In short, a vacuum annealing furnace is suitable for materials that are highly sensitive to oxidation and contamination at high temperatures. These include a wide range of metals like stainless steels, titanium and copper alloys, superalloys, and special materials like precious metals, as well as sensitive electronic components and certain advanced ceramics. The process is chosen specifically to protect the material's surface integrity and internal structure.
The decision to use a vacuum annealing furnace is less about which materials can be heated and more about which materials are damaged by reacting with air. The core purpose is to create a controlled, oxygen-free environment to achieve a pure, uncontaminated, and structurally uniform final product.
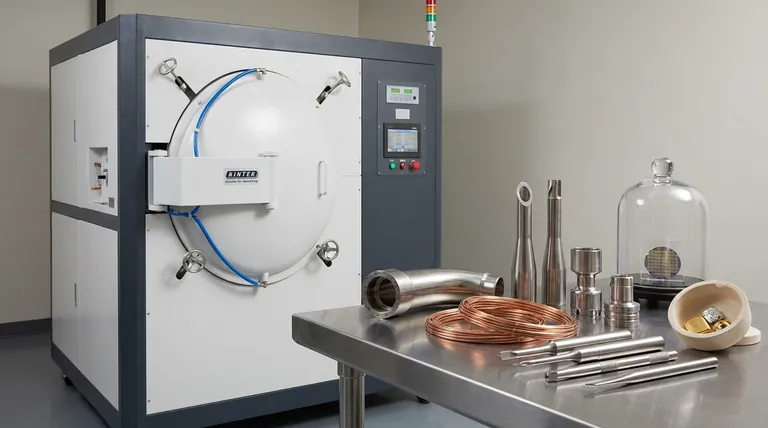

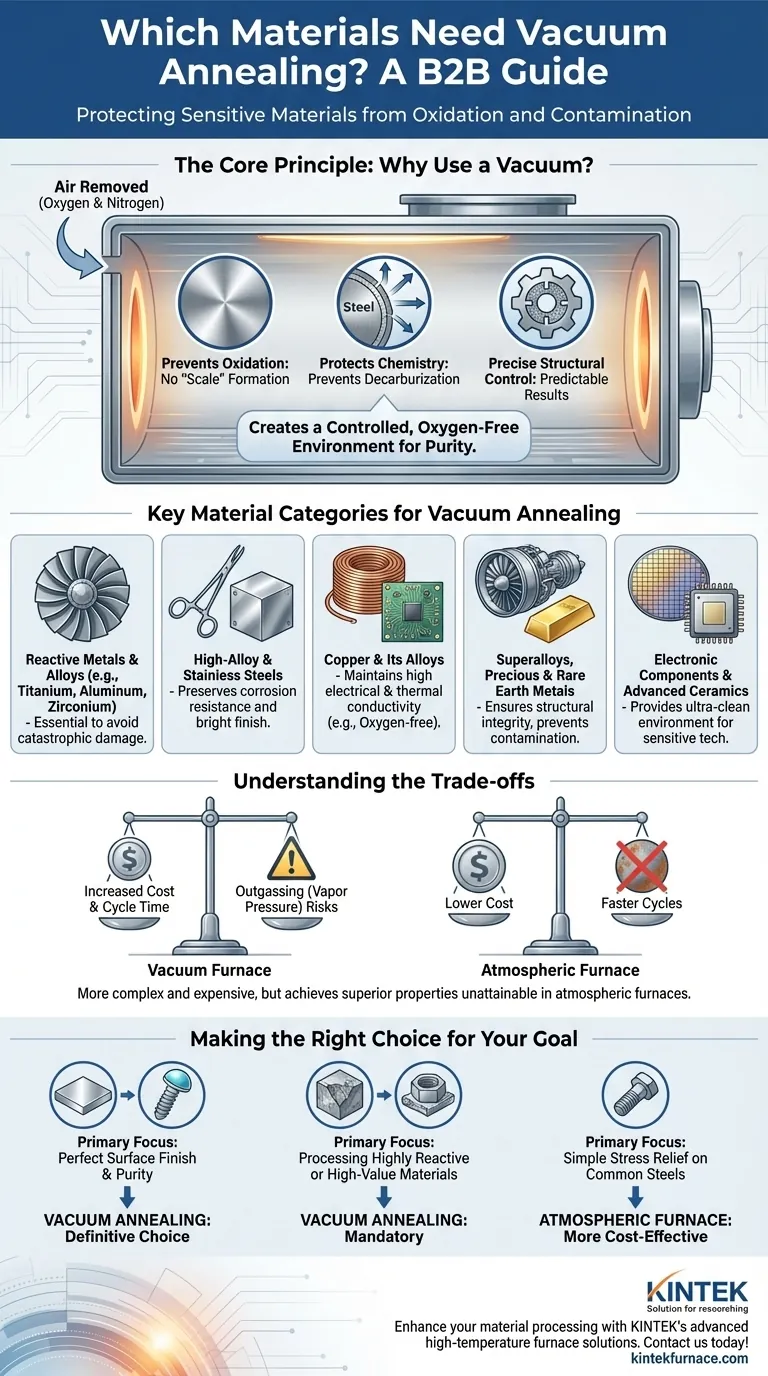
The Core Principle: Why Use a Vacuum?
