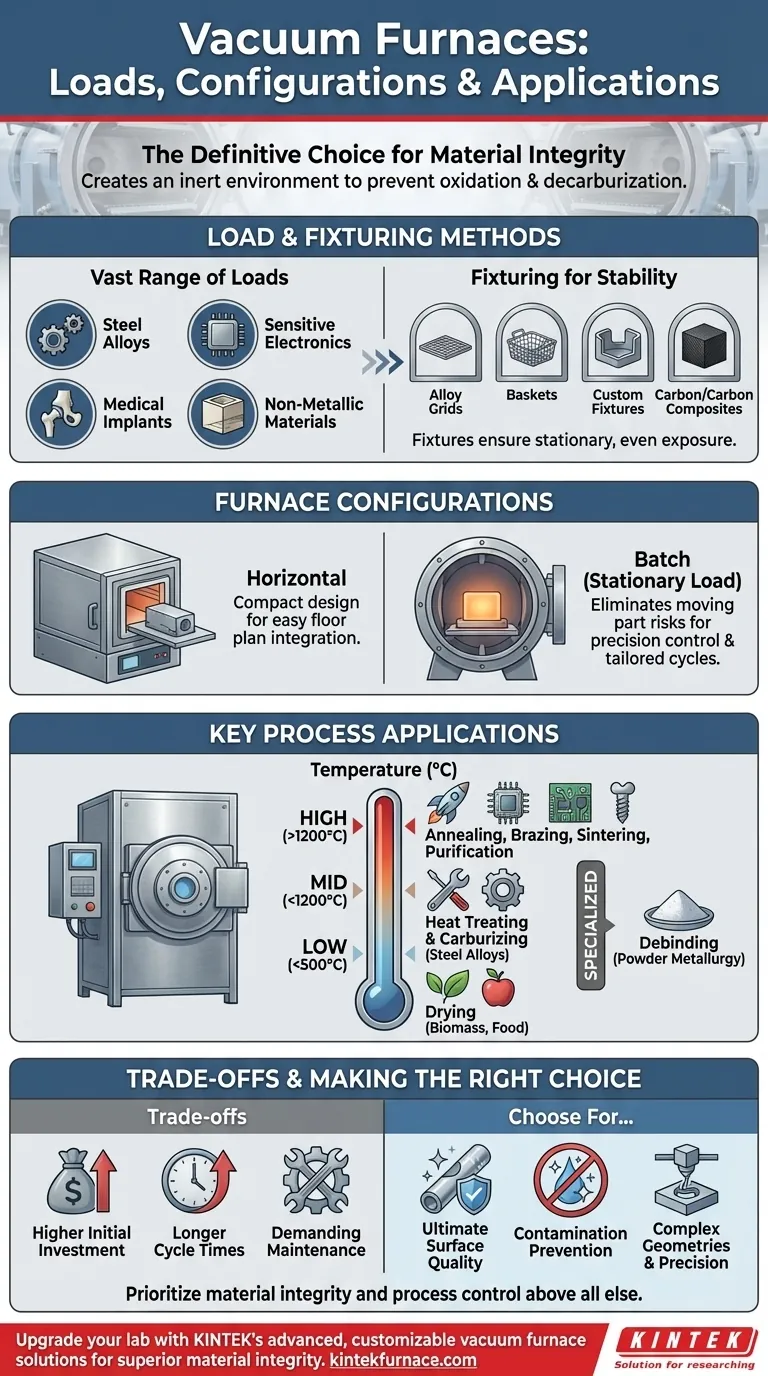
In short, vacuum furnaces handle a vast range of material loads by using alloy grids, baskets, or custom fixtures. They are uniquely capable of processing everything from standard steel alloys to highly sensitive electronics, medical implants, and advanced non-metallic materials, all within a precisely controlled, contamination-free environment.
The core function of a vacuum furnace isn't just to heat a part, but to create an inert environment. This prevents surface reactions like oxidation and decarburization, making it the definitive choice when material integrity and surface finish are more critical than raw throughput or initial equipment cost.

Understanding Load Configurations and Fixturing
How a part is held and oriented within the furnace is fundamental to achieving uniform results. The choice of fixturing and furnace layout depends on the material, geometry, and process temperature.
Common Fixturing Methods
Most loads in a vacuum furnace are held stationary on alloy grids, placed in baskets, or secured by custom fixtures. The primary goal is to ensure parts are stable and exposed evenly to heat and the vacuum environment.
