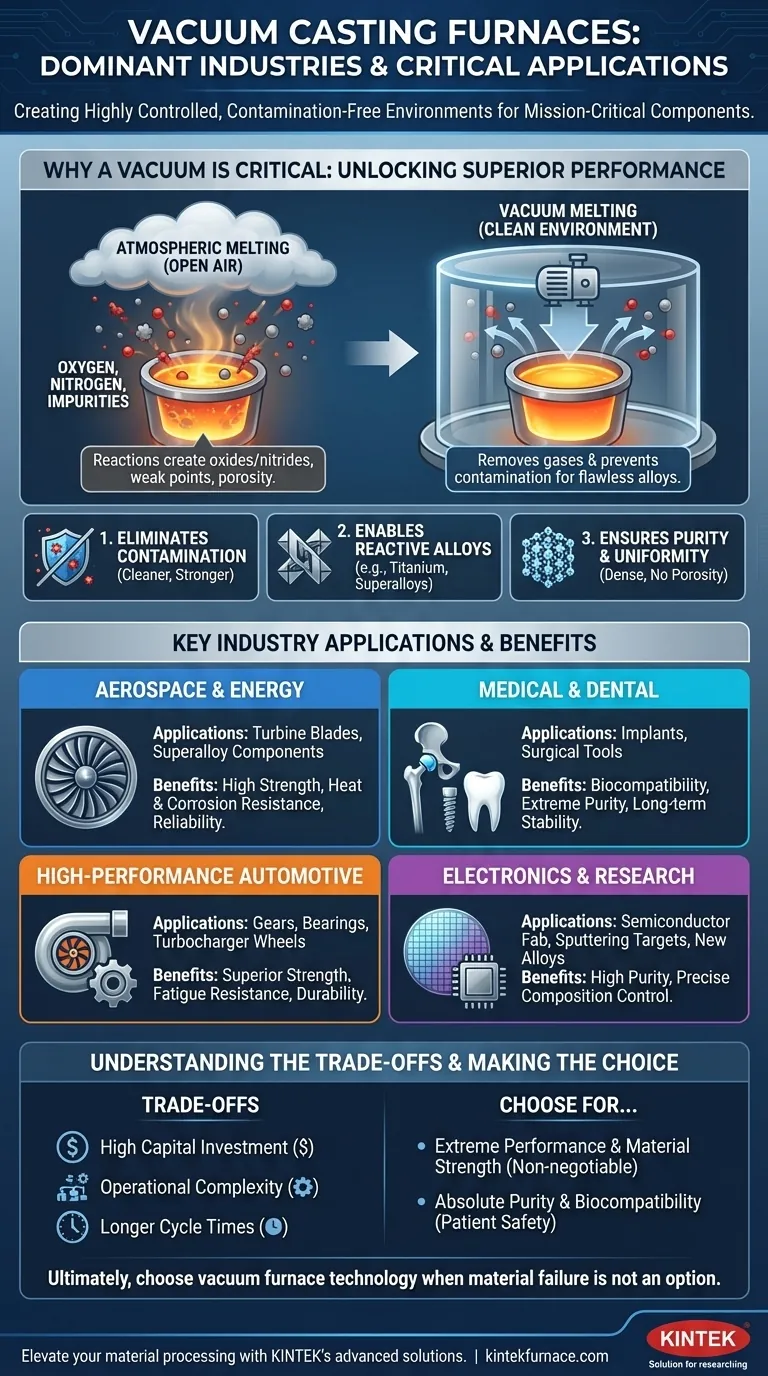
In short, vacuum casting furnaces are predominantly used in the aerospace, medical, automotive, and energy sectors. These industries rely on them to manufacture mission-critical components like jet engine turbine blades, medical implants, and high-performance engine parts where material purity and structural integrity are paramount.
The essential function of a vacuum furnace is not simply to melt metal, but to create a highly controlled, contamination-free environment. This process prevents oxidation and removes dissolved gases, enabling the creation of flawless, high-strength parts from advanced alloys that cannot be processed in open air.

Why a Vacuum is the Critical Element
The decision to use a vacuum furnace is driven by the need for ultimate material quality. The vacuum itself is the technology that unlocks superior performance in metal components.
