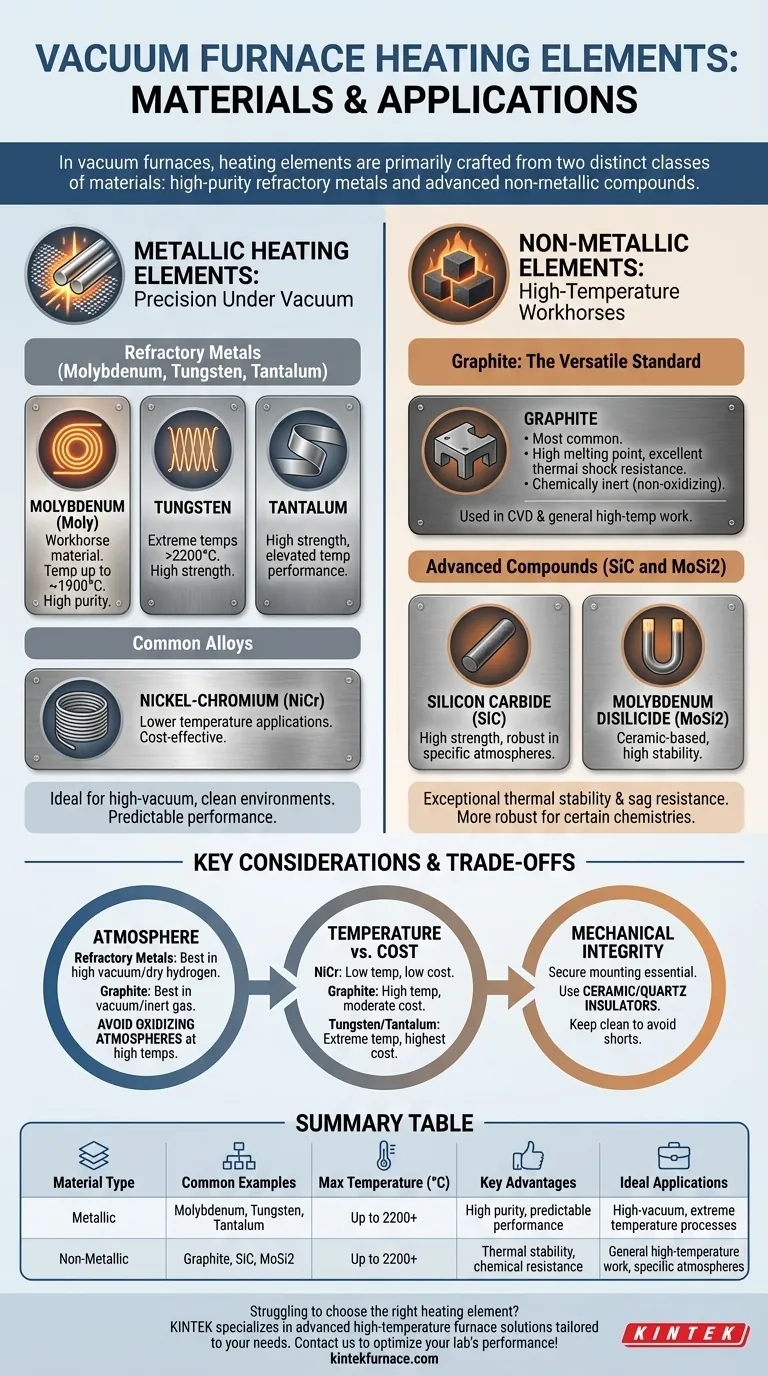
In vacuum furnaces, heating elements are primarily crafted from two distinct classes of materials: high-purity refractory metals and advanced non-metallic compounds. The most common metallic elements include molybdenum, tungsten, and tantalum, while the dominant non-metallic options are graphite, silicon carbide (SiC), and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2).
The choice of a heating element is not simply about reaching a target temperature. It is a critical engineering decision that balances maximum heat, chemical compatibility with the furnace atmosphere and workload, and the element's operational lifespan against its cost.
