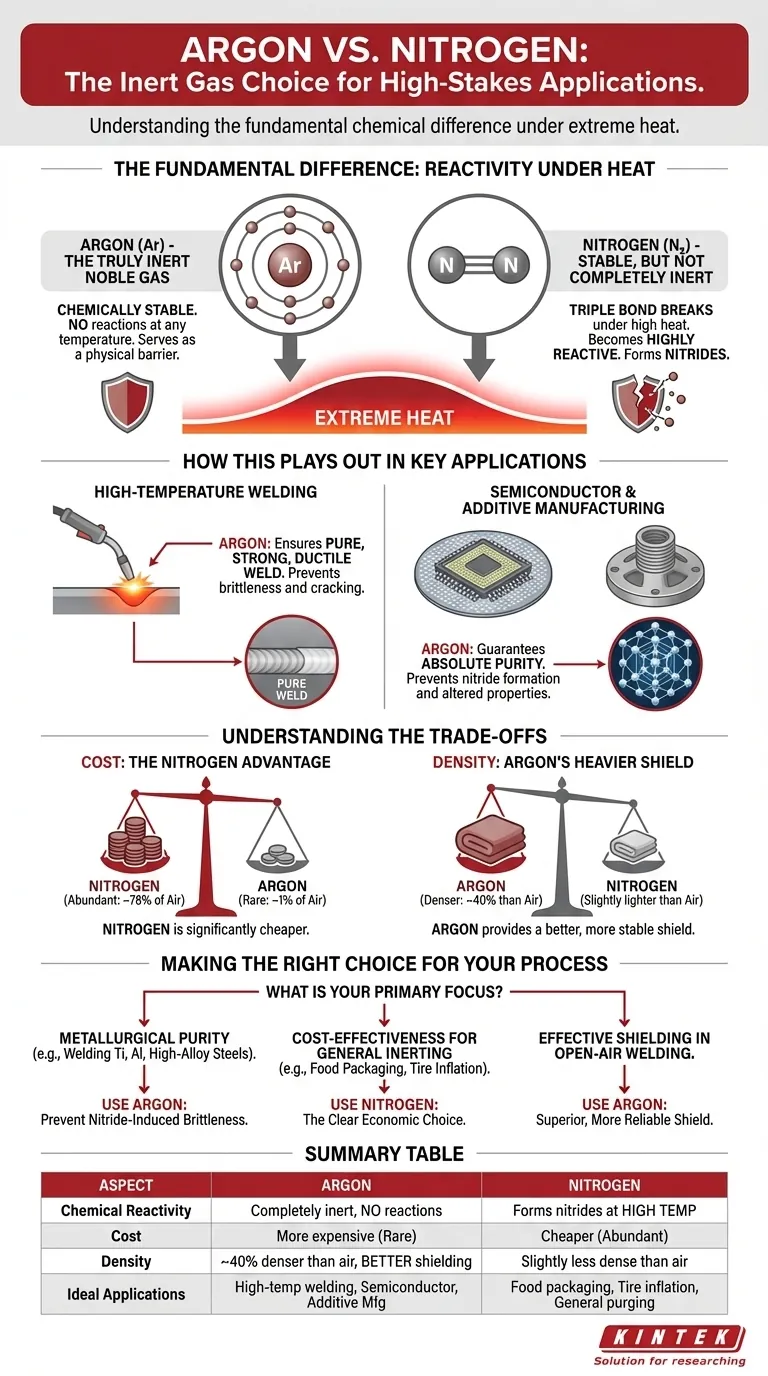
At first glance, argon and nitrogen appear to be interchangeable inert gases suitable for shielding sensitive processes. However, argon is decisively preferred in high-stakes applications because it remains completely inert at all temperatures, whereas nitrogen can become reactive under extreme heat. This fundamental chemical difference is critical in processes like specialized welding and semiconductor manufacturing, where even microscopic impurities can cause catastrophic failure.
The core decision between argon and nitrogen comes down to a trade-off between cost and chemical stability. Nitrogen is abundant and affordable, but can react with certain metals at high temperatures. Argon is more expensive but guarantees true inertness, protecting the integrity of the most sensitive materials.
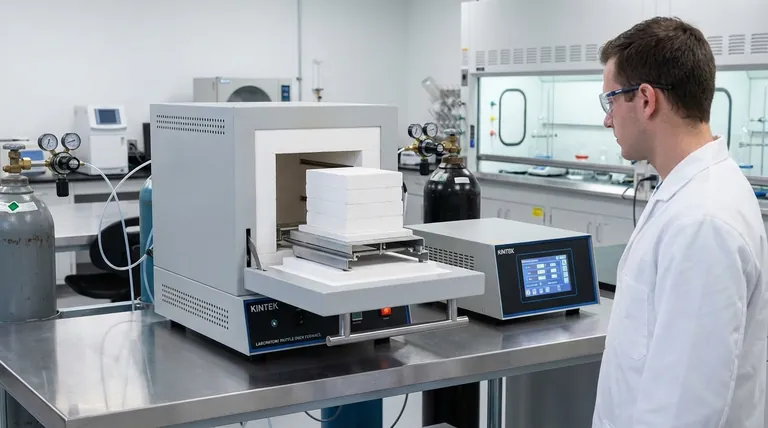

The Fundamental Difference: Reactivity Under Heat
To understand the preference for argon, we must look beyond the simple label of "inert gas" and examine their behavior at the atomic level, especially when exposed to high energy.
