In ceramics and glass manufacturing, silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements are the industrial workhorses responsible for generating the intense, consistent, and precisely controlled heat required for critical processes. They are essential for transforming raw materials into high-quality finished products by enabling shaping, fusing, annealing, and melting at extremely high temperatures.
The true value of silicon carbide heating elements isn't just their ability to get hot. It is their unique combination of material properties—high-temperature stability, thermal shock resistance, and chemical inertness—that allows them to deliver uniform, reliable heat in the harsh, demanding environments of furnaces.

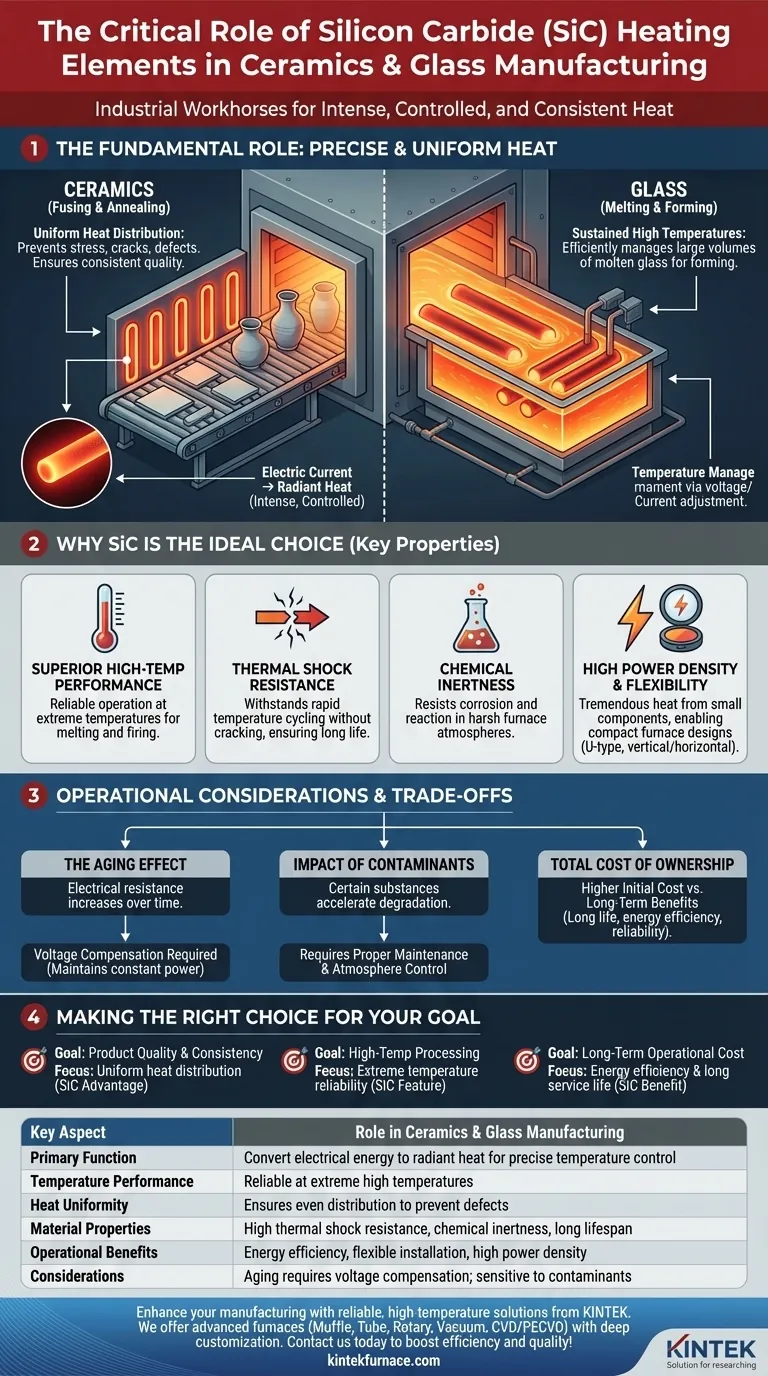
The Fundamental Role: Precise and Uniform Heat
The primary function of SiC elements is to convert electrical energy into radiant heat with exceptional control. This capability is foundational to achieving quality and consistency in both ceramics and glass production.
Achieving Consistency in Ceramics
In ceramic manufacturing, processes like fusing and annealing demand uniform temperature distribution across the entire product.
Any significant temperature variation can introduce stress, cracks, or other defects, leading to product failure. SiC elements radiate heat evenly, ensuring the entire ceramic piece is heated and cooled at the desired rate.
Enabling High-Temperature Glass Processing
Glass production requires sustained, extreme heat for melting raw materials and forming the molten glass.
