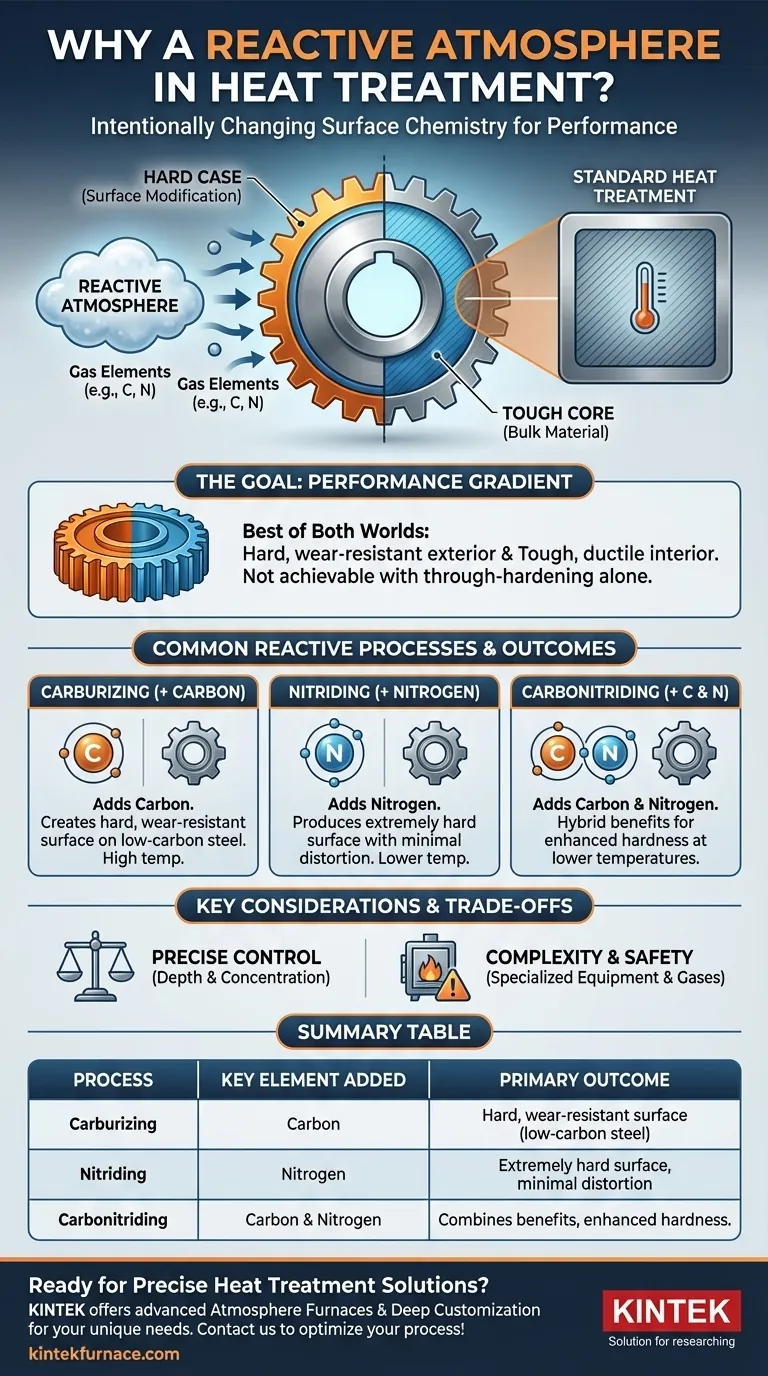
In heat treatment, a reactive atmosphere is required when the goal is not just to alter the material's internal structure, but to intentionally change its surface chemistry. This process, known as case hardening or surface modification, imbues a component with properties, such as extreme surface hardness, that the bulk material does not possess on its own.
While most heat treatment uses temperature to modify a material's existing properties, reactive atmospheres actively add new elements to the material's surface. This effectively creates a composite part with a hard, wear-resistant exterior and a tough, ductile interior.
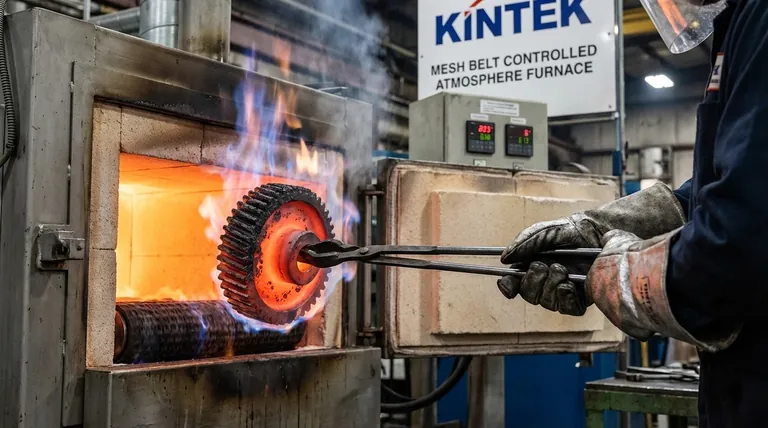

The Goal: Creating a Performance Gradient
Standard heat treatment, like quenching and tempering, changes the crystalline structure (phase) of an alloy to achieve a desired balance of hardness and toughness throughout the entire part. Reactive atmosphere treatments are fundamentally different.
