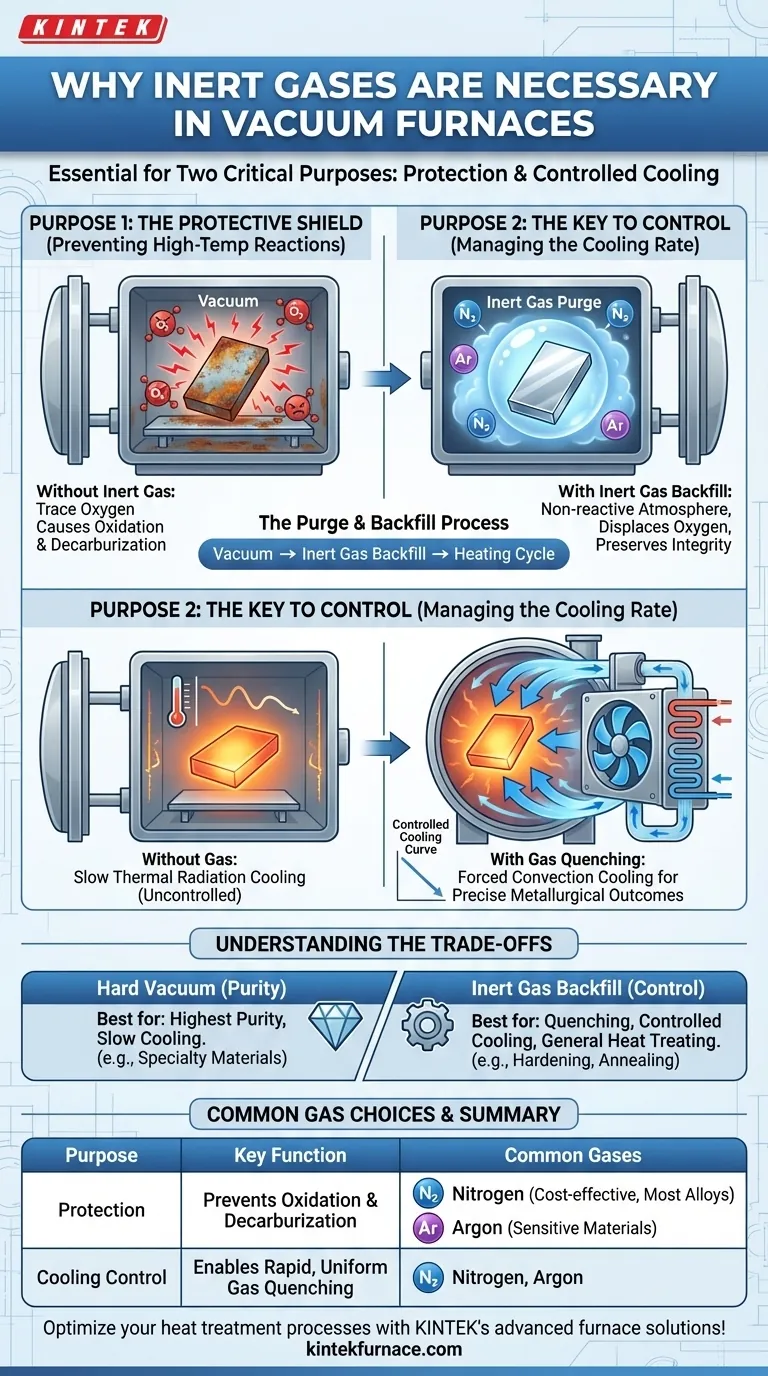
In a vacuum furnace, inert gases are necessary for two critical and distinct purposes. They first create a non-reactive atmosphere to prevent the high-temperature oxidation of materials. Second, they serve as a medium for controlled, rapid cooling, a process known as gas quenching, which is essential for achieving specific metallurgical properties.
The role of inert gas goes beyond simply replacing the vacuum. While a vacuum removes reactive elements, an inert gas backfill provides both a superior protective shield and, most importantly, a medium for precise and accelerated thermal control that a vacuum alone cannot provide.

The Protective Shield: Preventing High-Temperature Reactions
At the elevated temperatures inside a vacuum furnace, materials become highly susceptible to chemical reactions with any residual atmospheric gases. The primary function of an inert gas is to create a positive pressure environment that is chemically non-reactive.
