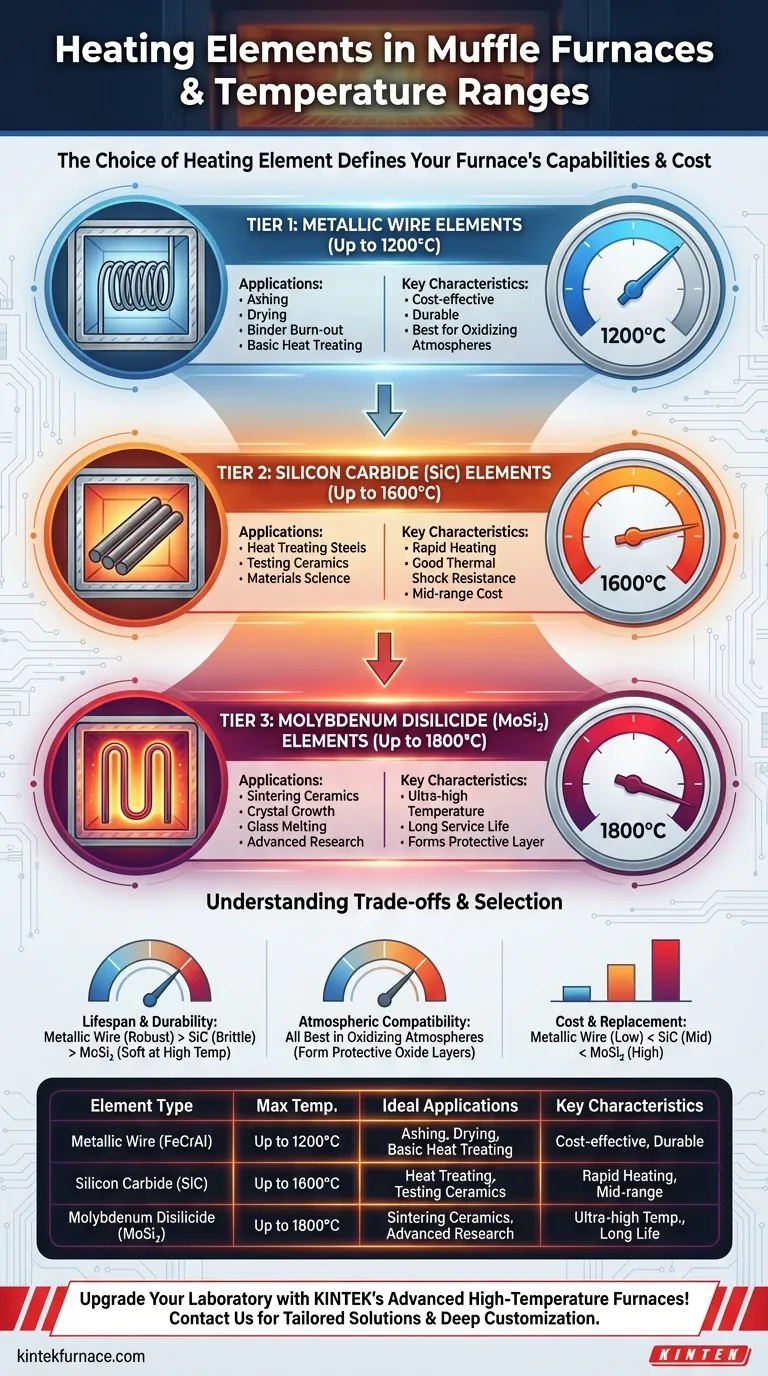
The three primary heating elements used in muffle furnaces are metallic wire, silicon carbide (SiC), and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂). These materials directly dictate the furnace's maximum operating temperature, with metallic wires used for applications up to 1200°C, SiC for temperatures up to 1600°C, and MoSi₂ for ultra-high-temperature work reaching 1800°C.
The choice of heating element is the single most critical factor defining a muffle furnace's capabilities and cost. Understanding the trade-offs between these three tiers of materials is essential for selecting the correct instrument for your specific thermal processing needs.