SiC elements provide the necessary high temperatures and stability to manage large volumes of molten glass efficiently, making them indispensable in modern glass furnaces.
How They Operate
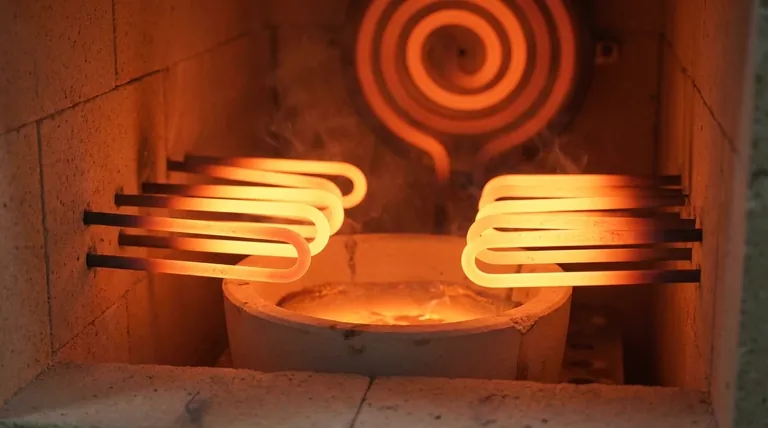
The mechanism is straightforward: an electric current is passed through the silicon carbide rod or spiral. The material's natural electrical resistance causes it to heat up intensely, radiating thermal energy into the furnace chamber to heat the target objects.
Temperature is managed by precisely adjusting the voltage and current supplied to the element.
Why Silicon Carbide is the Ideal Choice
Several material properties distinguish SiC elements and make them uniquely suited for these demanding applications. It is the combination of these traits, not just one, that makes them so effective.
Superior High-Temperature Performance
Silicon carbide can operate reliably at the very high temperatures required to melt glass and fire advanced ceramics, where lesser materials would quickly degrade or fail.
Resistance to Thermal Shock
Furnaces are often cycled on and off, creating rapid temperature changes. SiC's inherent resistance to thermal shock prevents it from cracking or breaking under this stress, contributing to a long and reliable operational life.
Chemical Inertness
Furnace atmospheres can contain volatile compounds and contaminants. SiC is chemically inert, meaning it resists corrosion and reaction in these harsh environments, ensuring its stability and longevity.
High Power Density
SiC elements can produce a tremendous amount of heat from a relatively small component. This high power density allows for more compact and efficient furnace designs, a critical factor where factory floor space is at a premium.
Flexible Installation
Modern SiC elements, such as U-type designs, offer significant flexibility. They can be installed vertically or horizontally, simplifying furnace construction and element replacement.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
While highly effective, SiC elements are not without operational considerations. Understanding these factors is key to maximizing their performance and lifespan.
The Aging Effect
Over time and with use, the electrical resistance of a silicon carbide element gradually increases. This is a natural aging process.
To maintain a consistent power output and temperature, the power supply system must be capable of increasing the voltage to compensate for this change in resistance.
Impact of Contaminants
While chemically inert, certain substances can accelerate the degradation of SiC elements at high temperatures. Proper furnace maintenance and control over the processing atmosphere are crucial for maximizing the element's service life.
Total Cost of Ownership
Silicon carbide elements may have a higher initial purchase price compared to some metallic elements. However, their long life, energy efficiency, and reliability in high-temperature applications often result in a lower total cost of ownership over the long term.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When evaluating heating systems, align the properties of SiC elements with your primary production goal.
- If your primary focus is product quality and consistency: SiC's uniform heat distribution is its most critical advantage for preventing defects in ceramics and glass.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing (like glass melting): The ability of SiC to operate reliably at extreme temperatures is its defining, non-negotiable feature.
- If your primary focus is long-term operational cost: The energy efficiency and long service life of SiC elements often justify their initial investment and reduce downtime.
Ultimately, understanding these properties empowers you to optimize your heating processes for greater efficiency, quality, and reliability.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Role in Ceramics & Glass Manufacturing |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Convert electrical energy to radiant heat for precise temperature control |
| Temperature Performance | Operates reliably at extreme high temperatures (e.g., for melting glass) |
| Heat Uniformity | Ensures even temperature distribution to prevent defects like cracks |
| Material Properties | High thermal shock resistance, chemical inertness, and long lifespan |
| Operational Benefits | Energy efficiency, flexible installation, and high power density |
| Considerations | Aging effect requires voltage compensation; sensitive to contaminants |
Ready to enhance your ceramics or glass manufacturing with reliable, high-temperature solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced heating systems tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental and production requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our silicon carbide heating elements can boost your efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability



