Eliminating Oxidation Risk
Even in a high-vacuum environment, trace amounts of oxygen can remain. When heated, metals will readily react with this oxygen, forming oxides on the surface that can compromise the material's structural integrity, conductivity, and appearance. An inert gas purge displaces this residual oxygen, effectively eliminating the risk of oxidation.
Preserving Material Integrity
Beyond oxygen, other reactive gases can cause unwanted changes. Introducing an inert gas like nitrogen or argon ensures the furnace atmosphere does not react with the workpiece. This is critical for preventing issues like decarburization in steels or other surface-level chemical changes that alter the material's intended characteristics.
The Purge and Backfill Process
The inert gas is typically introduced into the furnace chamber after the initial vacuum has been pulled but before the heating cycle begins. This "backfilling" process purges any remaining reactive molecules and establishes a stable, protective environment for the entire thermal cycle.
The Key to Control: Managing the Cooling Rate
Perhaps the most crucial role of inert gas in modern vacuum furnaces is to control the cooling phase. The rate at which a material cools determines its final microstructure and, therefore, its mechanical properties like hardness and strength.
Why Cooling Speed Matters
A pure vacuum is an excellent insulator. Cooling a part in a vacuum relies solely on slow thermal radiation, offering very little control. For many heat-treating processes, such as hardening or annealing, a specific, often rapid, cooling rate is required to lock in the desired crystalline structure.
The Mechanism of Gas Quenching
Inert gas enables forced convection cooling, or gas quenching. In this process, the inert gas is circulated by a powerful fan through a heat exchanger (typically water-cooled) and then injected back into the furnace's hot zone at high velocity. This cooled gas rapidly and uniformly absorbs heat from the workpiece, allowing for precise control over the cooling rate.
Superior Control Over Vacuum Cooling
By varying the gas pressure, type (argon vs. nitrogen), and fan speed, operators can precisely manage the cooling curve. This level of control is impossible in a pure vacuum, making inert gas essential for any process requiring a quench.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, an inert gas atmosphere is not the only option. The choice between a hard vacuum and an inert gas backfill depends entirely on the process goals.
When Pure Vacuum is Superior
For applications where the absolute highest purity is required and rapid cooling is not, a hard vacuum is ideal. Certain highly reactive or specialty materials may have subtle reactions even with nitrogen or argon. In these cases, a pure vacuum provides the most non-reactive environment possible, albeit with very slow, uncontrolled cooling.
When Inert Gas is Essential
If the process requires any form of quenching or controlled cooling to achieve specific mechanical properties, an inert gas backfill is non-negotiable. The ability to use convection for heat transfer is the only way to achieve the rapid cooling rates needed for hardening and similar treatments.
Common Gas Choices: Nitrogen vs. Argon
Nitrogen is the most common and cost-effective inert gas used in vacuum furnaces. It is suitable for most heat-treating applications involving steels and other common alloys.
Argon is denser and more chemically inert than nitrogen. It is used for more sensitive materials, like titanium or certain superalloys, where there is a risk of nitrogen reacting with the material at high temperatures to form undesirable nitrides.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct furnace atmosphere is fundamental to achieving the desired outcome. Your decision should be based on the material being processed and the final properties you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity with slow cooling: A hard vacuum without a gas backfill provides the most non-reactive environment.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation during general heat treating: Nitrogen is a cost-effective inert gas that provides excellent protection for most alloys.
- If your primary focus is rapid, controlled cooling (quenching): An inert gas backfill (nitrogen or argon) with a forced convection system is essential.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive metals like titanium: Argon is the preferred choice to eliminate any risk of forming nitrides at high temperatures.
Ultimately, the strategic use of inert gas transforms the vacuum furnace from a simple heating chamber into a precision tool for advanced materials processing.
Summary Table:
| Purpose | Key Function | Common Gases |
|---|---|---|
| Protection | Prevents oxidation and decarburization by creating a non-reactive atmosphere | Nitrogen, Argon |
| Cooling Control | Enables rapid, uniform gas quenching for precise metallurgical outcomes | Nitrogen, Argon |
Optimize your heat treatment processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your material processing efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety



















