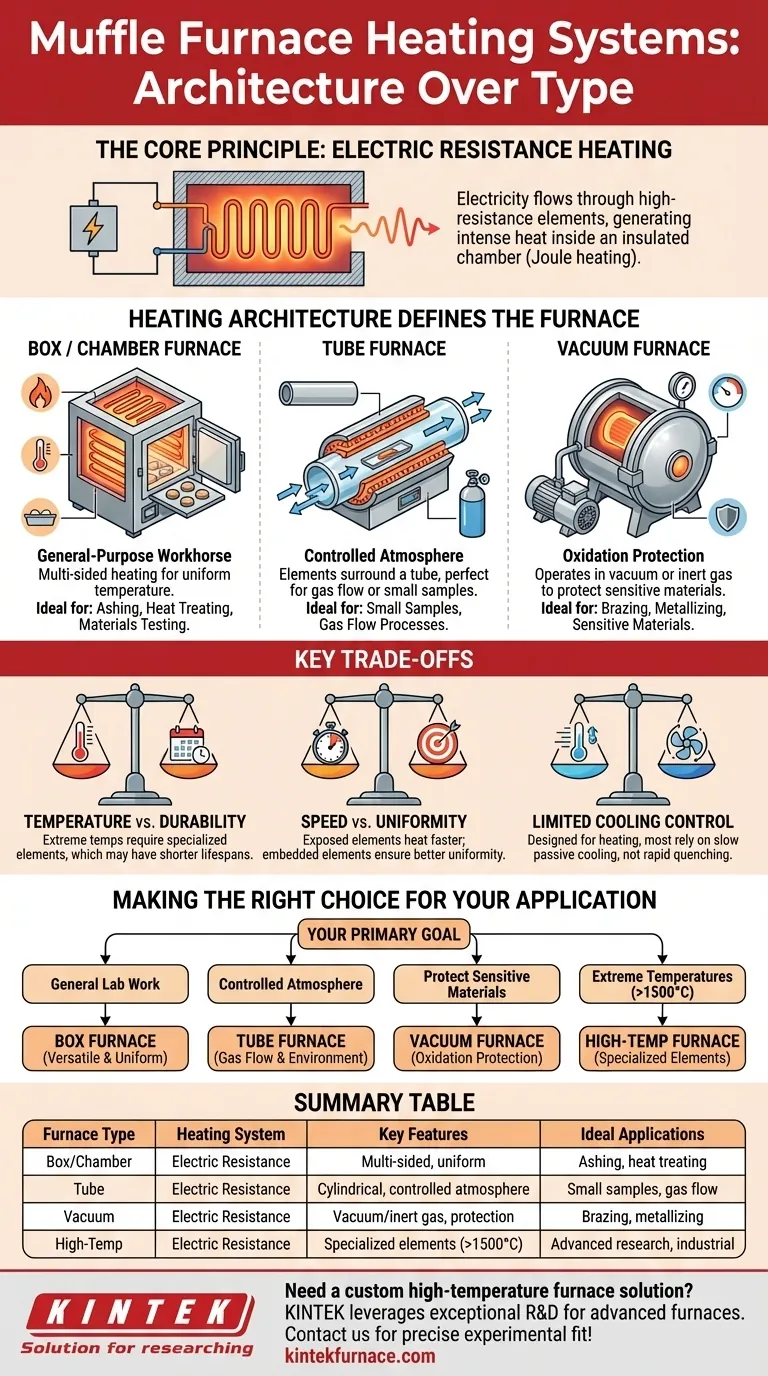
At its core, a muffle furnace operates on a single, primary heating principle. The vast majority of modern muffle furnaces, from small benchtop units to large industrial models, use electric resistance heating. This involves passing an electrical current through specialized, high-resistance materials known as heating elements, which generate intense heat inside an insulated chamber without direct combustion.
The critical distinction is not the type of heating system—which is almost always electric—but how that system is integrated into the furnace's physical design. Understanding the furnace's architecture (e.g., box, tube, vacuum) is the key to selecting the right tool for your specific high-temperature application.
