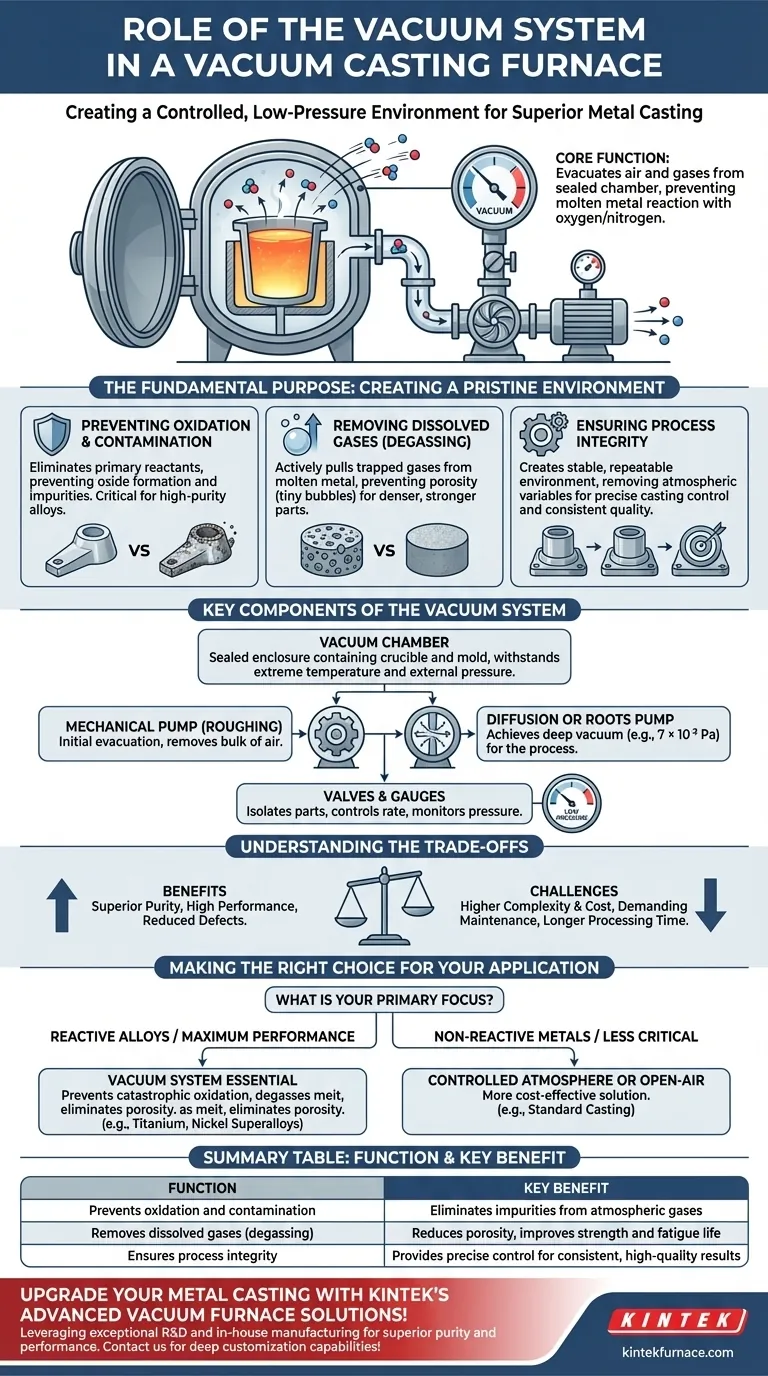
At its core, the vacuum system in a vacuum casting furnace is designed to create a controlled, low-pressure environment by evacuating air and other gases from a sealed chamber. This fundamental action prevents the molten metal from reacting with atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen, which would otherwise cause contamination, oxidation, and defects in the final cast part.
The role of the vacuum system transcends simple air removal. It is an active metallurgical tool that ensures material purity, not just by preventing atmospheric contamination, but by actively pulling dissolved gas impurities out of the molten metal itself, leading to superior mechanical properties and structural integrity.