The Three Tiers of Furnace Heating
A muffle furnace's performance is fundamentally tied to its heating element. The material must be able to withstand extreme temperatures repeatedly while efficiently converting electricity into heat.
Tier 1: Metallic Wire Elements (Up to 1200°C)
Metallic resistance wires, most commonly an iron-chromium-aluminum alloy (FeCrAl) like Kanthal, are the workhorse for standard laboratory and industrial furnaces.
These elements are coiled and mounted along the walls of the furnace chamber. They offer excellent durability and are the most cost-effective option available.
They are ideal for common applications like ashing, drying, binder burn-out, and basic heat treating that operate below 1200°C.
Tier 2: Silicon Carbide (SiC) Elements (Up to 1600°C)
For processes requiring temperatures beyond the limits of metallic wire, silicon carbide (SiC) is the next step up.
These elements are typically rigid, self-supporting rods that offer rapid heating rates and good thermal shock resistance. They represent the mid-range for both performance and cost.
SiC-equipped furnaces are frequently used for heat treating higher-grade steels, testing ceramics, and other materials science applications in the 1300°C to 1600°C range.
Tier 3: Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) Elements (Up to 1800°C)
Molybdenum disilicide (often called "silicon molybdenum rods") represents the pinnacle of heating element technology for standard air-atmosphere furnaces.
These U-shaped elements can achieve extremely high temperatures, reaching up to 1800°C. They are known for their long service life, as they form a protective quartz-glass layer on their surface during operation.
MoSi₂ elements are reserved for the most demanding applications, such as sintering advanced ceramics, growing crystals, melting glass, and research on exotic materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs Beyond Temperature
Selecting an element involves more than just matching a maximum temperature. Each material comes with distinct operational considerations and costs.
Lifespan and Durability
Metallic wire elements are generally robust and resistant to mechanical shock. SiC elements are harder but more brittle and must be handled with care. MoSi₂ elements become soft at very high temperatures and are susceptible to degradation from chemical reactions.
Atmospheric Compatibility
The furnace atmosphere profoundly impacts element life. FeCrAl, SiC, and MoSi₂ all perform best in oxidizing atmospheres (i.e., in the presence of air), where they form stable, protective oxide layers.
Using them in reducing atmospheres (like hydrogen or nitrogen) can lead to rapid degradation and premature failure unless the furnace and elements are specifically designed for such conditions.
Cost and Replacement
Cost scales directly with temperature capability. Metallic wire elements are the least expensive to purchase and replace. SiC elements are a significant step up in price, and MoSi₂ elements are the most expensive of the three by a considerable margin.
Selecting the Right Element for Your Application
Choosing the correct furnace ultimately comes down to a realistic assessment of your temperature needs and budget.
- If your primary focus is general lab work (ashing, drying) below 1200°C: Choose a furnace with metallic wire (FeCrAl) elements for maximum cost-effectiveness and reliability.
- If your primary focus is heat treating or materials testing up to 1600°C: Select a furnace with Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements as the ideal balance of high performance and moderate cost.
- If your primary focus is advanced research or processes requiring up to 1800°C: Invest in a furnace with Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) elements for their unmatched temperature capability in an air atmosphere.
Matching the heating element to your specific temperature and process requirements is the key to ensuring reliable, efficient, and cost-effective furnace operation.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element Type | Maximum Temperature Range | Ideal Applications | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metallic Wire (e.g., FeCrAl) | Up to 1200°C | Ashing, drying, binder burn-out, basic heat treating | Cost-effective, durable, best for oxidizing atmospheres |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Up to 1600°C | Heat treating steels, testing ceramics, materials science | Rapid heating, good thermal shock resistance, mid-range cost |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) | Up to 1800°C | Sintering ceramics, crystal growth, glass melting, advanced research | Ultra-high temperature, long service life, forms protective layer |
Upgrade your laboratory's thermal processing capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with tailored solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, delivering reliable performance and cost efficiency. Don't settle for less—contact us today to discuss how our heating elements and furnaces can optimize your processes and drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating



















