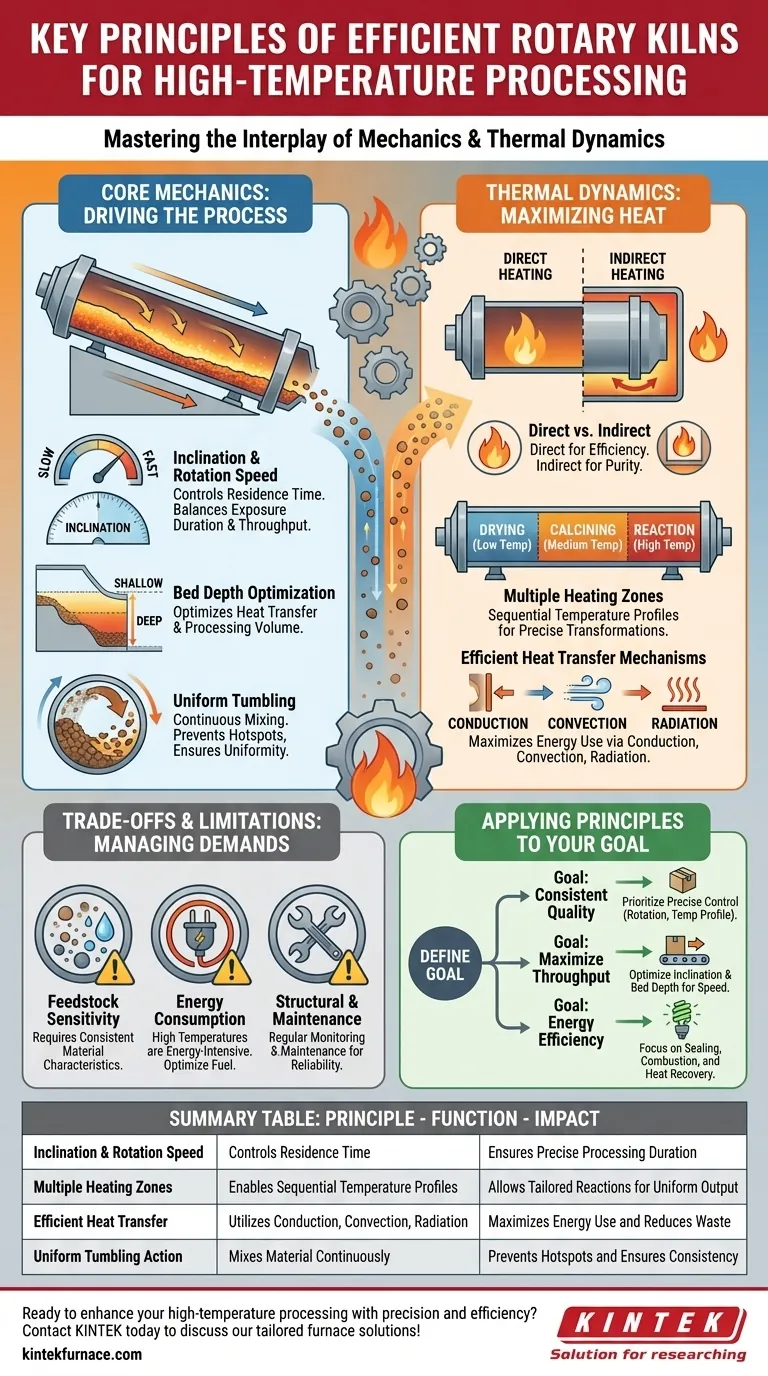
The efficiency of a rotary kiln is not the result of a single feature, but the interplay of several core engineering principles. These include its controlled inclination and rotation speed, the use of multiple distinct heating zones, highly efficient heat transfer, and the ability to process a wide variety of materials uniformly. By precisely managing how material moves and how it is heated, a rotary kiln creates an optimal environment for high-temperature chemical and physical transformations.
A rotary kiln’s effectiveness comes from its unique ability to combine mechanical motion with thermal dynamics. It uses controlled tumbling and forward movement to continuously expose every particle of a material to a precise temperature profile, ensuring uniform, efficient, and complete processing on a massive scale.

The Core Mechanics: How Motion Drives Processing
The genius of the rotary kiln lies in how it uses simple mechanical forces to achieve complex processing goals. The physical design and movement are fundamental to its efficiency.
The Role of Inclination and Rotation Speed
The kiln is a long, cylindrical shell mounted at a slight angle to the horizontal, known as its inclination. This angle, combined with the rotation speed, dictates how long the material stays inside the kiln—a critical parameter called residence time.
