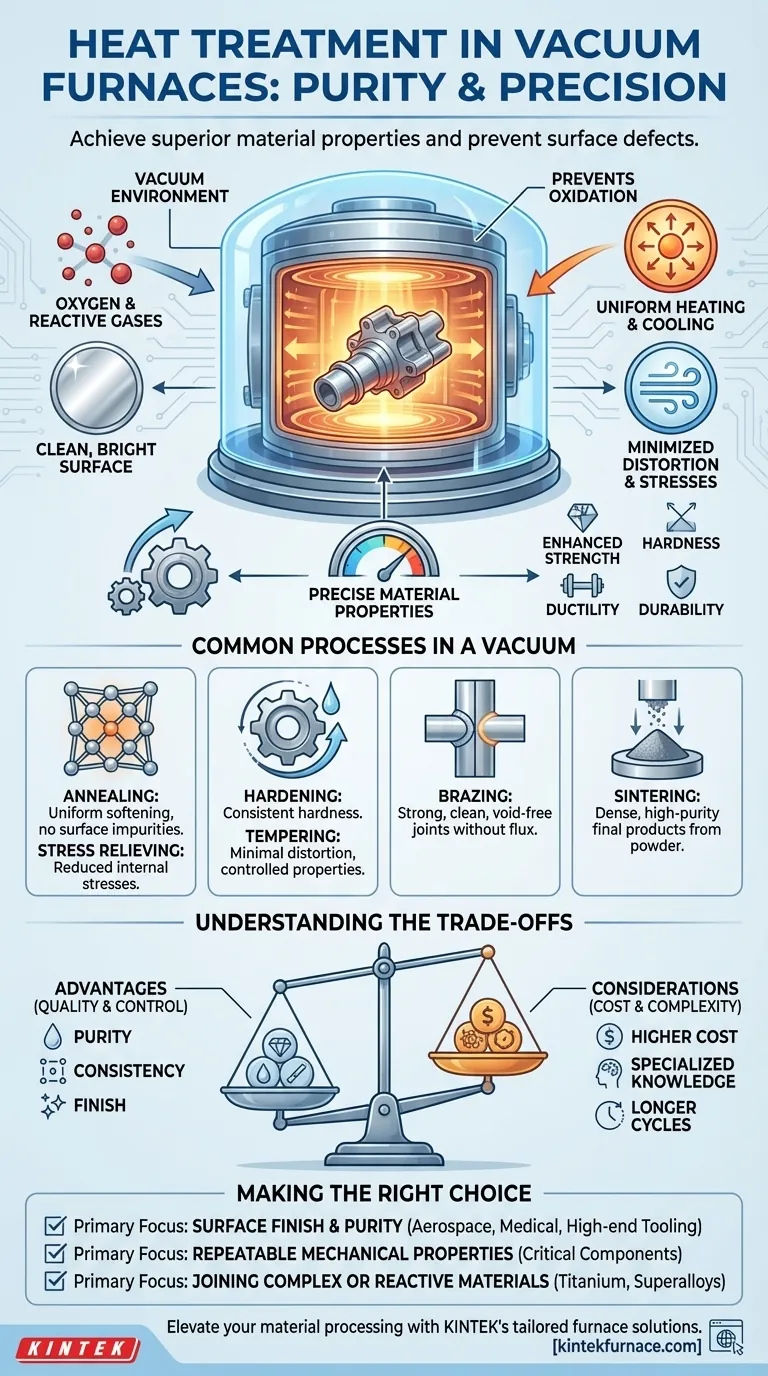
In short, a vacuum furnace is used for any heat treatment process where material purity and surface integrity are critical. This includes common processes like annealing, hardening, tempering, brazing, and sintering. By performing these operations in a controlled vacuum, manufacturers can achieve superior material properties and prevent surface defects that would occur in a standard atmosphere.
The primary purpose of using a vacuum is not the heat itself, but the elimination of atmospheric gases. By removing oxygen and other reactive elements, these furnaces prevent surface contamination and allow for precise control over the material's final properties, resulting in clean, high-performance components.

