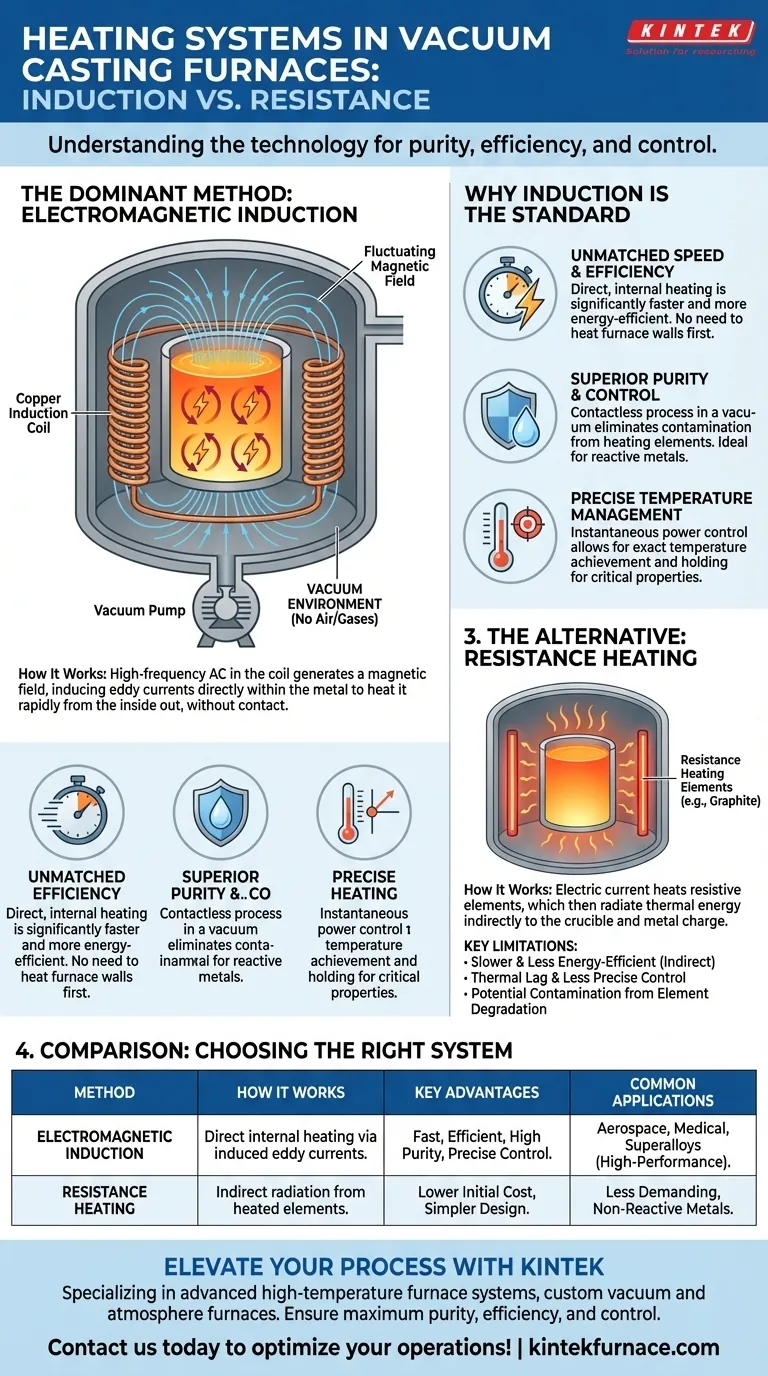
The dominant heating method in modern vacuum casting furnaces is electromagnetic induction. This technique uses a powerful, high-frequency alternating current passed through a copper coil, which generates a fluctuating magnetic field. This field induces electrical "eddy" currents directly within the metal charge, causing it to heat up rapidly and efficiently from the inside out, all without direct physical contact.
The core challenge in vacuum casting isn't just melting metal, but doing so with absolute purity and control. Induction heating is the standard because it is a non-contact method that heats the material directly, making it perfectly suited to the clean, airless environment of a vacuum chamber.
