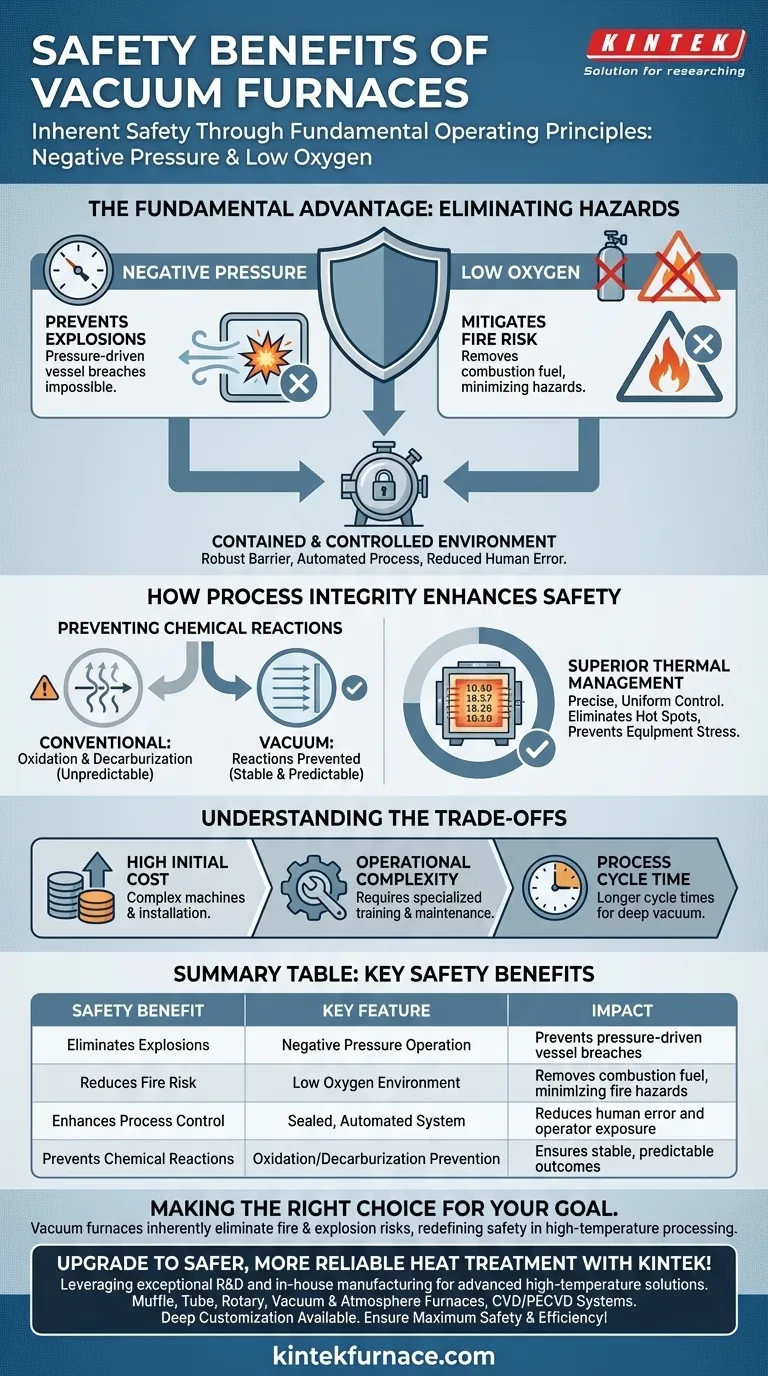
At their core, vacuum furnaces are inherently safer than conventional high-temperature furnaces because their fundamental operating principles eliminate the primary hazards of heat treatment: explosions and fire. By removing atmospheric pressure and oxygen, the vacuum environment neutralizes the conditions required for these catastrophic failures, creating a fundamentally more controlled and secure process.
The key safety benefit of a vacuum furnace is not an added feature, but a result of its basic design. Operating at negative pressure makes pressure-related explosions impossible, and the near-absence of oxygen removes the fuel for fires and uncontrolled oxidation.