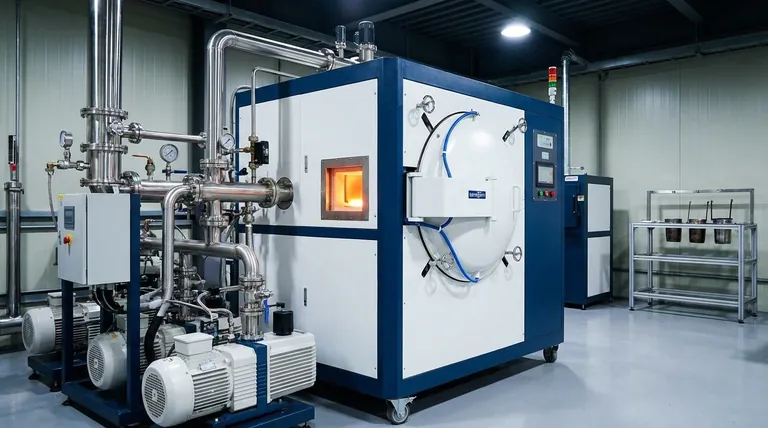

The Fundamental Purpose: Creating a Pristine Environment
A vacuum furnace isn't just a heater; it's a highly controlled environment. The vacuum system is the heart of that control, enabling processes that are impossible in a standard atmosphere.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
At the extreme temperatures required for melting metal, most alloys are highly reactive. Contact with oxygen in the air instantly creates oxides, which appear as impurities or slag in the melt.
By removing the air, the vacuum system eliminates the primary reactants that cause this contamination. This is critical for producing clean, high-purity metals and alloys.
Removing Dissolved Gases (Degassing)
Metals, even in their solid state, contain dissolved gases. When the metal becomes molten in a vacuum, these trapped gases are drawn out of the liquid.
This degassing effect is crucial for preventing porosity—tiny bubbles trapped within the cast part—which can severely compromise its strength and fatigue life. The result is a denser, more robust final product.
Ensuring Process Integrity
The vacuum creates a stable and repeatable environment. By removing the variable of atmospheric composition and pressure, engineers can achieve precise control over the casting process.
This leads to consistent quality from one batch to the next, a requirement for high-performance applications in industries like aerospace, medical, and electronics.
Key Components of the Vacuum System
The system is more than just a single pump. It is a carefully integrated set of components working together to achieve and maintain a specific low-pressure environment.
The Vacuum Chamber
This is the sealed enclosure that contains the crucible of metal and the mold. It is built to withstand both extreme temperatures and the immense external pressure when a vacuum is pulled.
The Pumping System
Achieving the high vacuum needed for casting (often down to levels like 7 × 10⁻³ Pa) typically requires a multi-stage pumping process.
- A mechanical pump (or "roughing pump") does the initial work, removing the bulk of the air.
- A diffusion pump or Roots pump then takes over to achieve the much deeper vacuum required for the process.
Valves and Gauges
A series of valves isolates different parts of the system and controls the rate of evacuation. High-precision gauges are essential for monitoring the pressure inside the chamber, ensuring the correct vacuum level is reached and maintained throughout the melt and pour.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum casting is not the solution for every application. Its benefits come with inherent complexities and costs.
Higher Complexity and Cost
Vacuum furnaces are significantly more complex and expensive to build and operate than furnaces that run in a normal atmosphere. The pumps, seals, and control systems require a substantial initial investment.
Maintenance Requirements
Maintaining a high-quality vacuum is demanding. The system requires regular maintenance to check for leaks, service the pumps, and ensure the integrity of all seals. Failure to do so compromises the entire process.
Processing Time
The time it takes to pump down the chamber to the target vacuum level adds to the overall cycle time for each casting, which can impact throughput.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right casting process depends entirely on the material and the performance requirements of the final component.
- If your primary focus is reactive alloys (titanium, nickel superalloys): A vacuum furnace is non-negotiable to prevent catastrophic oxidation and contamination.
- If your primary focus is maximum mechanical performance and fatigue life: A vacuum system is essential for degassing the melt and eliminating porosity.
- If your primary focus is casting non-reactive metals for less critical applications: A simpler controlled-atmosphere or even an open-air furnace may be a more cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, employing a vacuum system is a deliberate choice to achieve absolute control over the material's purity and final structure.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Prevents oxidation and contamination | Eliminates impurities from atmospheric gases |
| Removes dissolved gases (degassing) | Reduces porosity, improves strength and fatigue life |
| Ensures process integrity | Provides precise control for consistent, high-quality results |
Upgrade your metal casting with KINTEK's advanced vacuum furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer high-temperature furnaces like Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, tailored to your unique needs for superior purity and performance in industries such as aerospace and medical. Contact us today to discuss how our deep customization capabilities can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control



















