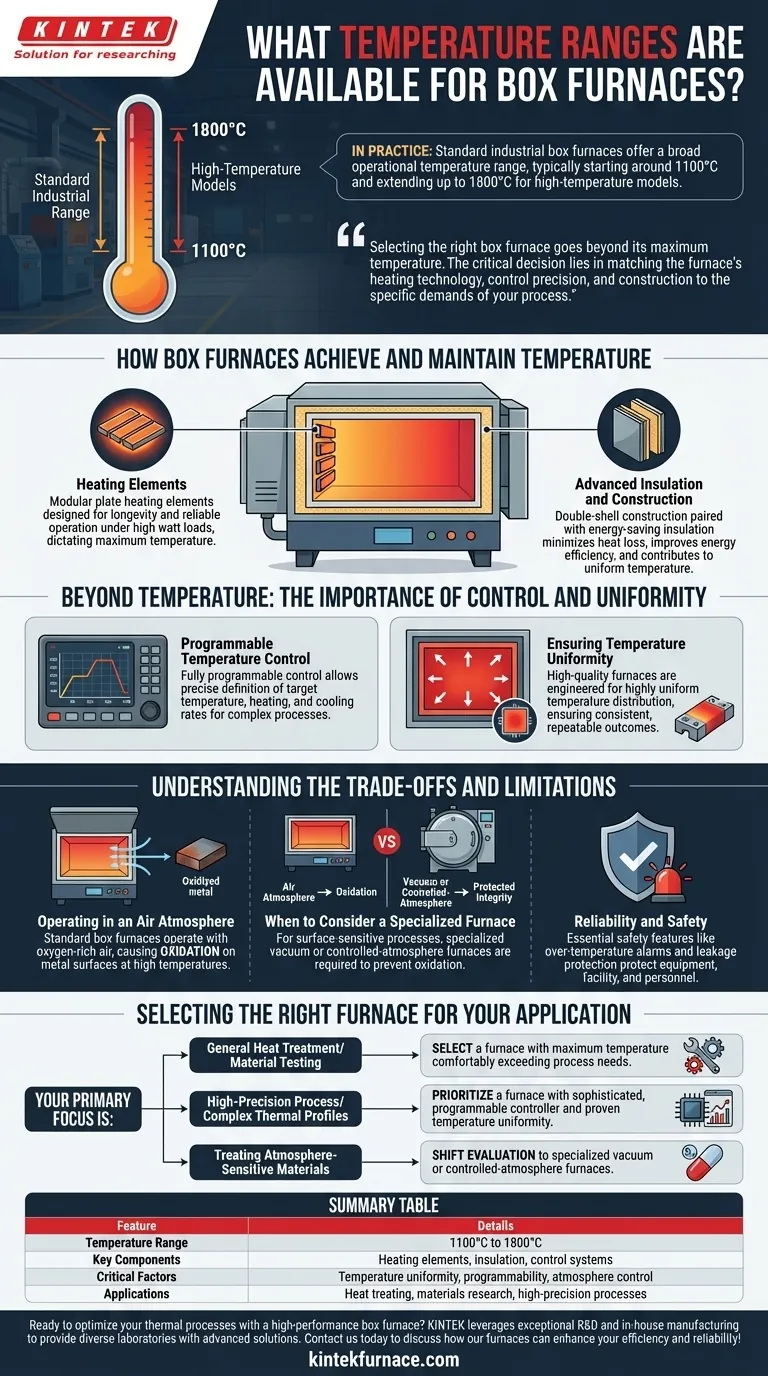
In practice, standard industrial box furnaces offer a broad operational temperature range, typically starting around 1100°C and extending up to 1800°C for high-temperature models. This range is designed to accommodate a wide variety of materials and thermal processes, from simple heat treating to advanced materials research.
Selecting the right box furnace goes beyond its maximum temperature. The critical decision lies in matching the furnace's heating technology, control precision, and construction to the specific demands of your process to ensure consistent, efficient, and reliable results.

How Box Furnaces Achieve and Maintain Temperature
The ability of a box furnace to reliably reach and hold high temperatures is not accidental; it is the result of specific engineering choices. Understanding these components helps clarify why different models have different capabilities.
The Role of Heating Elements
The core of the furnace's thermal capability lies in its heating elements. High-performance models often use modular plate heating elements, which are designed for longevity and reliable operation even under high watt loads. The material and design of these elements directly dictate the furnace's maximum achievable temperature.
Advanced Insulation and Construction
Reaching a high temperature is only half the battle; maintaining it efficiently is equally important. Modern box furnaces utilize a double-shell construction paired with advanced, energy-saving insulation. This design minimizes heat loss to the exterior, improves energy efficiency, and contributes to a more uniform temperature inside the chamber.
Beyond Temperature: The Importance of Control and Uniformity
A furnace's datasheet might highlight its maximum temperature, but for most industrial and laboratory applications, control and consistency are far more critical metrics.
Programmable Temperature Control
The true value of a modern box furnace is its fully programmable control system. This allows operators to precisely define not just the target temperature, but also the heating and cooling rates. This level of control is essential for complex processes that require specific thermal profiles to achieve the desired material properties.
Ensuring Temperature Uniformity
A temperature reading of 1500°C is meaningless if one part of the chamber is 50°C hotter or colder than another. High-quality box furnaces are engineered to provide highly uniform temperature distribution, ensuring that every part of your component or sample experiences the same thermal conditions for consistent, repeatable outcomes.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While versatile, a standard box furnace is not the universal solution for all thermal processes. Understanding its inherent limitations is key to avoiding costly mistakes.
Operating in an Air Atmosphere
A crucial point to remember is that a standard box furnace operates with air inside the chamber. At high temperatures, this oxygen-rich atmosphere will cause oxidation on the surface of most metals. For many applications, this is acceptable, but for others, it can be detrimental.
When to Consider a Specialized Furnace
If your process is sensitive to surface reactions like oxidation or decarburization, a standard box furnace is the wrong tool. In these cases, you must use a furnace that can control its atmosphere, such as a vacuum furnace, which removes the reactive gases to protect the product's integrity.
Reliability and Safety
Continuous operation at extreme temperatures puts significant stress on components. Furnaces built with premium, reliable components and sturdy construction are designed for long-term use. Essential safety features like over-temperature alarms and leakage protection are not just conveniences; they are critical for protecting your equipment, facility, and personnel.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Application
Use your specific process requirements to guide your decision, focusing on the features that matter most for your goal.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment or material testing: Select a furnace with a maximum temperature that comfortably exceeds your process needs, ensuring it is not constantly running at its absolute limit.
- If your primary focus is a high-precision process with complex thermal profiles: Prioritize a furnace with a sophisticated, programmable controller and proven temperature uniformity over one that simply boasts the highest temperature.
- If your primary focus is treating atmosphere-sensitive materials: Recognize that a standard box furnace is likely unsuitable and your evaluation should shift toward specialized vacuum or controlled-atmosphere furnaces.
Making an informed choice requires looking past the maximum temperature and analyzing how the furnace’s design aligns with the true needs of your work.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 1100°C to 1800°C |
| Key Components | Heating elements, insulation, control systems |
| Critical Factors | Temperature uniformity, programmability, atmosphere control |
| Applications | Heat treating, materials research, high-precision processes |
Ready to optimize your thermal processes with a high-performance box furnace? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with advanced solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