The Fundamental Safety Advantage: Eliminating Fuel and Pressure
The safety of a vacuum furnace stems from its unique, controlled environment. Unlike atmospheric furnaces that must manage volatile conditions, a vacuum furnace simply removes them.
Negative Pressure Prevents Explosions
Conventional furnaces often operate at positive pressure, which carries an inherent risk of a vessel breach or explosion if pressure builds excessively.
Vacuum furnaces operate at negative pressure, meaning the pressure inside the vessel is lower than the atmospheric pressure outside. This physical reality makes a pressure-driven explosion impossible.
Low Oxygen Mitigates Fire Risk
The fire triangle requires three components: heat, fuel, and oxygen. High-temperature furnaces provide abundant heat, and the workpiece itself can act as fuel.
A vacuum furnace works by removing nearly all of the oxygen from the chamber. By eliminating this critical component, it makes combustion and the risk of a widespread fire practically non-existent.
A Contained and Controlled Environment
The sealed nature of a vacuum furnace vessel provides a robust barrier between the operator and the extreme heat inside.
Furthermore, modern vacuum furnaces are highly automated. Computer-controlled cycles manage the entire process without manual intervention, significantly reducing the potential for human error and operator exposure to hazards.
How Process Integrity Enhances Safety
The benefits that improve material quality in a vacuum furnace are directly linked to improved operational safety. A predictable process is a safe process.
Preventing Unwanted Chemical Reactions
In a conventional furnace, the presence of oxygen at high temperatures causes oxidation (scaling) and decarburization, which degrade the workpiece.
These reactions can sometimes be unpredictable, especially with reactive metals like titanium or molybdenum. A vacuum furnace prevents these reactions, ensuring a clean surface finish and, more importantly, a stable and predictable chemical process.
Superior Thermal Management
The vacuum environment allows for extremely precise and uniform temperature control. This eliminates hot spots that could damage the part or create thermal stresses within the furnace equipment itself.
This level of control ensures that the process stays within its intended parameters, preventing unexpected events that could compromise safety or equipment integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While exceptionally safe, vacuum furnaces are not the universal solution for all heat treatment needs. Their benefits must be weighed against practical considerations.
High Initial Cost
The primary barrier to adopting vacuum furnace technology is its cost. These are complex machines, and their purchase price and installation are significantly higher than for most conventional atmospheric furnaces.
Operational Complexity
While cycles are automated, the systems themselves are sophisticated. Proper operation, and especially maintenance, requires specialized training and knowledge to manage the vacuum pumps, seals, and control systems.
Process Cycle Time
Achieving a deep vacuum can be time-consuming, potentially leading to longer overall cycle times compared to some atmospheric processes. This is a crucial factor to consider for high-volume production environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision to use a vacuum furnace should be driven by your specific material, process requirements, and safety priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximum personnel and facility safety: A vacuum furnace is the definitive choice, as its design inherently eliminates the risks of fire and explosion.
- If you are processing highly reactive or high-value materials: A vacuum furnace is essential to prevent contamination and ensure the integrity and quality of the final product.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of simple, non-reactive parts on a tight budget: A conventional atmospheric furnace may be sufficient, but it demands rigorous safety protocols to manage its inherent hazards.
By fundamentally removing pressure and oxygen from the process, a vacuum furnace doesn't just manage risk—it redefines the nature of safety in high-temperature processing.
Summary Table:
| Safety Benefit | Key Feature | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Eliminates Explosions | Negative Pressure Operation | Prevents pressure-driven vessel breaches |
| Reduces Fire Risk | Low Oxygen Environment | Removes combustion fuel, minimizing fire hazards |
| Enhances Process Control | Sealed, Automated System | Reduces human error and operator exposure |
| Prevents Chemical Reactions | Oxidation and Decarburization Prevention | Ensures stable, predictable outcomes |
Upgrade to safer, more reliable heat treatment with KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Ensure maximum safety and efficiency in your processes—contact us today to discuss how our vacuum furnaces can benefit your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability



