The Role of the Vacuum in Heat Treatment
A vacuum furnace provides a fundamentally different environment than a conventional furnace. This controlled atmosphere is the key to its advantages.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
The most immediate benefit of a vacuum is the removal of oxygen. In a traditional furnace, high temperatures cause oxygen to react with a metal's surface, creating scale and discoloration.
A vacuum environment prevents these reactions entirely. This results in parts that emerge from the furnace with a clean, bright surface, eliminating the need for post-process cleaning.
Ensuring Uniform Heating and Cooling
A vacuum improves heat transfer through radiation, allowing heat to be applied evenly to all surfaces of a part, even complex geometries.
When it's time to cool, the chamber can be backfilled with a high-purity inert gas like nitrogen or argon. This enables controlled, uniform cooling (convection), which is critical for minimizing distortion and internal stresses.
Achieving Precise Material Properties
The combination of a clean environment and uniform temperature control allows for highly repeatable and predictable outcomes.
This precision is essential for developing specific microstructures within a material to achieve desired properties like enhanced strength, hardness, ductility, and durability. Industries like aerospace and medical manufacturing depend on this level of control.
Common Heat Treatment Processes in a Vacuum
While many processes can be performed in a vacuum, several are particularly well-suited to its advantages.
Annealing and Stress Relieving
Annealing softens a material to make it more ductile and easier to work with. Stress relieving reduces internal stresses caused by prior manufacturing steps.
Performing these in a vacuum ensures the material is softened uniformly without introducing surface hardening or impurities, which could compromise later forming operations.
Hardening and Tempering
Hardening involves heating a metal and then cooling it rapidly (quenching) to increase its strength and wear resistance. Tempering is a subsequent, lower-temperature treatment to reduce brittleness.
A vacuum provides an ideal environment for clean hardening. The quenching process, often done with high-pressure gas, is highly controllable, leading to consistent hardness and minimal part distortion.
Brazing
Vacuum brazing is a process for joining two or more metal components using a filler metal. The vacuum prevents oxidation on both the base materials and the filler alloy.
This results in an exceptionally strong, clean, and void-free joint without the need for corrosive fluxes, making it a preferred method for critical assemblies.
Sintering
Sintering is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material from powder by applying heat.
Using a vacuum is crucial for removing trapped air and other gases from the powder before fusion. This prevents porosity and contamination, leading to a dense, high-purity final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its advantages, a vacuum furnace is not the default choice for every application. It involves specific requirements and trade-offs.
Higher Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are more complex and have a higher initial investment cost compared to standard atmospheric furnaces. The need for vacuum pumps, chamber seals, and sophisticated controls adds to this expense.
Specialized Operator Knowledge
Operating a vacuum furnace effectively requires specialized training. Technicians must understand not only the heat treatment process but also vacuum technology and advanced control systems to ensure quality and prevent equipment damage.
Potentially Longer Cycle Times
Achieving a deep vacuum can be time-consuming. The pump-down phase adds time to the overall process cycle compared to simply heating a part in an atmospheric furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding whether to use a vacuum furnace depends entirely on the required quality and performance of the final component.
- If your primary focus is surface finish and purity: A vacuum furnace is essential for applications in aerospace, medical, and high-end tooling where a clean, unoxidized surface is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is repeatable mechanical properties: The precise control over heating and cooling makes a vacuum ideal for achieving consistent hardness, strength, and ductility in critical components.
- If your primary focus is joining complex or reactive materials: Vacuum brazing is the superior method for creating strong, flux-free joints, especially with materials like titanium, stainless steels, and superalloys.
Ultimately, selecting a vacuum furnace is a strategic decision to prioritize material integrity and process control over lower initial equipment cost.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Benefits | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Uniform softening, no surface impurities | Stress relief, improved ductility |
| Hardening & Tempering | Consistent hardness, minimal distortion | High-strength, wear-resistant parts |
| Brazing | Strong, clean joints without flux | Critical assemblies in aerospace, medical |
| Sintering | Dense, high-purity products from powders | Advanced ceramics, metal components |
Ready to elevate your material processing with precision heat treatment solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in aerospace, medical, or high-end tooling, we can help you achieve superior purity, surface integrity, and mechanical properties. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can optimize your processes and deliver high-performance results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety



















