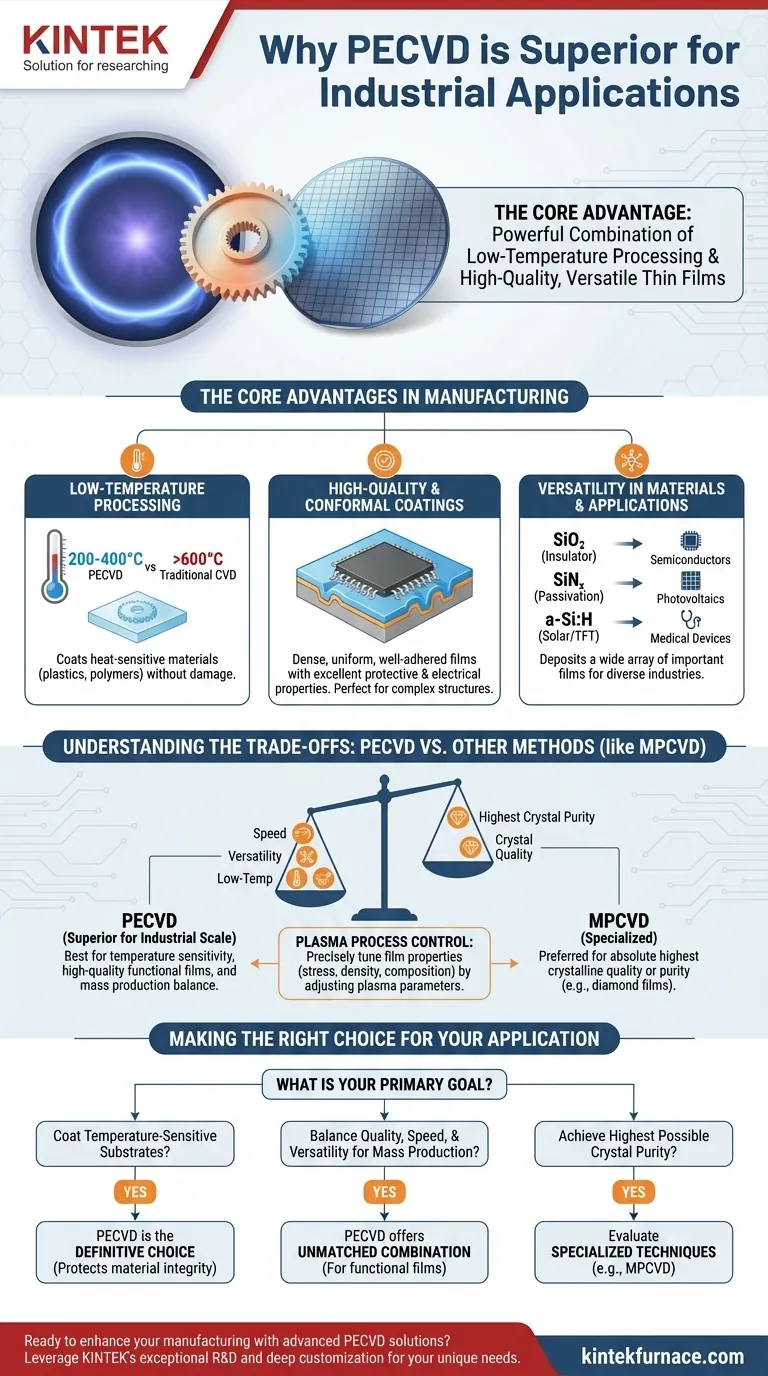
At its core, PECVD's superiority for industrial applications stems from a powerful combination of low-temperature processing and the ability to produce high-quality, versatile thin films. This unique pairing allows manufacturers to apply advanced coatings to a wide range of materials—including heat-sensitive plastics and polymers—without causing damage, unlocking new product possibilities and enhancing performance efficiently.
The choice of a deposition technology is never about finding a single "best" method, but about matching the right tool to the specific problem. PECVD excels in applications where material integrity and coating quality on temperature-sensitive substrates are paramount, offering a balance of speed, versatility, and performance that traditional high-temperature methods cannot match.

