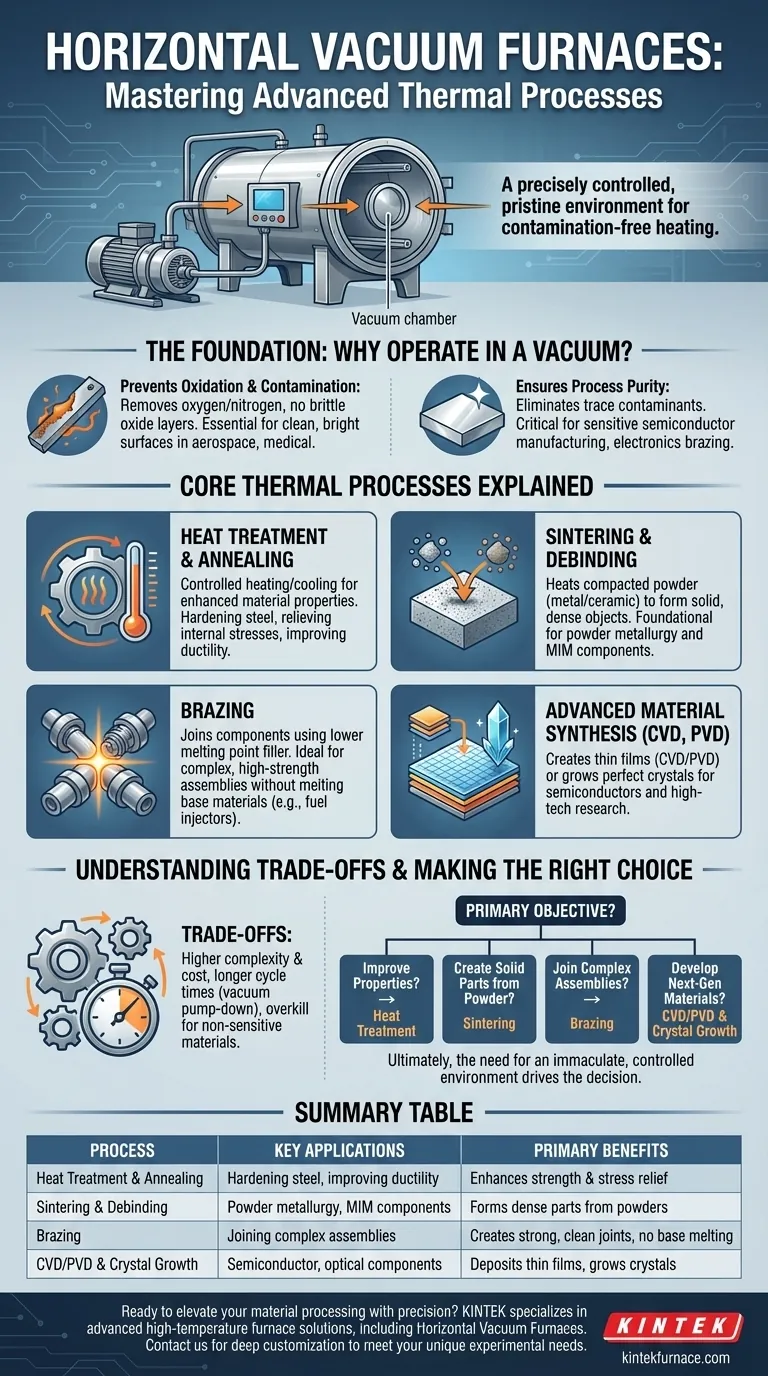
At its core, a horizontal vacuum furnace is a highly versatile tool used for a range of sophisticated thermal processes where atmospheric contamination must be eliminated. These furnaces are essential for applications including vacuum heat treatment, sintering, brazing, and advanced material synthesis like chemical vapor deposition (CVD). The controlled vacuum or inert gas environment is the key to achieving specific material properties that are impossible to attain in an open-air furnace.
A vacuum furnace is not simply a heater; it is a precisely controlled environment. Its primary function is to enable thermal processes that require pristine, oxygen-free conditions to enhance, join, or create high-performance materials.

The Foundation: Why Operate in a Vacuum?
