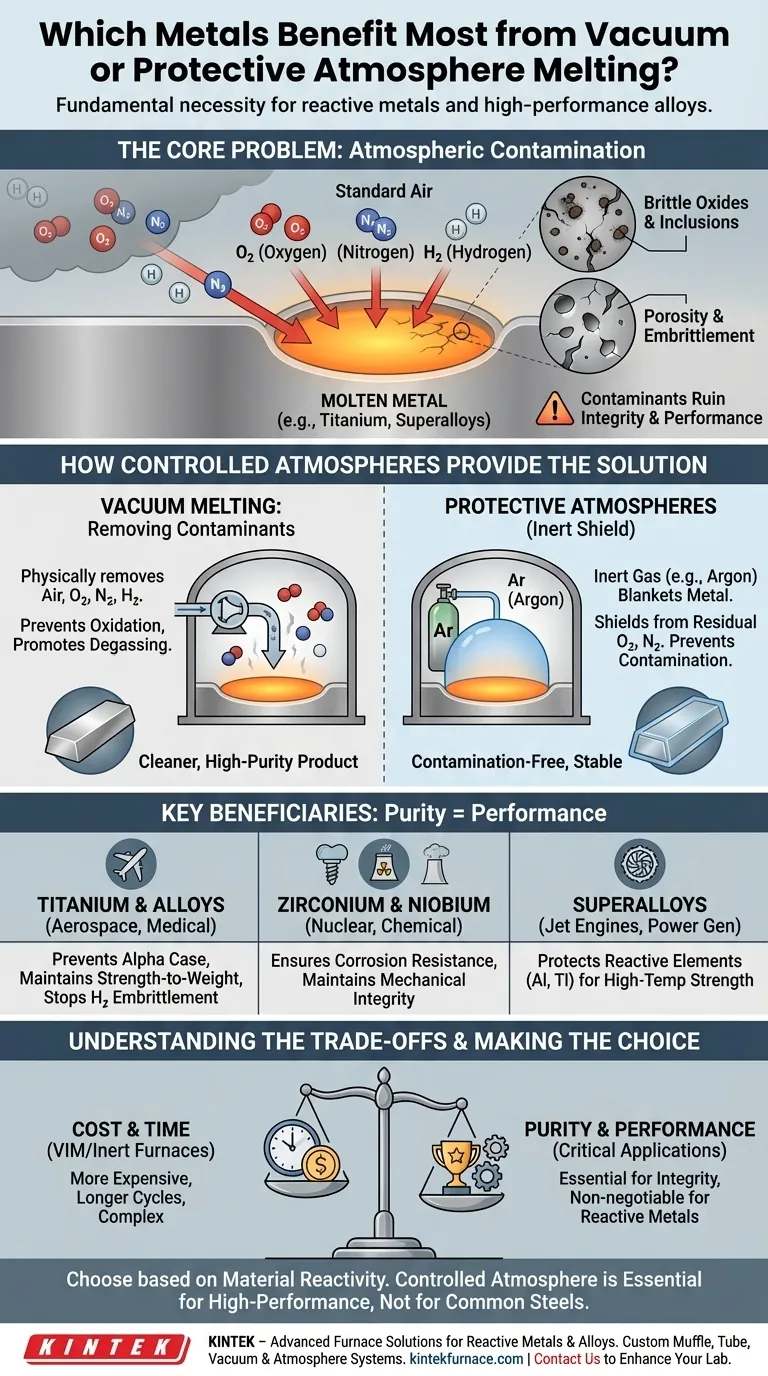
The short answer is that reactive metals and specific high-performance alloys benefit most from melting in a vacuum or a protective atmosphere. This category is dominated by materials like titanium, zirconium, and niobium, as well as complex superalloys, whose chemical nature makes them extremely susceptible to contamination from the air when molten.
The decision to use vacuum or protective atmosphere melting isn't an optional upgrade; it's a fundamental necessity driven by a material's chemistry. For reactive metals, exposure to air during melting leads to irreversible damage that compromises their integrity and performance.
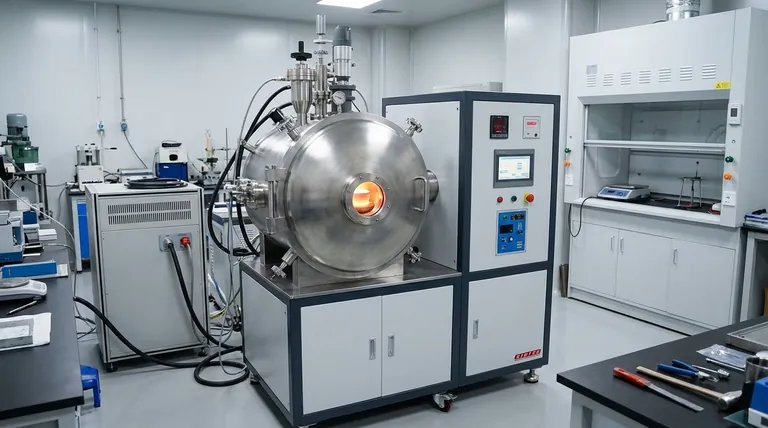

The Core Problem: Atmospheric Contamination
At room temperature, the air around us seems harmless. But for a molten metal, the gases in our atmosphere—primarily nitrogen and oxygen—become aggressive contaminants that can ruin the final product.