Metallic Heating Elements: Precision Under Vacuum
Metallic elements are often chosen for their purity and predictable performance in high-vacuum environments where contamination is a primary concern. They are typically shaped into rods, ribbons, or mesh cylinders.
Refractory Metals (Molybdenum, Tungsten, Tantalum)
These metals are defined by their extremely high melting points and strength at elevated temperatures. Molybdenum (Moly) is a workhorse material, widely used for temperatures up to approximately 1900°C (3452°F).
For even more demanding applications, tungsten and tantalum are employed. Tungsten can operate in temperatures well above 2200°C (3992°F), making it suitable for the most extreme high-temperature vacuum processes.
Common Alloys (Nickel-Chromium)
Alloys like nickel-chromium (NiCr) are also used, but typically in lower-temperature vacuum applications. They offer a cost-effective solution when the process does not require the extreme temperature capabilities of refractory metals.
Non-Metallic Elements: The High-Temperature Workhorses
Non-metallic elements are valued for their exceptional thermal stability and resistance to sag at very high temperatures. They are often more robust for certain process chemistries.
Graphite: The Versatile Standard
Graphite is arguably the most common heating element material for a wide range of vacuum furnaces, especially for processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD). It is easily machined into complex shapes and is relatively low-cost.
Its key advantages include a very high melting point, excellent thermal shock resistance, and chemical inertness in non-oxidizing atmospheres. This makes it exceptionally reliable and durable for general-purpose, high-temperature work.
Advanced Compounds (SiC and MoSi2)
Silicon carbide (SiC) and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) are ceramic-based compounds frequently used in modern sintering furnaces. They are known for their high strength and ability to operate in atmospheres that might be damaging to pure graphite or refractory metals.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Practical Considerations
Selecting the ideal heating element requires a clear understanding of the operational environment and its constraints. No single material is perfect for every scenario.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere
The furnace atmosphere is a deciding factor. Refractory metals perform best in a high vacuum or pure, dry hydrogen. The presence of even small amounts of oxygen or water vapor at high temperatures can cause rapid oxidation and failure.
Conversely, graphite excels in vacuum or inert gas but will quickly be consumed in an oxidizing atmosphere at high temperatures.
Temperature vs. Cost
There is a direct correlation between maximum operating temperature and cost. NiCr alloys are the most economical but have the lowest temperature limit. Graphite provides an excellent balance of high-temperature performance and moderate cost. Tungsten and tantalum represent the highest performance and the highest cost.
Mechanical Integrity and Installation
Heating elements must be mounted securely to ensure temperature uniformity and prevent electrical shorts. Graphite elements are often connected using bolted graphite bridges.
All elements rely on ceramic or quartz insulators for electrical isolation. It is critical to keep these insulators clean, as metallic condensation or carbon dust from the process can create a conductive path, leading to a short circuit and element failure.
Selecting the Right Material for Your Application
Your choice should be guided by your specific process requirements. Consider these factors to make an informed decision.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperatures (>2000°C) in a clean, high-vacuum environment: Refractory metals like tungsten or tantalum are the necessary choice for their purity and performance.
- If you need a versatile, cost-effective solution for general high-temperature work (up to 2200°C) in vacuum or inert gas: Graphite offers the best overall balance of performance, cost, and long service life.
- If you are operating at lower temperatures or in specific atmospheres where oxidation is a concern: Specialized alloys like nickel-chromium or robust compounds like silicon carbide provide reliable performance where other materials might fail.
Understanding these core material properties empowers you to select a heating element that ensures both process success and operational reliability.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Common Examples | Max Temperature (°C) | Key Advantages | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metallic | Molybdenum, Tungsten, Tantalum | Up to 2200+ | High purity, predictable performance | High-vacuum, extreme temperature processes |
| Non-Metallic | Graphite, SiC, MoSi2 | Up to 2200+ | Thermal stability, chemical resistance | General high-temperature work, specific atmospheres |
Struggling to choose the right heating element for your vacuum furnace? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your lab's performance with the perfect heating element solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing



