The defining feature of these furnaces is the vacuum. By removing atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen, we fundamentally change the environment in which materials are heated.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
The most critical benefit is the prevention of oxidation. When heated, most metals react with oxygen, forming a brittle oxide layer that degrades their mechanical and electrical properties. A vacuum environment eliminates this risk entirely.
This ensures the final product has a clean, bright surface and maintains its intended structural integrity, which is non-negotiable for industries like aerospace and medical devices.
Ensuring Process Purity
Beyond oxidation, a vacuum removes other potential contaminants. This purity is essential for sensitive processes where even trace amounts of unwanted elements can ruin the outcome, such as in semiconductor manufacturing or the brazing of electronic components.
Core Thermal Processes Explained
A horizontal vacuum furnace can be configured to execute several distinct thermal processes, each tailored to a different engineering goal.
Heat Treatment and Annealing
Heat treatment involves controlled heating and cooling to alter a material's physical and mechanical properties. This can include hardening steel for automotive gears or tool bits to improve wear resistance.
Annealing is a specific type of heat treatment used to soften materials, relieve internal stresses, and improve ductility. This makes them easier to work with in subsequent manufacturing steps.
Sintering and Debinding
Sintering is the process of taking a compacted powder—be it metal, ceramic, or a composite—and heating it below its melting point until the particles bond together, forming a solid, dense object.
This is the foundational technology behind powder metallurgy, used to create everything from hard alloy cutting tools to complex metal injection molded (MIM) components. Often, a debinding step precedes sintering to remove binder materials used in the initial molding process.
Brazing
Vacuum brazing is an advanced joining technique where a filler metal with a lower melting point is used to join two components. The assembly is heated in the vacuum, causing the filler to melt and flow into the joint via capillary action.
Because this happens without melting the base materials, it's ideal for creating complex, high-strength assemblies with tight tolerances, such as fuel injectors or vacuum interrupters for the electrical grid.
Advanced Material Synthesis
For research and high-tech manufacturing, vacuum furnaces are used for creating new materials. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) are processes that deposit thin films onto a substrate to create durable coatings or electronic layers.
These furnaces are also used for crystal growth, a highly controlled process essential for producing the perfect monocrystalline silicon used in semiconductors and specialized optical components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly powerful, vacuum furnaces are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Complexity and Cost
Vacuum furnaces are significantly more complex and expensive than their atmospheric counterparts. The systems required to create, maintain, and monitor the vacuum add substantial cost and require specialized operator knowledge.
Cycle Time
Achieving a high vacuum takes time. The pump-down and backfill stages add to the overall process cycle time, which can make it slower than atmospheric heating for certain high-volume, low-spec applications. The heating and cooling rates must also be carefully controlled.
Suitability for the Material
These furnaces are overkill for processes and materials that are not sensitive to atmospheric contamination. Simple heat treating of low-carbon steel, for example, rarely requires the expense and complexity of a vacuum environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if a vacuum furnace fits your needs, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is improving material properties: You will likely use heat treatment processes like hardening, tempering, or annealing to increase strength or relieve stress.
- If your primary focus is creating solid parts from powder: Your core process will be sintering, often combined with a pre-sintering debinding cycle.
- If your primary focus is joining complex assemblies: You need vacuum brazing to create strong, clean, and precise joints without distorting the parent materials.
- If your primary focus is developing next-generation materials: You will leverage advanced processes like CVD, PVD, or controlled crystal growth for research and high-tech applications.
Ultimately, the decision to use a horizontal vacuum furnace is driven by the material's need for an immaculate, controlled thermal environment.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Applications | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Treatment & Annealing | Hardening steel, improving ductility | Enhances material strength and stress relief |
| Sintering & Debinding | Powder metallurgy, MIM components | Forms dense parts from powders |
| Brazing | Joining complex assemblies like fuel injectors | Creates strong, clean joints without base material melting |
| CVD/PVD & Crystal Growth | Semiconductor manufacturing, optical components | Deposits thin films, grows crystals for advanced materials |
Ready to elevate your material processing with precision? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Horizontal Vacuum Furnaces tailored for heat treatment, sintering, brazing, and CVD/PVD. With our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and results—get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density



