Argon: The Truly Inert Noble Gas
Argon is a noble gas. This means its outermost electron shell is completely full, making it chemically stable and extremely reluctant to react with any other element.
Even under the intense heat of a welding arc or inside a plasma chamber, argon atoms will not bond with other materials. They simply serve as a physical barrier, displacing atmospheric oxygen and moisture.
Nitrogen: Stable, But Not Completely Inert
Nitrogen gas (N₂) is also very stable due to the powerful triple bond holding its two atoms together. A great deal of energy is required to break this bond.
However, in high-temperature environments like welding, that energy is readily available. Once the triple bond breaks, nitrogen atoms become highly reactive and can form compounds called nitrides with metals like titanium, aluminum, and certain high-alloy steels.
How This Plays Out in Key Applications
This difference in high-temperature reactivity is not just academic; it has direct, practical consequences in manufacturing and science.
In High-Temperature Welding
When welding reactive metals, the formation of nitrides is a primary concern. Nitrides introduce impurities into the metal's grain structure, making the final weld brittle and prone to cracking.
For critical applications like aerospace components or high-pressure vessels made from titanium or aluminum, using nitrogen as a shielding gas would compromise the structural integrity of the weld. Argon, being completely non-reactive, ensures a pure, strong, and ductile weld.
In Semiconductor and Additive Manufacturing
In processes like semiconductor fabrication or metal 3D printing (additive manufacturing), the goal is absolute purity. The environment must be perfectly controlled.
The formation of nitrides on a silicon wafer would alter its electronic properties, rendering the microchips useless. Similarly, in 3D printing with metal powders, nitride formation can create weak points in the final part. Argon provides the guaranteed inert atmosphere necessary for these precision processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between argon and nitrogen isn't always about picking the "best" gas, but the right gas for the job, which involves balancing performance against practical constraints.
Cost: The Nitrogen Advantage
Nitrogen makes up approximately 78% of the Earth's atmosphere, while argon accounts for just under 1%. This vast difference in abundance makes nitrogen significantly cheaper to produce and procure.
For applications where absolute inertness is not the primary driver—such as food packaging, tire inflation, or purging pipelines—nitrogen is the far more economical and perfectly suitable choice.
Density: Argon's Heavier Shield
Argon is about 40% denser than air, while nitrogen is slightly less dense than air. This gives argon a distinct physical advantage in shielding applications.
Because it is heavier, argon effectively creates a "blanket" over the work area, displacing lighter atmospheric gases more efficiently. This is especially useful in flat or open-area welding, where it provides a more stable and robust shield against contamination.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your choice of gas should be directly aligned with the technical requirements and budget of your specific application.
- If your primary focus is metallurgical purity: For welding titanium, aluminum, magnesium, or high-alloy stainless steels, you must use argon to prevent nitride-induced brittleness.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for general inerting: For applications like food preservation, tire inflation, or purging systems of oxygen, nitrogen is the clear economic choice.
- If your primary focus is effective shielding in open-air welding: Argon's higher density provides a more reliable shield that is less susceptible to disruption from drafts, making it superior for critical welds outside of a contained chamber.
Ultimately, selecting the correct gas is a foundational decision based on understanding the true chemical behavior of each element under your specific process conditions.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Argon | Nitrogen |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Reactivity | Completely inert, no reactions at any temperature | Can form nitrides with metals at high temperatures |
| Cost | More expensive due to rarity (~1% of atmosphere) | Cheaper, abundant (~78% of atmosphere) |
| Density | ~40% denser than air, better shielding | Slightly less dense than air |
| Ideal Applications | High-temperature welding, semiconductor fabrication, additive manufacturing | Food packaging, tire inflation, general purging |
Need a Reliable High-Temperature Furnace Solution for Your Lab?
At KINTEK, we understand the critical role of inert atmospheres in processes like welding and semiconductor manufacturing. Our advanced high-temperature furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, are designed to deliver precise temperature control and superior shielding capabilities. With our strong in-house R&D and manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs, ensuring optimal performance and purity in your applications.
Contact us today via our contact form to discuss how KINTEK can enhance your lab's efficiency and results with tailored furnace solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment



















