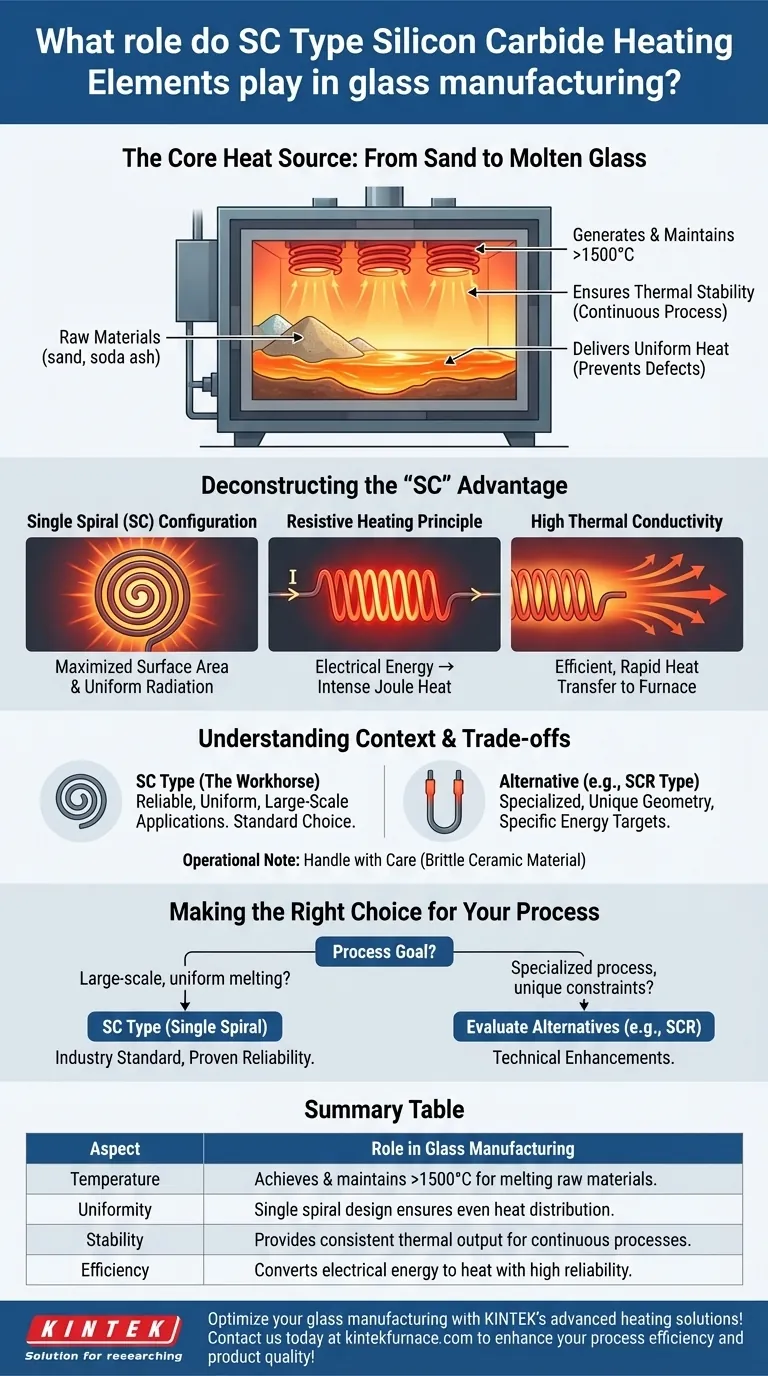
In glass manufacturing, SC Type Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements serve as the core heat source inside industrial furnaces. They are responsible for generating and maintaining the extremely high and stable temperatures necessary to melt raw materials into molten glass and keep it workable for forming processes. Their specific design ensures this heat is delivered uniformly and efficiently, which is critical for final product quality.
The "SC" designation refers to the element's Single Spiral configuration. This design is the key to its performance, enabling it to deliver the uniform, high-temperature heat required for consistent glass melting and forming, directly converting electrical energy into thermal energy with high reliability and control.

The Fundamental Role: From Sand to Molten Glass
The journey from raw materials like sand to a finished glass product is entirely dependent on precise thermal management. SC Type SiC elements are the enabling technology for this critical stage.
Achieving Critical Melting Temperatures
Glass production requires temperatures often exceeding 1500°C (2732°F). Silicon carbide is a ceramic material capable of withstanding these extreme conditions and operating reliably for extended periods, making it an ideal choice for furnace heating.
Ensuring Thermal Stability
Molten glass processes can be continuous, running for days or weeks at a time. The inherent durability of SiC elements provides the thermal stability required to maintain a consistent melt, preventing defects and ensuring process continuity.
The Importance of Uniform Heating
Any temperature variance within the furnace can create stress, bubbles, or other imperfections in the final glass product. The single spiral design and high thermal conductivity of SC elements work together to radiate heat evenly, minimizing temperature differences throughout the furnace.
Deconstructing the "SC" Advantage
The effectiveness of these elements is not an accident; it is a direct result of their material properties and physical design.
The Single Spiral (SC) Configuration
The "SC" in the name stands for Single Spiral. This design maximizes the element's heat-radiating surface area within a compact, robust form factor, making it particularly effective for large box and trolley furnaces common in the glass industry.
The Principle of Resistive Heating
Silicon carbide has a controlled electrical resistance. When a high electrical current is passed through the element, this resistance causes it to heat up intensely (an effect known as Joule heating). This allows for the direct and efficient conversion of electrical power into usable thermal energy.
High Thermal Conductivity
Once heat is generated within the element, the material's excellent thermal conductivity allows it to be transferred and radiated efficiently into the furnace chamber. This property is what ensures the heat distribution is both rapid and uniform.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Alternatives
While the SC Type is a dominant technology, it is essential to understand its place within the broader landscape of industrial heating.
The SC Type in Context
The SC (Single Spiral) element is the workhorse of the industry. It is valued for its straightforward design, reliability, and excellent performance in applications where a large, uniform heating zone is the primary requirement.
Considering Alternatives: The SCR Type
Other configurations exist, such as the SCR Type. The SCR design is often an enhancement of a U-shaped rod, engineered for specific technical demands that may involve different energy efficiency profiles or unique furnace geometries.
Operational Considerations
SC elements offer practical benefits like convenient wiring and predictable performance. However, as ceramic components, they are brittle and require careful handling during installation and maintenance to prevent mechanical shock or fracture.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The selection of a heating element must align with the specific goals and constraints of your glass manufacturing operation.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, uniform melting: The SC (Single Spiral) type is the industry standard, proven for its reliability and superior heat distribution in large furnace applications.
- If your primary focus is a specialized process with unique geometric constraints or advanced energy efficiency targets: It is wise to evaluate other configurations, such as the SCR type, which are designed for specific technical enhancements.
Ultimately, understanding the design principles behind your heating elements empowers you to optimize furnace performance and ensure final product quality.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role in Glass Manufacturing |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Achieves and maintains >1500°C for melting raw materials. |
| Uniformity | Single spiral design ensures even heat distribution to prevent defects. |
| Stability | Provides consistent thermal output for continuous, long-term processes. |
| Efficiency | Converts electrical energy to heat with high reliability and control. |
Optimize your glass manufacturing with KINTEK's advanced heating solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise solutions for your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your process efficiency and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability



















