In essence, it is about achieving high-energy chemistry without high heat. Plasmas with low fractional ionization are valuable because they create a unique state where electrons are extremely energetic, while the surrounding neutral gas and the material being processed remain near room temperature. This allows for precise chemical reactions, such as breaking down precursor molecules and forming reactive species, without causing thermal damage to the underlying substrate.
The core advantage of low fractional ionization plasma is its non-thermal equilibrium. This condition allows highly energetic electrons to act as precision chemical tools, driving reactions at the atomic level while keeping the overall process temperature low, thereby protecting sensitive materials.
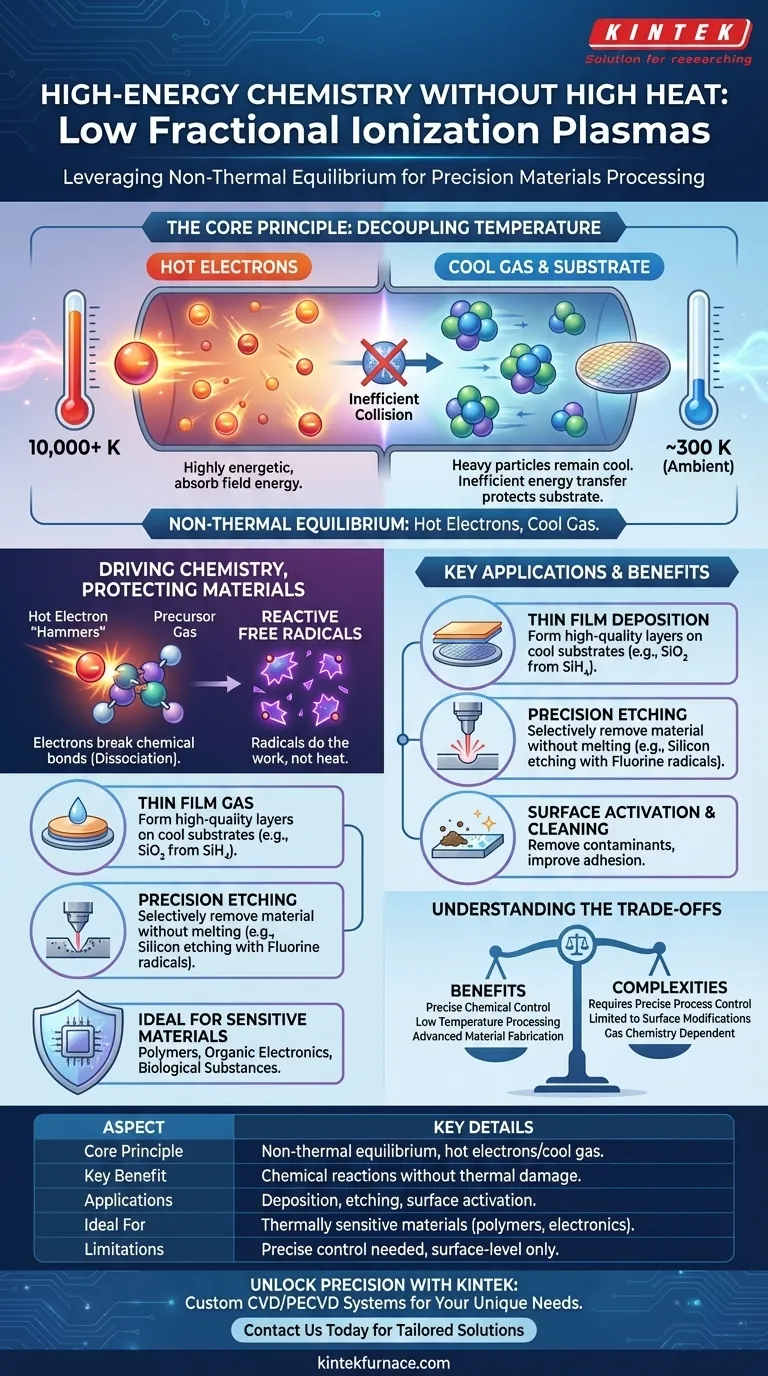
The Core Principle: Decoupling Temperature
To understand the value of these plasmas, we must first grasp the concept of non-thermal equilibrium, where different particles within the plasma exist at radically different temperatures.