Why Air is the Enemy
Standard air is approximately 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen. At the extreme temperatures required for melting, these gases are no longer inert bystanders. They actively seek to react with and dissolve into the liquid metal.
The Mechanism of Oxidation
Reactive metals have a very high affinity for oxygen. When melted in air, they rapidly form stable oxides. This isn't just a surface-level tarnish; these oxides manifest as brittle inclusions within the solidified metal, acting as microscopic crack initiation points that drastically reduce strength and ductility.
The Challenge of Gas Absorption
Beyond oxygen, gases like nitrogen and hydrogen can dissolve into the molten metal. As the metal cools and solidifies, this trapped gas can form pores (porosity) or cause severe embrittlement, rendering the material useless for any demanding application. Titanium, for example, is notoriously prone to hydrogen embrittlement.
How Controlled Atmospheres Provide the Solution
The entire purpose of vacuum or protective atmosphere melting is to control the environment around the molten metal, either by removing the harmful gases or by replacing them with harmless ones.
Vacuum Melting: Removing the Contaminants
By placing the metal in a sealed chamber and pumping out the air, we create a vacuum. This physically removes the vast majority of oxygen, nitrogen, and other gas molecules.
This process not only prevents oxidation but also promotes degassing, where dissolved gases already present within the raw material are pulled out of the liquid metal, leading to a cleaner, higher-purity final product.
Protective Atmospheres: Creating an Inert Shield
An alternative to a vacuum is to purge the melting chamber of air and backfill it with a high-purity inert gas, most commonly argon.
This inert gas creates a positive pressure and a protective blanket over the melt. Since argon does not react with the metal, it effectively shields the molten pool from any residual oxygen or nitrogen, preventing contamination.
Key Beneficiaries in Detail
The metals that demand these processes are those where purity directly translates to performance.
- Titanium and its Alloys: These are poster children for controlled melting. Oxygen contamination creates a brittle "alpha case" layer and internal oxides that destroy the material's exceptional strength-to-weight ratio.
- Zirconium and Niobium: Used in nuclear, medical, and aerospace applications, these metals have an extremely low tolerance for impurities. Contamination compromises their corrosion resistance and mechanical integrity.
- Nickel- and Cobalt-Based Superalloys: These alloys, used in jet engine turbines, derive their incredible high-temperature strength from reactive elements like aluminum and titanium. Melting in air would oxidize these critical elements, preventing the formation of the strengthening phases they are designed to create.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While essential for certain materials, these advanced melting techniques are not a universal solution due to their inherent complexity and cost.
Cost and Process Time
Vacuum induction melting (VIM) or inert gas furnaces are significantly more expensive to build, operate, and maintain than simple air-melt furnaces. The process cycles are also longer due to the time required to pump down a vacuum or purge a chamber with inert gas.
Vacuum vs. Inert Gas
The choice between vacuum and inert gas is not arbitrary. A deep vacuum is excellent for removing dissolved gases but can cause the "boil-off" of alloying elements with high vapor pressure (like manganese or chromium). An inert gas atmosphere prevents this boil-off but is less effective at removing dissolved hydrogen.
When It's Unnecessary
For the vast majority of metals produced globally, such as common carbon steels, stainless steels, and most aluminum alloys, controlled atmosphere melting is overkill. Their chemistry is less sensitive, and any oxidation can be managed effectively and economically with fluxes and deoxidizing agents added during a standard air melt.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct melting process is a critical decision that balances material requirements against economic reality. The material's inherent reactivity is the deciding factor.
- If your primary focus is on reactive metals like titanium or zirconium: Vacuum or inert gas melting is non-negotiable to prevent catastrophic embrittlement and ensure material integrity.
- If your primary focus is on high-performance superalloys: A controlled atmosphere is essential to protect the precise chemistry of reactive alloying elements vital for high-temperature strength.
- If your primary focus is on cost-effective production of common steels or aluminum: Standard air melting with appropriate metallurgical practices is the correct and most economical choice.
Ultimately, the goal is to match the melting environment to the chemical nature of the metal to ensure its final properties are not compromised.
Summary Table:
| Metal Type | Key Benefits of Controlled Atmosphere Melting | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Titanium & Alloys | Prevents oxidation and hydrogen embrittlement, maintains strength-to-weight ratio | Aerospace, medical implants |
| Zirconium & Niobium | Ensures corrosion resistance and mechanical integrity | Nuclear reactors, aerospace |
| Nickel- & Cobalt-Based Superalloys | Protects reactive elements for high-temperature strength | Jet engine turbines, power generation |
Need high-temperature furnace solutions for your reactive metals or alloys? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and material quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys



















