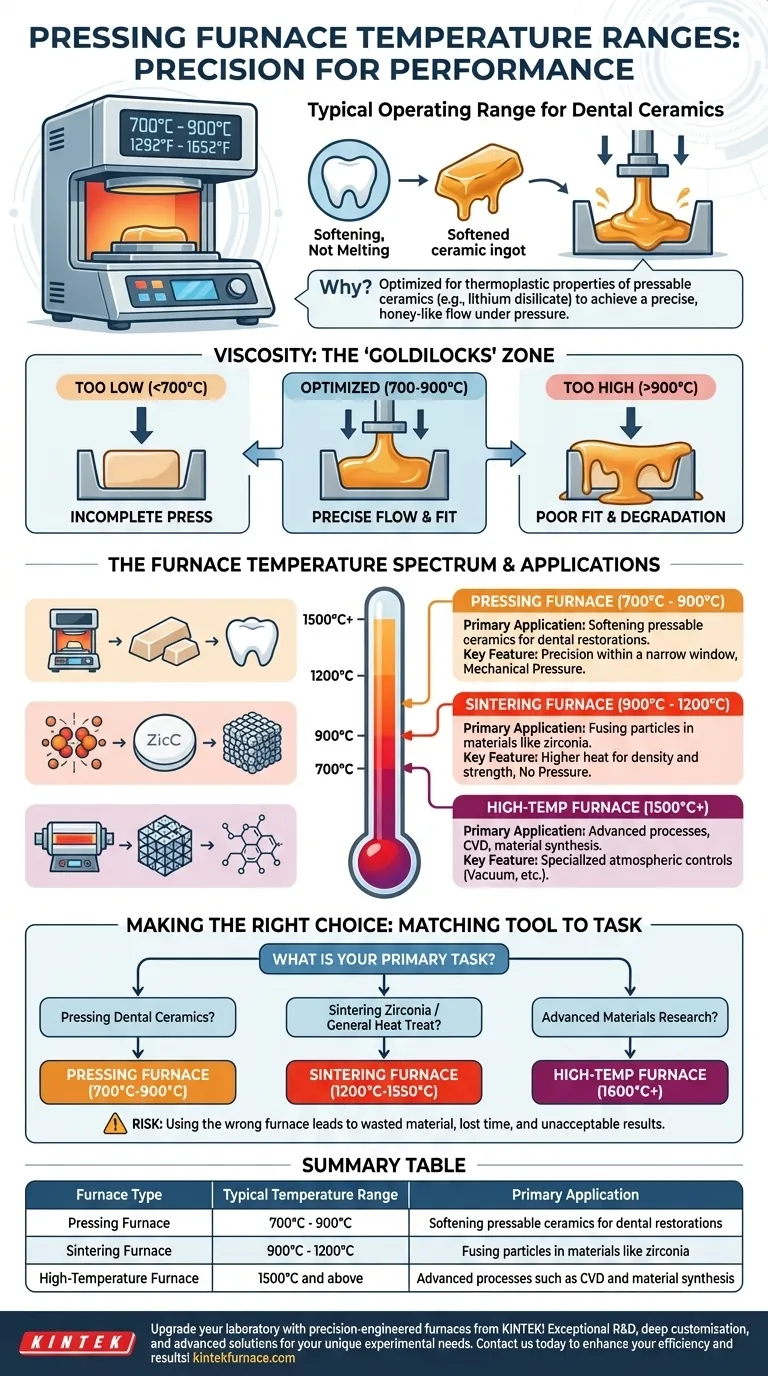
To be precise, a typical pressing furnace operates within a narrow temperature range of 700°C to 900°C (1292°F to 1652°F). This specific range is not arbitrary; it is meticulously calibrated for the thermoplastic properties of pressable ceramic materials used in applications like dental restorations.
The function of a furnace dictates its temperature range. A pressing furnace uses a relatively moderate temperature to soften ceramic for pressing, distinguishing it from general-purpose or high-temperature furnaces designed for entirely different material transformations like sintering or synthesis.

