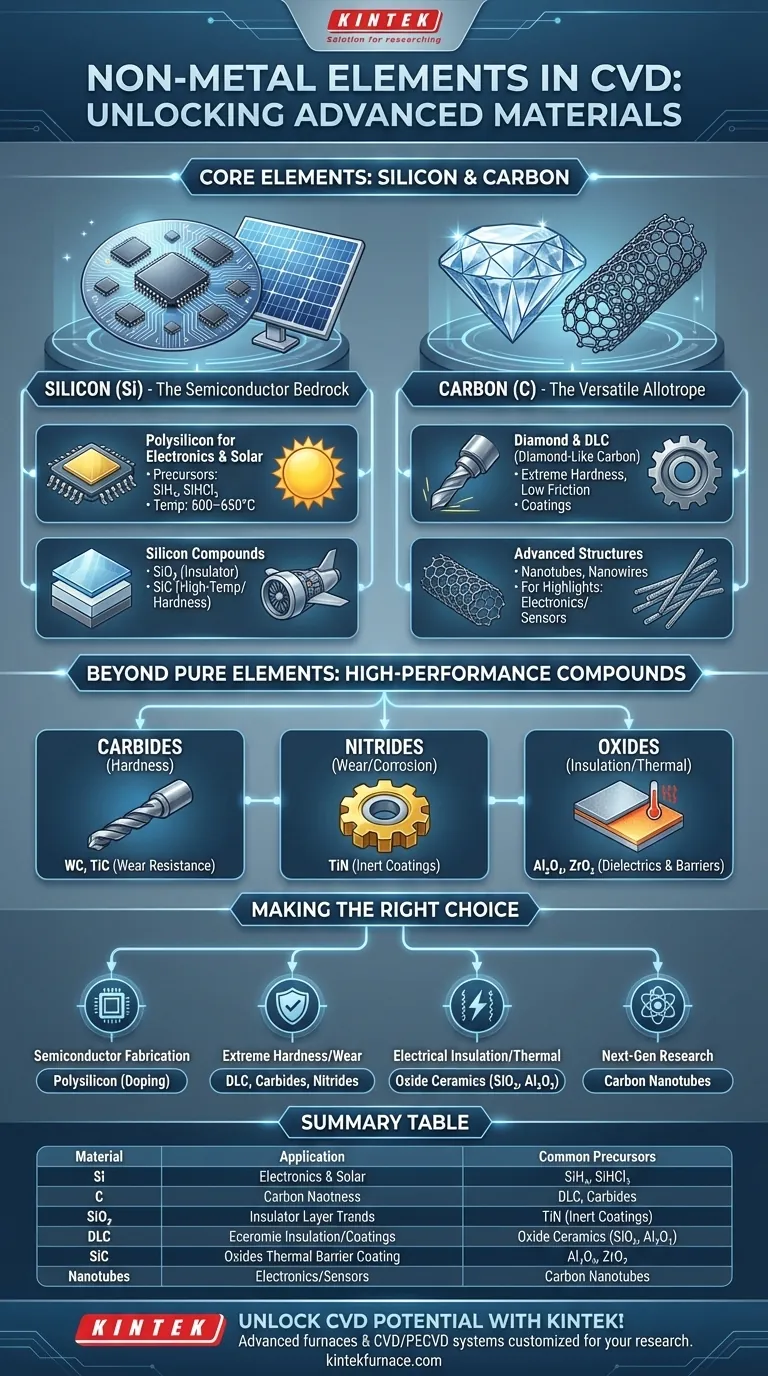
At its core, the most common non-metal elements deposited using Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) are silicon (Si) and carbon (C). These two elements form the foundation for a vast range of materials critical to modern technology, from the silicon wafers in microchips to the diamond-like carbon coatings on high-performance tools.
The true power of CVD is not just in depositing pure elements, but in its ability to precisely control chemistry and structure to create a wide array of non-metallic compounds and allotropes—including essential semiconductors, insulators, and ultra-hard ceramics.
The Central Role of Silicon in CVD
Silicon is arguably the most important element deposited via CVD, primarily because it is the bedrock of the entire semiconductor industry.
Polysilicon for Electronics and Solar
Polycrystalline silicon, or polysilicon, is a key material for manufacturing integrated circuits (CMOS devices) and photovoltaic solar cells.