The Rise of Carbon/Carbon Composites
While traditional alloy fixtures are common, carbon/carbon composite fixtures are increasingly popular. Their stability at high temperatures and lighter weight make them an excellent choice for demanding applications, improving energy efficiency and handling.
The Horizontal Furnace Configuration
Horizontal vacuum furnaces are a prevalent configuration, prized for being relatively compact. This design allows for easier integration into existing manufacturing floor plans where space may be at a premium.
Key Process Applications
The defining feature of a vacuum furnace is its versatility across a wide temperature spectrum. Applications are typically categorized by the temperature required to achieve the desired material properties.
Low-Temperature Applications
Even at lower temperatures, a vacuum environment is beneficial for processes like drying sensitive materials such as biomass or food products, where removing moisture without causing oxidation is critical.
Mid-Temperature Heat Treatment
This is a common range for treating steel alloys, typically below 1200°C. Processes include hardening and tempering, where the vacuum prevents surface decarburization, resulting in a stronger, cleaner part.
A key process in this range is vacuum carburizing, or case hardening, performed between 870–1070°C. It produces a hard, wear-resistant surface layer on components with superior uniformity.
High-Temperature Processing
For temperatures exceeding 1200°C, vacuum furnaces are essential. They serve advanced industries like electronics, medical, aerospace, and energy for processes such as:
- Annealing: Softening materials to improve ductility.
- Brazing: Joining components with a filler metal.
- Sintering: Fusing powdered materials to create a solid mass.
- Purification: Removing impurities from high-purity metals.
Specialized Processes like Debinding
Vacuum furnaces are also used for debinding, a critical step in powder metallurgy and additive manufacturing. This process carefully removes binder materials from "green" parts before the final sintering stage.
The Batch Furnace Advantage
The vast majority of vacuum furnaces operate on a batch model, which provides distinct advantages for precision work.
Stationary Load, Precision Control
In a batch furnace, the load remains stationary throughout the entire heating and cooling cycle. This eliminates the risks associated with moving parts at high temperatures and allows for extremely precise temperature control.
Tailored Cycles for Every Part
Each batch can run a unique, pre-programmed recipe. Operators can precisely define vacuum levels, temperature ramp rates, soak times, and even the type and pressure of cooling gas, tailoring the cycle to specific part geometries and material requirements.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a vacuum furnace is not the universal solution for all heating applications. Its advantages come with clear and important trade-offs.
Higher Initial Investment
Vacuum furnaces represent a significantly higher equipment cost compared to their atmospheric counterparts. The complexity of the vacuum system, chamber, and controls contributes to this expense.
Longer Cycle Times
Achieving a deep vacuum is not instantaneous. The pump-down time required to evacuate the chamber adds to the overall cycle duration, which can impact throughput.
Demanding Maintenance Requirements
The stringent requirements for maintaining a vacuum-tight system make maintenance more complex and costly. Seals, pumps, and sensors all require regular, specialized attention to ensure reliable operation and prevent leaks.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right thermal processing technology depends entirely on your end goal. The decision to use a vacuum furnace is a strategic one that balances process quality against operational cost and complexity.
- If your primary focus is ultimate surface quality and preventing contamination: A vacuum furnace is the superior choice for processes like brazing, medical implant sintering, or treating reactive metals.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, general-purpose heat treating of standard steels: The longer cycle times and higher cost of a vacuum furnace may be unnecessary compared to simpler atmospheric furnaces.
- If your primary focus is processing complex geometries with precise, repeatable results: The programmable batch model of a vacuum furnace offers unparalleled control over every variable of the thermal cycle.
Ultimately, selecting a vacuum furnace is a decision that prioritizes material integrity and process control above all else.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Load Types | Steel alloys, electronics, medical implants, non-metallic materials |
| Fixturing Methods | Alloy grids, baskets, custom fixtures, carbon/carbon composites |
| Furnace Configurations | Horizontal (compact), batch (stationary load) |
| Temperature Ranges | Low (drying), Mid (up to 1200°C for steel), High (above 1200°C for advanced processes) |
| Key Applications | Drying, hardening, vacuum carburizing, annealing, brazing, sintering, purification, debinding |
| Trade-offs | Higher cost, longer cycle times, demanding maintenance |
Upgrade your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced vacuum furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, delivering contamination-free processing and superior material integrity. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your precision and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision



