Why This Specific Temperature Range?
The operating temperature of any furnace is a direct consequence of the material it is designed to process. For a pressing furnace, the goal is not to melt or chemically alter the ceramic, but to make it viscous enough to be pressed.
Material Properties Dictate Temperature
The 700°C to 900°C range is optimized for materials like lithium disilicate or other pressable glass-ceramics.
At these temperatures, the ceramic ingot softens to a precise, honey-like consistency. This state allows it to flow under pressure without breaking or losing its structural integrity.
The Critical Role of Viscosity
The term "pressing" is key. The furnace heats the material, and a plunger then applies mechanical pressure to force the softened ceramic into a mold.
If the temperature is too low, the ceramic will be too viscous, resulting in an incomplete press. If it is too high, the material can become too fluid, leading to a poor fit and potential degradation of its properties.
How Pressing Furnaces Compare to Other Types
Understanding the broader landscape of laboratory furnaces clarifies why the temperature range for pressing is so specific. Different furnaces are built for fundamentally different tasks.
General Laboratory & Sintering Furnaces (900°C - 1200°C)
These are the workhorses for many labs and are often used for sintering. Sintering is a process that uses higher heat to fuse particles together, increasing the density and strength of a material like zirconia.
This process requires significantly more thermal energy than simply softening a material for pressing.
High-Temperature & Specialized Furnaces (1500°C+)
Furnaces operating above 1500°C are highly specialized. This category includes certain muffle, tube, and vacuum furnaces.
Their purpose is to process advanced materials or enable specific chemical reactions, such as Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), which can require temperatures approaching 1950°C. These are not used for standard pressable ceramics.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing precision, versatility, and cost. The temperature range is the single most important factor in this decision.
Precision vs. Versatility
A pressing furnace offers extreme precision within its specific, narrow temperature window, which is essential for predictable clinical results.
A general-purpose sintering furnace is more versatile, able to handle a wider variety of materials and processes, but it lacks the specialized pressing mechanism.
Cost and Complexity
As the maximum operating temperature of a furnace increases, so do its cost and complexity.
High-temperature furnaces require more exotic heating elements, advanced insulation, and often, specialized atmospheric controls (like a vacuum), making them a significant investment.
The Risk of Using the Wrong Tool
Attempting to press ceramics in a furnace not designed for it, or using incorrect temperature programs, is a primary source of failure in a dental lab. The result is wasted material, lost time, and clinically unacceptable restorations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be guided by the primary task you need to accomplish.
- If your primary focus is pressing dental ceramics (e.g., lithium disilicate): You must use a dedicated pressing furnace engineered to operate precisely within the 700°C to 900°C range.
- If your primary focus is sintering zirconia or general heat treatment: You require a sintering furnace capable of reliably reaching temperatures between 1200°C and 1550°C.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials research or synthesis: You need a specialized high-temperature furnace with a range tailored to your specific materials, which could exceed 1600°C.
Ultimately, selecting the correct furnace is about matching the tool directly to the thermal requirements of your material and process.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Typical Temperature Range | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Pressing Furnace | 700°C to 900°C | Softening pressable ceramics for dental restorations |
| Sintering Furnace | 900°C to 1200°C | Fusing particles in materials like zirconia |
| High-Temperature Furnace | 1500°C and above | Advanced processes such as CVD and material synthesis |
Upgrade your laboratory with precision-engineered furnaces from KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs, whether for dental ceramics or high-temperature applications. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the effects of overloading a dental sintering furnace? Ensure Predictable, High-Quality Zirconia Restorations
- Why is proper ventilation important in dental sintering furnaces? Ensure Quality and Safety in Your Lab
- What is a dental sintering furnace and what is its purpose? Achieve High-Strength Dental Restorations
- What factors should be considered when choosing a dental sintering furnace? Ensure Quality and Efficiency for Your Lab
- How has the sintering process innovated dental zirconia applications? Boost Strength, Precision, and Efficiency



















