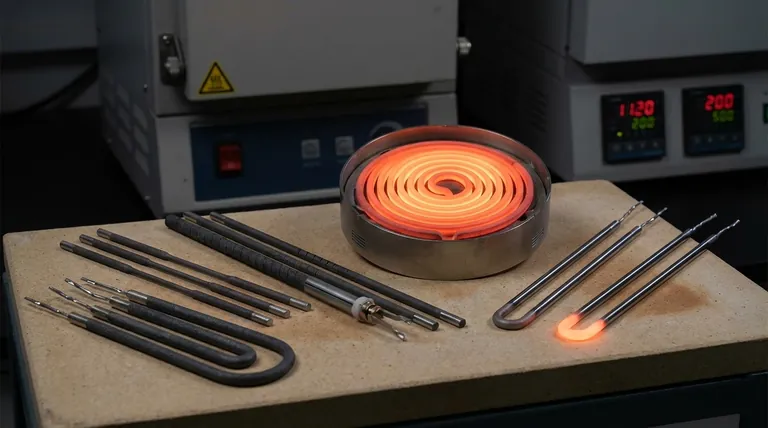
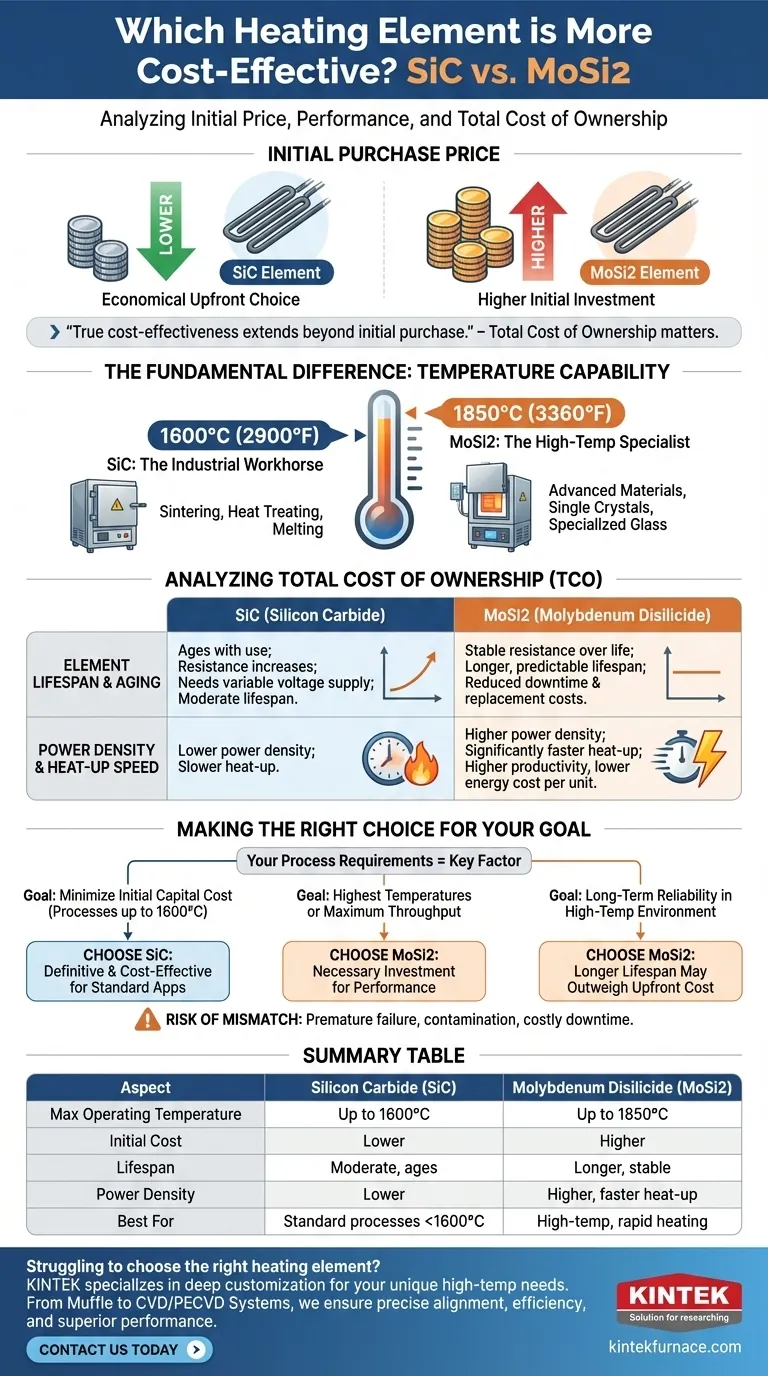
In terms of initial purchase price, Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements are generally less expensive than Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) elements. This makes SiC a more economical upfront choice for many standard industrial and laboratory furnace applications.