Eliminating Atmospheric Contamination
When metal is melted in the open air, it reacts with oxygen and nitrogen. These reactions create impurities (oxides and nitrides) within the metal's structure, which introduce weak points and can lead to premature failure.
A vacuum furnace removes these reactive gases. This prevents the formation of impurities, resulting in a cleaner, stronger, and more reliable final product.
Enabling Advanced and Reactive Alloys
Many of the most advanced materials, such as titanium alloys and nickel-based superalloys, are highly reactive with oxygen, especially at high temperatures.
Melting these materials in a conventional furnace would destroy their unique properties. A vacuum is the only environment where they can be processed correctly, preserving the chemical composition and structural integrity required for extreme applications.
Ensuring Purity and Uniformity
The vacuum environment also helps pull dissolved gases like hydrogen out of the molten metal. The removal of these gases prevents porosity (tiny bubbles) from forming as the metal solidifies.
This results in a dense, uniform material structure, which dramatically improves mechanical properties like fatigue resistance and tensile strength.
Key Industry Applications in Detail
The need for flawless, high-purity components drives the adoption of vacuum furnaces across several high-stakes industries.
Aerospace and Energy
In both jet engines and power generation turbines, components like turbine blades operate under immense stress and extreme temperatures.
Vacuum casting is used to produce these parts from superalloys. The resulting components possess the high strength and resistance to heat and corrosion necessary to perform reliably for thousands of hours without failure.
Medical and Dental
For components placed inside the human body, material purity is a matter of safety. Medical implants, such as hip joints, dental roots, and surgical tools, must be perfectly biocompatible.
Vacuum furnaces produce implants from materials like titanium with exceptionally high purity. This pristine quality minimizes the risk of the patient's body rejecting the implant and ensures long-term stability.
High-Performance Automotive
In motorsport and high-end vehicles, engine and drivetrain components are pushed to their absolute limits. Vacuum casting is used for parts like gears, bearings, and turbocharger wheels.
This process delivers the superior strength and fatigue resistance needed to handle extreme loads and high RPMs, ensuring both performance and durability.
Electronics and Research
The electronics industry uses vacuum furnaces for processes like semiconductor fabrication and creating high-purity metals for sputtering targets.
In research and development, these furnaces are essential for developing new alloys and materials where precise control over the material's composition is critical.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the benefits are significant, vacuum furnace technology involves clear trade-offs that make it unsuitable for general-purpose applications.
High Capital Investment
Vacuum furnaces and their supporting systems (pumps, controls) are significantly more expensive than traditional atmosphere furnaces. This cost is only justifiable when the application demands the highest possible material quality.
Operational Complexity
Operating a vacuum furnace requires specialized training. Managing vacuum levels, controlling precise heating and cooling cycles, and maintaining the complex system is far more demanding than standard casting.
Longer Cycle Times
The process of pumping down the chamber to create a vacuum adds significant time to each production cycle. This makes it a slower, lower-volume process compared to conventional casting methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a vacuum casting furnace hinges entirely on whether your application's demands justify the investment in quality.
- If your primary focus is extreme performance and material strength: Vacuum casting is non-negotiable for producing reliable parts from superalloys and titanium for aerospace or high-performance automotive use.
- If your primary focus is absolute purity and biocompatibility: The pristine environment of a vacuum furnace is essential for manufacturing medical implants that ensure patient safety and long-term success.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production of simple parts: Traditional sand casting or die casting in a standard atmosphere furnace is a far more practical and economical choice.
Ultimately, you choose vacuum furnace technology when material failure is not an option and performance cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace & Energy | Turbine blades, superalloy components | High strength, heat resistance, corrosion resistance |
| Medical & Dental | Implants (e.g., hip joints), surgical tools | Biocompatibility, purity, long-term stability |
| Automotive | Gears, bearings, turbocharger wheels | Superior strength, fatigue resistance, durability |
| Electronics & Research | Semiconductor fabrication, sputtering targets | High purity, precise composition control |
Elevate your material processing with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line—including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—to meet the unique demands of industries like aerospace, medical, and automotive. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely tailor solutions to your experimental and production needs, delivering superior purity, strength, and reliability. Don't compromise on quality—contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today



