Slower rotation and a shallower angle increase residence time, which is ideal for reactions that require prolonged exposure to heat. Faster rotation and a steeper angle move material through more quickly, increasing throughput for faster processes.
The Impact of Bed Depth
The bed depth, or the volume of material inside the kiln at any given time, is carefully controlled. A deeper bed can increase throughput, but it may hinder heat transfer to the lower layers.
Conversely, a shallower bed ensures every particle is exposed to the heat source but reduces the overall processing volume. Optimizing this depth is a key operational balance.
Ensuring Uniformity Through Tumbling
As the kiln rotates, the material bed is continuously lifted up the side of the shell and then tumbles back down. This constant mixing is crucial.
This tumbling action prevents localized overheating and ensures that all particles are uniformly exposed to the internal atmosphere and heat, leading to a highly consistent final product.
Mastering Thermal Dynamics for Efficiency
A rotary kiln is fundamentally a heat exchanger. How it generates and transfers heat is central to its performance and efficiency.
Direct vs. Indirect Heating
Kilns can be directly heated, where a flame and hot combustion gases pass through the cylinder in direct contact with the material. This is common and highly efficient for processes like cement production.
In indirectly heated kilns, the shell is heated from the outside, and the heat transfers through the cylinder wall to the material inside. This is used when the material cannot come into contact with combustion gases, preserving its purity.
Creating Multiple Heating Zones
A long kiln is not kept at a single temperature. It is engineered with multiple heating zones along its length.
This allows for a precise temperature profile, enabling different reactions to occur in sequence. For example, a material might first pass through a low-temperature drying zone, then a medium-temperature calcining zone, and finally a high-temperature reaction zone.
Optimizing Heat Transfer Mechanisms
Efficiency depends on maximizing three forms of heat transfer:
- Conduction: Heat transfer through direct contact between hot refractory walls and the material.
- Convection: Heat transfer from the hot gases flowing through the kiln to the material.
- Radiation: Heat transfer from the flame, hot gases, and glowing refractory walls, which is the dominant mechanism at very high temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, the rotary kiln is not a universal solution. Understanding its operational demands is critical for successful implementation.
Feedstock Sensitivity
The kiln's performance is sensitive to the physical characteristics of the feed material. Variations in particle size, density, and moisture content can alter the flow dynamics and required residence time.
Consistent and properly prepared feedstock is essential for maintaining stable and efficient operation.
Energy Consumption
Achieving temperatures over 1400°C (2500°F) is an energy-intensive process. Inefficient operation, poor sealing that allows cold air in, or unoptimized combustion can lead to extremely high fuel costs.
Continuous monitoring and control systems are vital to optimize fuel use and minimize thermal losses.
Structural and Maintenance Demands
A rotary kiln is a massive, heavy-duty piece of machinery operating in a demanding environment. The rotating shell, support systems, and refractory lining are subject to immense thermal and mechanical stress.
Regular maintenance and monitoring are non-negotiable to ensure long-term reliability and prevent costly downtime.
Applying Kiln Principles to Your Goal
The way you operate a rotary kiln should be directly tied to your primary processing objective.
- If your primary focus is consistent product quality: Prioritize precise control over rotation speed, feed rate, and the temperature profile across all heating zones to ensure every particle undergoes the exact same transformation.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: Carefully optimize the kiln's inclination and bed depth to find the fastest processing speed that still allows for complete reaction and desired product quality.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Emphasize maintaining perfect seals at the feed and discharge ends, optimizing fuel combustion for complete heat release, and using a counter-current gas flow to preheat incoming material.
When its core principles are understood and correctly applied, the rotary kiln stands as one of the most robust and effective tools for high-volume thermal processing.
Summary Table:
| Principle | Key Function | Impact on Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Inclination & Rotation Speed | Controls material residence time | Ensures precise processing duration |
| Multiple Heating Zones | Enables sequential temperature profiles | Allows tailored reactions for uniform output |
| Efficient Heat Transfer | Utilizes conduction, convection, radiation | Maximizes energy use and reduces waste |
| Uniform Tumbling Action | Mixes material continuously | Prevents hotspots and ensures consistency |
Ready to enhance your high-temperature processing with precision and efficiency? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental requirements, whether you're focused on consistent product quality, maximizing throughput, or improving energy efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored high-temperature furnace solutions can drive success for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity



