The true measure of cost-effectiveness, however, extends beyond the initial purchase. While SiC is cheaper to buy, MoSi2 often provides a lower total cost of ownership in applications requiring extremely high temperatures or rapid heating, due to its superior durability and performance under those specific conditions.

The Fundamental Difference: Temperature Capability
The most critical factor distinguishing these two materials is their maximum recommended operating temperature. This single variable is the primary driver of both cost and application suitability.
Silicon Carbide (SiC): The Industrial Workhorse
SiC elements are the default choice for a vast range of heating processes. They are robust, reliable, and perform exceptionally well in applications running up to approximately 1600°C (2900°F).
Their combination of moderate cost and high performance makes them ideal for processes like sintering, heat treating, and melting in many ceramics, metals, and electronics industries.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2): The High-Temperature Specialist
MoSi2 elements are engineered for the most demanding thermal environments. They can operate consistently at very high temperatures, often up to 1850°C (3360°F).
This capability makes them essential for advanced materials research, growing single crystals, and specialized glass manufacturing where temperatures exceed the limits of SiC.
Beyond Purchase Price: Analyzing Total Cost of Ownership
A truly cost-effective decision requires looking at the element's entire lifecycle. The higher initial investment for MoSi2 can be justified by its long-term performance benefits in the right application.
Element Lifespan and Aging
SiC elements "age" during use, meaning their electrical resistance gradually increases over time. This requires a power supply with a variable voltage output to compensate, and eventually, the elements must be replaced.
MoSi2 elements, by contrast, exhibit very little resistance change over their operational life. This stability can lead to a longer lifespan and more predictable performance, reducing downtime and replacement costs in high-demand operations.
Power Density and Heat-Up Speed
MoSi2 elements can handle a much higher watt loading, or power density, than SiC. This allows them to heat a furnace to its target temperature significantly faster.
For facilities where process throughput is critical, these faster cycle times can translate directly into higher productivity and lower energy cost per unit produced, quickly offsetting the higher initial element cost.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong element is the most expensive mistake you can make. It leads to premature failure, process contamination, and costly operational downtime.
The Case for SiC
Choose SiC when your process operates comfortably below 1600°C and does not require extremely rapid thermal cycling. Its lower capital cost and proven reliability make it the clear economic choice for the majority of standard high-temperature applications.
The Case for MoSi2
Invest in MoSi2 only when your process demands it. If you need to exceed the thermal limits of SiC or if rapid heating is critical to your productivity, the superior performance and longer life of MoSi2 will deliver a better return on investment.
The Risk of Mismatch
Using an SiC element in an application that is too hot will cause it to fail quickly. Conversely, using a more expensive MoSi2 element in a simple, lower-temperature process is an unnecessary capital expenditure that offers no tangible benefit.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific process requirements are the only factor that matters. The most "cost-effective" element is the one that is correctly matched to the job.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial capital cost for processes up to 1600°C: SiC is the definitive and most cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible temperatures or maximum process throughput: The capabilities of MoSi2 are a necessary investment, and it will prove more cost-effective through its unique performance.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability in a continuous, high-temperature environment: You must carefully calculate the total cost, as the longer lifespan of MoSi2 may outweigh its higher upfront price.
Ultimately, true cost-effectiveness is achieved by precisely matching the heating element's capabilities to your specific operational demands.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) |
|---|---|---|
| Max Operating Temperature | Up to 1600°C | Up to 1850°C |
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Lifespan | Moderate, ages over time | Longer, stable resistance |
| Power Density | Lower | Higher, faster heat-up |
| Best For | Standard processes below 1600°C | High-temp, rapid heating applications |
Struggling to choose the right heating element for your lab's furnace? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure precise alignment with your experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs. Don't let equipment mismatches slow you down—contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your processes and deliver superior performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability



