The Core Advantages of PECVD in Manufacturing
To understand why PECVD is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, we must look at how it solves critical production challenges. Its defining characteristic is the use of plasma to initiate chemical reactions at low temperatures.
Low-Temperature Processing: A Game-Changer
Traditional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) requires very high temperatures (often >600°C) to break down precursor gases and deposit a film. This thermal budget severely limits the types of materials that can be coated.
PECVD circumvents this by using an electromagnetic field to create plasma, which energizes the gases and enables deposition at much lower temperatures (typically 200-400°C). This fundamental difference allows for coating on temperature-sensitive substrates like plastics, polymers, and fully assembled electronic devices.
High-Quality and Conformal Coatings
The plasma environment promotes the formation of dense, uniform, and well-adhered films. This results in coatings with excellent properties for protection, electronic insulation, or optical performance.
Furthermore, PECVD provides conformal coverage, meaning it can deposit a uniform layer over complex, three-dimensional topographies. This is critical for microelectronics and MEMS devices, where even coverage over intricate structures is essential for device function.
Versatility in Materials and Applications
PECVD is not limited to a single type of material. It is used to deposit a wide array of important films, including:
- Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂): Used as an electrical insulator.
- Silicon Nitride (SiNₓ): Used for passivation, providing a hard, chemically-resistant protective barrier.
- Amorphous Silicon (a-Si:H): A key material in solar cells and thin-film transistors.
This versatility makes PECVD a foundational process in industries from semiconductors and photovoltaics to data storage and medical devices.
Understanding the Trade-offs: PECVD vs. Other Methods
No single technology is universally superior. Acknowledging PECVD's limitations provides a clearer picture of where it truly shines.
When PECVD Excels
PECVD is the go-to choice when the primary constraints are substrate temperature sensitivity and the need for a high-quality, functional film at industrial scale. Its balance of deposition rate, film quality, and process temperature is its key industrial advantage.
Where Other Methods (like MPCVD) Might Be Preferred
For applications demanding the absolute highest crystalline quality and purity, other methods may be more suitable. Microwave Plasma CVD (MPCVD), for example, is often favored for growing high-quality diamond films or for certain semiconductor applications where freedom from impurities is the single most critical factor.
These specialized processes may trade the speed and versatility of PECVD for superior performance in a single metric, such as crystal quality or purity. The choice depends entirely on the end-product's non-negotiable requirements.
The Role of Plasma in Process Control
The plasma itself offers another layer of control. By tuning plasma parameters like power, frequency, and gas chemistry, engineers can precisely influence the final properties of the deposited film. This allows for fine-tuning film stress, density, and chemical composition to meet specific performance targets.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct deposition technology requires a clear understanding of your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is coating temperature-sensitive substrates: PECVD is the definitive choice, as its low-temperature operation protects material integrity.
- If your primary focus is balancing quality, speed, and versatility for mass production: PECVD offers an unmatched combination for depositing functional films like dielectrics and passivation layers.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible crystal purity for specialized applications: You should evaluate more specialized techniques like MPCVD, which are optimized for crystal structure over other factors.
Ultimately, choosing the right deposition technology is about aligning the process capabilities with your specific manufacturing goals and material constraints.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Low-Temperature Processing | Enables coating of heat-sensitive materials (e.g., plastics) at 200-400°C, preventing damage. |
| High-Quality Coatings | Produces dense, uniform, and conformal films for protection, insulation, and optical uses. |
| Versatility | Deposits various materials like SiO₂, SiNₓ, and a-Si:H for semiconductors, photovoltaics, and more. |
| Industrial Advantages | Balances speed, quality, and scalability for mass production in diverse applications. |
Ready to enhance your manufacturing with advanced PECVD solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature furnace systems, including CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental and production needs for temperature-sensitive substrates and high-quality coatings. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your industrial processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the main components of a PECVD system? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings



