Vacuum annealing is a specific form of heat treatment. Its value comes from removing the atmosphere—primarily oxygen and nitrogen—that would normally react with a workpiece at high temperatures.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
At elevated temperatures, most metals readily react with oxygen, forming an oxide layer or "scale." This is detrimental for materials where surface finish is critical.
A vacuum furnace uses a system of pumps to remove air from the sealed chamber before heating begins. This starves the environment of the oxygen needed for these unwanted chemical reactions to occur, resulting in a bright, clean surface finish.
Protecting Material Chemistry
For certain steel alloys, the carbon near the surface can react with oxygen in a conventional furnace, a process known as decarburization. This softens the surface and degrades performance.
Vacuum annealing completely prevents decarburization, ensuring the material's chemical composition and intended mechanical properties are preserved from the core to the surface.
Enabling Precise Structural Control
The primary goals of annealing are to relieve internal stresses, increase ductility, and create a more uniform internal grain structure.
By eliminating unwanted chemical variables, a vacuum environment allows for extremely precise temperature control. This ensures that the only changes occurring within the material are the desired metallurgical transformations, leading to highly predictable and repeatable results.
Key Material Categories for Vacuum Annealing
While many materials can be treated in a vacuum, some benefit far more than others and are considered primary candidates.
Reactive Metals and Alloys
Materials like titanium alloys, aluminum alloys, and zirconium are extremely reactive with oxygen at annealing temperatures. For these, vacuum treatment is not just beneficial—it is often essential to avoid catastrophic damage to the material's properties.
High-Alloy and Stainless Steels
Stainless steels, tool steels, and other high-alloy steels contain significant amounts of chromium, molybdenum, or other elements that readily oxidize. Vacuum annealing protects these expensive alloys, preserving both their corrosion resistance and their bright finish.
Copper and Its Alloys
For applications in electronics and vacuum technology, oxygen-free copper is critical. Vacuum annealing ensures no oxygen is introduced into the material, maintaining its high electrical and thermal conductivity.
Superalloys, Precious Metals, and Special Materials
Nickel-based superalloys, used in aerospace and turbine engines, demand perfect structural integrity. Likewise, precious metals (gold, silver, platinum) and rare earth metals are treated in a vacuum to prevent any material loss or surface contamination, preserving their high value.
Electronic Components and Advanced Ceramics
Semiconductors, electronic packaging, and some advanced ceramics are extremely sensitive to even trace amounts of contamination. Vacuum processing provides the ultra-clean environment necessary for these high-technology applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Vacuum annealing is a powerful tool, but it is not the universal solution for all heat treatment needs.
Increased Cost and Cycle Time
Vacuum furnaces are more complex and expensive to build and operate than atmospheric furnaces. The process also takes longer due to the time required to pump the chamber down to the target vacuum level and later backfill it for cooling.
Outgassing and Vapor Pressure
A key consideration is the vapor pressure of the elements within an alloy. In a high vacuum, some elements with a low boiling point (like zinc in brass or cadmium in certain steels) can literally boil out of the material's surface at high temperatures. This phenomenon, known as outgassing, can alter the alloy's composition and must be carefully managed.
When a Vacuum Isn't Necessary
For simple, low-carbon steels where a surface oxide layer is acceptable or will be removed by subsequent machining, a more economical atmospheric furnace is often sufficient. The added expense of vacuum processing provides no significant benefit in these cases.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct annealing process requires balancing the material's needs with the final application's requirements.
- If your primary focus is a perfect surface finish and purity: For medical implants, aerospace components, or electronic parts, vacuum annealing is the definitive choice.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive or high-value materials: For titanium, superalloys, or precious metals, vacuum annealing is mandatory to protect the material's integrity.
- If your primary focus is simple stress relief on common steels: For non-critical components made of plain carbon or low-alloy steel, a conventional atmospheric furnace is typically more cost-effective.
Ultimately, choosing vacuum annealing is an investment in achieving superior material properties and purity that cannot be attained in a conventional atmosphere.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Key Examples | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Reactive Metals and Alloys | Titanium, Aluminum, Zirconium | Prevents catastrophic oxidation and damage |
| High-Alloy and Stainless Steels | Stainless steel, Tool steel | Preserves corrosion resistance and surface finish |
| Copper and Its Alloys | Oxygen-free copper | Maintains high electrical and thermal conductivity |
| Superalloys and Precious Metals | Nickel superalloys, Gold, Platinum | Ensures structural integrity and prevents contamination |
| Electronic Components and Ceramics | Semiconductors, Advanced ceramics | Provides ultra-clean environment for sensitive applications |
Ready to enhance your material processing with precision and purity? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, tailored for industries like aerospace, electronics, and medical devices. Our expertise in R&D and in-house manufacturing ensures deep customization to meet your unique needs. Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum annealing furnaces can protect your high-value materials and improve your outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety



