What is Low Fractional Ionization?
Fractional ionization is simply the ratio of charged particles (ions and electrons) to the total number of particles in the gas.
In a low fractional ionization plasma, the vast majority of the gas—often more than 99.99%—consists of neutral atoms or molecules. The ionized component is a tiny fraction.
The Key to Non-Thermal Equilibrium
When an electric field is applied to create the plasma, it primarily accelerates the lightest charged particles: the electrons.
Because electrons are thousands of times lighter than neutral atoms, collisions between them are highly inefficient at transferring energy. Think of a ping-pong ball (an electron) bouncing off a bowling ball (a neutral atom); the ping-pong ball rebounds with most of its speed, barely nudging the bowling ball.
Hot Electrons, Cool Gas
This inefficient energy transfer leads to a dramatic temperature disparity. The electrons absorb energy from the electric field and reach very high equivalent temperatures—often tens of thousands of kelvins.
Simultaneously, the heavy neutral gas particles and the material substrate remain "cold," staying close to ambient temperature.
Why This Matters for Materials Processing
This unique "hot electron, cold gas" environment is ideal for performing delicate work on material surfaces. It enables chemistry that would otherwise require destructive, high-temperature conditions.
Driving Chemistry Without Heat
The highly energetic electrons act like microscopic hammers. Their kinetic energy is sufficient to collide with and break the chemical bonds of precursor gas molecules introduced into the plasma. This process is called dissociation.
Creating Reactive Species (Free Radicals)
This bond-breaking creates free radicals—atoms or molecular fragments with unpaired electrons. These species are extremely chemically reactive.
It is these radicals, not the heat, that do the primary work of materials processing. They react with the substrate's surface to either remove material (etching) or form a new layer on top of it (deposition).
Protecting Sensitive Substrates
Because the bulk gas and substrate remain cool, this technique is perfectly suited for processing thermally sensitive materials.
This includes polymers, organic electronics, plastics, and biological materials that would be damaged or destroyed by conventional high-temperature processing methods.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, this technology is not without its complexities. A clear understanding of its limitations is critical for successful implementation.
Process Control Complexity
Maintaining a stable, non-thermal plasma requires precise control over multiple variables, including gas pressure, gas flow rates, and the power supplied to the electric field. Small deviations can alter the electron temperature and radical density, affecting process results.
Limited to Surface Modification
These plasma processes are inherently surface-level phenomena. They are ideal for creating thin films (nanometers to micrometers thick), cleaning a surface, or etching fine patterns. They cannot be used to modify the bulk properties of a thick material.
Dependence on Gas Chemistry
The outcome is entirely dependent on the precursor gases used. Choosing the right chemistry is crucial. For example, fluorine-based gases (like CF₄) are used to generate fluorine radicals for etching silicon, whereas silane (SiH₄) is used to deposit films of silicon dioxide (SiO₂).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this effectively, you must align the plasma chemistry with your specific materials processing objective.
- If your primary focus is thin film deposition: Use the plasma to dissociate precursor gases, allowing reactive species to settle and form a high-quality film on a cool substrate.
- If your primary focus is precision etching: Use the plasma to generate aggressive radicals that selectively remove material from a substrate without causing thermal damage or melting.
- If your primary focus is surface activation or cleaning: Use a simpler plasma (like argon or oxygen) to create radicals that remove organic contaminants and modify the surface energy to improve adhesion for subsequent coatings.
By leveraging this targeted transfer of energy, you gain precise control over surface chemistry, enabling the fabrication of advanced materials and devices.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Non-thermal equilibrium with hot electrons and cool gas/substrate |
| Key Benefit | Enables chemical reactions without thermal damage to materials |
| Applications | Thin film deposition, precision etching, surface activation |
| Ideal For | Thermally sensitive materials like polymers, electronics, and biological substances |
| Limitations | Requires precise control, limited to surface-level modifications |
Unlock the Power of Precision Plasma Processing with KINTEK
Are you working with thermally sensitive materials and need advanced solutions for thin film deposition, etching, or surface activation? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature furnace systems, including CVD/PECVD Systems, designed to support low fractional ionization plasma applications. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs.
Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your materials processing efficiency and protect your substrates from thermal damage!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance



