It is typically deposited in Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD) systems using precursor gases like silane (SiH₄) or trichlorosilane (SiHCl₃) at temperatures between 600–650°C. The material's electronic properties can be precisely tuned by introducing dopant gases like phosphine or arsine during deposition.
Silicon Compounds for Insulation and Protection
CVD is also used to create crucial silicon compounds. Silicon dioxide (SiO₂) is an excellent electrical insulator (a dielectric), vital for isolating components within a microchip.
Meanwhile, silicon carbide (SiC) is a ceramic known for its extreme hardness and stability at high temperatures, making it suitable for demanding applications in aerospace and power electronics.
The Unmatched Versatility of Carbon
Carbon's ability to form different structures, known as allotropes, makes it an exceptionally versatile element for CVD applications, ranging from wear-resistant coatings to next-generation electronics.
Diamond and Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC)
CVD can produce thin films of synthetic diamond and diamond-like carbon (DLC). These materials are valued for their extreme hardness, low friction, and chemical inertness.
They are widely used as protective coatings on cutting tools, automotive engine parts, and medical implants to dramatically increase lifespan and performance.
Advanced Carbon Structures
The precision of CVD enables the growth of complex carbon structures with unique properties. Carbon nanotubes and nanowires are examples of materials with extraordinary strength and electrical conductivity, holding immense promise for future applications in electronics, composites, and sensors.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Elements vs. Compounds
Focusing only on pure non-metal elements misses the bigger picture. The primary industrial strength of CVD lies in its ability to form high-performance non-metallic compounds.
Carbides for Extreme Hardness
Compounds of carbon and a metal, known as carbides, are exceptionally hard. Materials like tungsten carbide (WC) and titanium carbide (TiC) are deposited on tools and industrial components to provide superior wear resistance.
Nitrides for Wear and Corrosion Resistance
Similarly, nitrides like titanium nitride (TiN) are used as hard, inert coatings. They provide not only wear resistance but also a barrier against corrosion, often recognizable by their characteristic gold color.
Oxides for Dielectric and Thermal Barriers
Oxide ceramics such as alumina (Al₂O₃) and zirconia (ZrO₂) are deposited via CVD for use as electrical insulators and thermal barrier coatings in high-temperature environments like jet engines.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of non-metallic CVD material is dictated entirely by the final property you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is semiconductor fabrication: You will be depositing high-purity polysilicon and tuning its properties through controlled doping.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness and wear resistance: Your best options are carbon films like DLC or compound ceramics like tungsten carbide and titanium nitride.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation or thermal barriers: You should explore oxide ceramics like silicon dioxide or alumina.
- If your primary focus is next-generation materials research: The synthesis of advanced structures like carbon nanotubes offers a frontier for exploration.
Ultimately, understanding the specific non-metallic film—whether an element, allotrope, or compound—is the key to unlocking the right performance for your application.

Summary Table:
| Element/Compound | Key Applications | Common CVD Precursors |
|---|---|---|
| Silicon (Si) | Semiconductors, solar cells | Silane (SiH₄), Trichlorosilane (SiHCl₃) |
| Carbon (C) | Hard coatings, electronics | Methane (CH₄), Acetylene (C₂H₂) |
| Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂) | Electrical insulation | Silane with oxygen |
| Diamond-like Carbon (DLC) | Wear-resistant coatings | Hydrocarbon gases |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | High-temperature applications | Silane with methane |
| Carbon Nanotubes | Advanced electronics, sensors | Carbon-containing gases |
Unlock the full potential of CVD for your laboratory with KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're working with semiconductors, wear-resistant coatings, or next-generation materials, KINTEK delivers reliable, high-performance solutions. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your research and production processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the practical applications of gate media prepared by CVD tube furnaces? Unlock Advanced Electronics and More
- What are the operational benefits of using a CVD Tube Furnace? Enhance Precision and Efficiency in Your Lab
- What future trends are expected in the development of CVD tube furnaces? Discover Smarter, More Versatile Systems
- What are the key design features of a CVD Tube Furnace? Optimize Your Material Synthesis with Precision
- What are the advantages of CVD tube furnace sintering systems? Achieve Superior Material Control and Purity



