What is a Reactive Atmosphere?
A reactive atmosphere is a precisely controlled gas environment that is designed to donate elements to the surface of a metal part at high temperatures. The process relies on the principle of chemical potential and diffusion.
The atmosphere contains a higher concentration of a specific element (like carbon or nitrogen) than the steel. At elevated temperatures, the steel's crystal lattice is more open, and the atoms are more mobile, allowing these elements to diffuse from the gas into the surface of the part.
Why Not Just Use a Harder Steel?
Using a reactive process allows for the "best of both worlds." You can start with a less expensive, tougher, and more machinable low-carbon steel for the bulk of the component (the "core") and then add a hard, wear-resistant "case" only where it's needed—on the surface.
A through-hardened high-carbon steel part would be brittle and more prone to fracture under impact, whereas a case-hardened part maintains its core toughness to absorb shock.
Common Reactive Processes and Their Outcomes
Different reactive gases are used to achieve different surface properties. The two most common processes for steel are carburizing and nitriding.
Carburizing: Adding Carbon
Carburizing involves heating a low-carbon steel in an atmosphere rich in carbon, typically from carbon monoxide (CO) or decomposed hydrocarbons.
The diffused carbon raises the carbon content of the surface layer, allowing it to form a very hard martensitic structure upon quenching. This creates an excellent wear-resistant case while the low-carbon core remains tough and ductile.
Nitriding: Adding Nitrogen
Nitriding involves heating steel in an atmosphere containing dissociated nitrogen, usually from ammonia (NH₃). The nitrogen atoms diffuse into the surface and form extremely hard iron nitride compounds.
Nitriding is performed at lower temperatures than carburizing, which significantly reduces part distortion. It produces one of the hardest surfaces achievable, offering exceptional wear and fatigue resistance.
Carbonitriding: A Hybrid Approach
This process introduces both carbon and nitrogen into the surface of the steel simultaneously. It combines some of the benefits of both processes, often providing a harder case than carburizing at a lower temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a reactive atmosphere is a deliberate engineering decision that involves significant process control and complexity. It is not a simple or inexpensive operation.
The Need for Precise Control
The depth and concentration of the diffused elements must be meticulously controlled. Too little carbon or nitrogen results in an ineffective case. Too much can lead to the formation of brittle compounds, retained austenite, or soot, which can compromise the part's integrity.
Equipment and Safety
Generating and monitoring reactive atmospheres requires specialized furnaces with sealed retorts and sophisticated gas control systems. The gases used, such as carbon monoxide and ammonia, are toxic and flammable, necessitating strict safety protocols.
The Contrast with Protective Atmospheres
It's crucial to distinguish reactive atmospheres from protective ones. A protective atmosphere (using inert gases like nitrogen, argon, or a vacuum) is designed to do the exact opposite: prevent any chemical reaction with the part's surface, primarily oxidation (scale) and decarburization (carbon loss).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The choice of furnace atmosphere is dictated entirely by the final performance requirements of the component.
- If your primary focus is creating a hard, wear-resistant surface on a tough, low-cost steel: A reactive carburizing or nitriding process is the correct approach.
- If your primary focus is hardening a high-carbon steel without changing its surface chemistry: A protective atmosphere (inert gas or vacuum) is required to prevent damaging oxidation or decarburization.
- If your primary focus is simply annealing or stress-relieving a part where surface finish is not critical: A simple air atmosphere may be sufficient, but you must accept that some surface scaling will occur.
Ultimately, the atmosphere inside a furnace is not a background condition; it is a critical engineering tool used to define a component's final properties.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Element Added | Primary Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Carburizing | Carbon | Creates a hard, wear-resistant surface on low-carbon steel |
| Nitriding | Nitrogen | Produces an extremely hard surface with minimal distortion |
| Carbonitriding | Carbon & Nitrogen | Combines benefits for enhanced hardness at lower temperatures |
Ready to enhance your materials with precise heat treatment solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs for reactive atmosphere processes. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your heat treatment for superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the two main types of atmosphere furnaces and their characteristics? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What is the relationship between temperature and the furnace atmosphere in material processing? Master the Critical Heat-Environment Balance
- What is the significance of nitrogen in atmosphere furnaces? Unlock Enhanced Heat Treatment and Surface Hardening
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance



