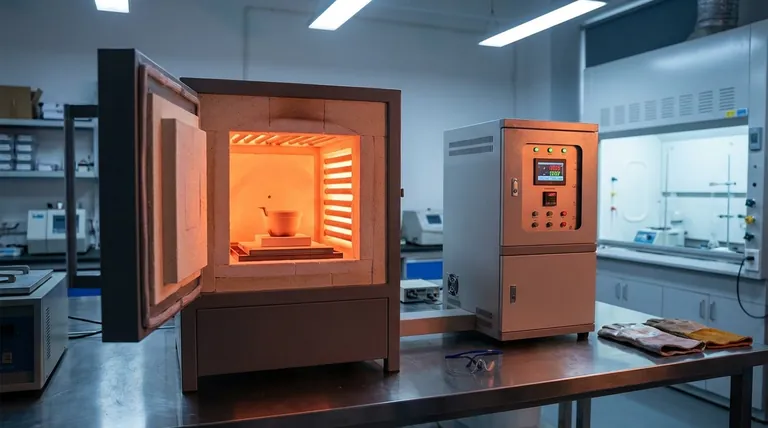

The Core Technology: Electric Resistance Heating
How Electric Heating Works
The principle is straightforward: electricity flows through heating elements made of materials with high electrical resistance. This resistance converts electrical energy into thermal energy, or heat, a phenomenon known as Joule heating.
These elements are mounted inside an insulated chamber, which minimizes heat loss and allows the furnace to reach and maintain extremely high temperatures efficiently and with precise control.
Element Placement and Heat Distribution
The placement of these heating elements is a critical design factor that directly impacts performance. Common configurations include heating from multiple sides to ensure uniform temperature throughout the chamber.
Furnaces may feature three-sided heating (elements on both sides and the top) or top and bottom heating. The goal is to create a consistent thermal environment, which is crucial for scientific experiments and manufacturing processes like annealing and sintering.
How Heating Architecture Defines Furnace Type
While the heating source is consistent, its application within different furnace structures is what creates distinct categories. The furnace's architecture is designed to meet the demands of specific processes.
Box or Chamber Furnaces
This is the most common design, resembling a simple insulated box. It is a general-purpose workhorse for a wide range of applications like ashing, heat treating, and materials testing in a standard air atmosphere.
Tube Furnaces
In a tube furnace, the heating elements surround a cylindrical tube, often made of ceramic or quartz. This design is ideal for heating small samples, performing processes that require a controlled gas atmosphere, or for continuous-flow applications.
Vacuum Furnaces
For materials that would be damaged or oxidized by exposure to air at high temperatures, a vacuum furnace is necessary. The heating elements operate within a chamber that has been evacuated of air, creating a vacuum or an inert gas environment to protect sensitive materials during processes like brazing or metallizing.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Choosing a muffle furnace requires balancing performance characteristics. The design of the heating system introduces important trade-offs you must consider.
Temperature Range vs. Element Durability
Furnaces capable of reaching very high temperatures (above 1500°C) require specialized and more expensive heating element materials. These high-performance elements can have a shorter operational lifespan and may be more sensitive to thermal shock compared to standard elements used in furnaces up to 1200°C.
Speed vs. Uniformity
Furnaces with exposed heating elements tend to heat up more quickly. However, elements that are embedded within the refractory insulation often provide better temperature uniformity throughout the chamber, which is critical for repeatable results.
Limited Cooling Control
Most laboratory muffle furnaces are designed for heating, not rapid cooling. Cooling is typically passive, relying on the furnace's insulation to slowly dissipate heat. Some models include a simple fan-based exhaust, but sophisticated, controlled cooling systems are not a standard feature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific process dictates which furnace architecture is most suitable. Focus on your primary goal to determine the best fit.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab work: A standard box-type muffle furnace with multi-sided heating offers the best balance of versatility and performance for tasks like ashing, melting, or annealing.
- If your primary focus is working with a controlled atmosphere: A tube furnace is the definitive choice for flowing specific gases over a sample or maintaining a particular environment.
- If your primary focus is protecting sensitive materials from oxidation: A vacuum furnace is non-negotiable for high-temperature processes involving reactive metals or advanced ceramics.
- If your primary focus is reaching extreme temperatures (above 1500°C): You will need a specialized high-temperature furnace with appropriate heating elements designed for advanced industrial or research applications.
Ultimately, success depends on matching the furnace's design and capabilities directly to the requirements of your material and process.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Heating System | Key Features | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Box/Chamber | Electric Resistance | Multi-sided heating, uniform temperature | Ashing, heat treating, materials testing |
| Tube | Electric Resistance | Cylindrical design, controlled atmosphere | Small samples, gas flow processes |
| Vacuum | Electric Resistance | Vacuum/inert gas environment, oxidation protection | Brazing, metallizing, sensitive materials |
| High-Temperature | Electric Resistance | Specialized elements, extreme temperatures (>1500°C) | Advanced research, industrial processes |
Need a custom high-temperature furnace solution? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control



















