltage electrical components can cause a direct short circuit and arcing.
Even more critically, if water comes into contact with the molten metal bath, it can flash into steam instantaneously, causing a violent steam explosion that can endanger personnel and destroy equipment.
How to Apply This to Your Operation
The health of your cooling system is a direct reflection of your operational priorities. Your approach to its maintenance should be guided by your primary goals.
- If your primary focus is reliability and longevity: Invest in a closed-loop, deionized water system and implement a rigorous preventive maintenance schedule for water quality testing, filter changes, and pump inspections.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: Regularly monitor the temperature differential (Delta-T) between the water entering and leaving the coil; a rising temperature difference can indicate scaling or reduced flow before it causes a shutdown.
- If your primary focus is safety: Implement strict, zero-tolerance protocols for leak detection and ensure all operators are trained to recognize the signs of a cooling system malfunction.
Ultimately, viewing the cooling system as a core production asset, not a utility, is the key to a safe, efficient, and profitable furnace operation.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Impact |
|---|---|
| Component Protection | Prevents overheating and failure of induction coils and power supplies |
| Efficiency | Reduces energy losses, enabling faster melt times and lower costs |
| Safety | Mitigates risks of leaks, steam explosions, and electrical hazards |
| Uptime | Ensures consistent operation at full power, avoiding shutdowns |
| Maintenance | Requires water quality control and regular inspections for reliability |
Upgrade your lab's performance with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for enhanced safety, efficiency, and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your furnace operations and deliver tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does inert atmosphere heat treating benefit aluminum? Prevent Oxide Buildup for Superior Results
- Why are inert atmosphere furnaces important for graphite and carbon products? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure High-Performance Results
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.



