How Induction Heating Works in a Vacuum
The Core Principle: Electromagnetic Induction
An induction furnace is built around a water-cooled copper coil. When a high-frequency alternating current (AC) is applied to this coil, it produces a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field in the space within the coil.
The metal to be melted, known as the "charge," is placed in a crucible inside this coil. It does not touch the coil itself.
Generating Heat via Eddy Currents
The magnetic field passes through the metal charge and, according to Faraday's law of induction, induces circular electrical currents within it. These are called eddy currents.
Because the metal has inherent electrical resistance, the flow of these powerful eddy currents generates immense heat. The metal essentially becomes its own heating element, allowing for extremely rapid and uniform temperature increases.
The Role of the Vacuum Environment
The entire process takes place inside a sealed chamber from which air has been removed to create a vacuum. This is critical because it prevents oxygen and other atmospheric gases from reacting with the molten metal.
In a vacuum, heat transfer via convection (air movement) is eliminated. Heat is primarily transferred through radiation. A direct heating method like induction is therefore far more efficient than methods that must first heat the surrounding environment.
Why Induction is the Standard for Vacuum Casting
Unmatched Speed and Efficiency
Because induction heats the metal directly from within, it is significantly faster and more energy-efficient than traditional methods. It avoids the need to first heat the furnace walls and then radiate that heat to the crucible, saving both time and energy.
Superior Purity and Control
Induction is a contactless heating process. The only thing touching the molten metal is the inert crucible. This eliminates the risk of contamination that can occur when metal touches heating elements, which is a common issue in other furnace types.
Combined with the vacuum, this process ensures the highest possible purity for reactive metals and superalloys used in aerospace, medical, and other critical applications.
Precise Temperature Management
Induction power supplies allow for instantaneous and precise control over the energy delivered to the metal. This enables operators to achieve and hold exact temperatures, which is crucial for the metallurgical properties of the final cast part.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Alternatives
The Primary Alternative: Resistance Heating
Some vacuum furnaces use resistance heating. This method works much like a household oven, where electrical current is passed through high-resistance heating elements (often made of graphite or molybdenum).
These elements become extremely hot and radiate thermal energy, which heats the crucible and, in turn, the metal charge.
Key Limitations of Resistance Heating
Resistance heating is generally slower and less energy-efficient than induction. It relies on indirect heating, which introduces thermal lag and makes precise temperature control more challenging.
Furthermore, the heating elements themselves can degrade over time and become a source of contamination within the vacuum chamber, potentially compromising the purity of the melt.
The Cost and Complexity Factor
Induction heating systems typically have a higher initial capital cost and can be more complex than their resistance-heated counterparts. The choice between them often depends on the specific alloys being cast and the required level of purity and process control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When evaluating a vacuum furnace, the heating system is a defining factor that directly impacts process outcomes.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and rapid casting of high-performance alloys: Induction heating is the unequivocal industry standard and the superior technical choice.
- If your primary focus is lower initial cost for less demanding, non-reactive metals: Resistance heating can be a viable option, but you must accept the trade-offs in speed, efficiency, and potential contamination.
Understanding the heating method is the first step to mastering the quality and consistency of your vacuum casting process.

Summary Table:
| Heating Method | How It Works | Key Advantages | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electromagnetic Induction | High-frequency AC in copper coil induces eddy currents in metal, heating it directly without contact. | Fast, energy-efficient, high purity, precise temperature control. | Aerospace alloys, medical implants, superalloys. |
| Resistance Heating | Electric current heats elements (e.g., graphite), radiating heat to metal indirectly. | Lower initial cost, simpler design. | Less demanding, non-reactive metals. |
Ready to elevate your vacuum casting process with superior heating solutions? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace systems, including custom vacuum and atmosphere furnaces, tailored to meet your unique experimental needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we ensure maximum purity, efficiency, and control for industries like aerospace and medical. Contact us today to discuss how our induction heating technologies can optimize your operations and deliver unmatched results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications



















