At its core, a vacuum sintering furnace is a high-temperature chamber designed to fuse powdered materials, like metals and ceramics, into a solid, dense object. It performs this process, known as sintering, in a vacuum or a controlled low-pressure atmosphere to prevent the material from reacting with air, which would otherwise compromise its final properties.
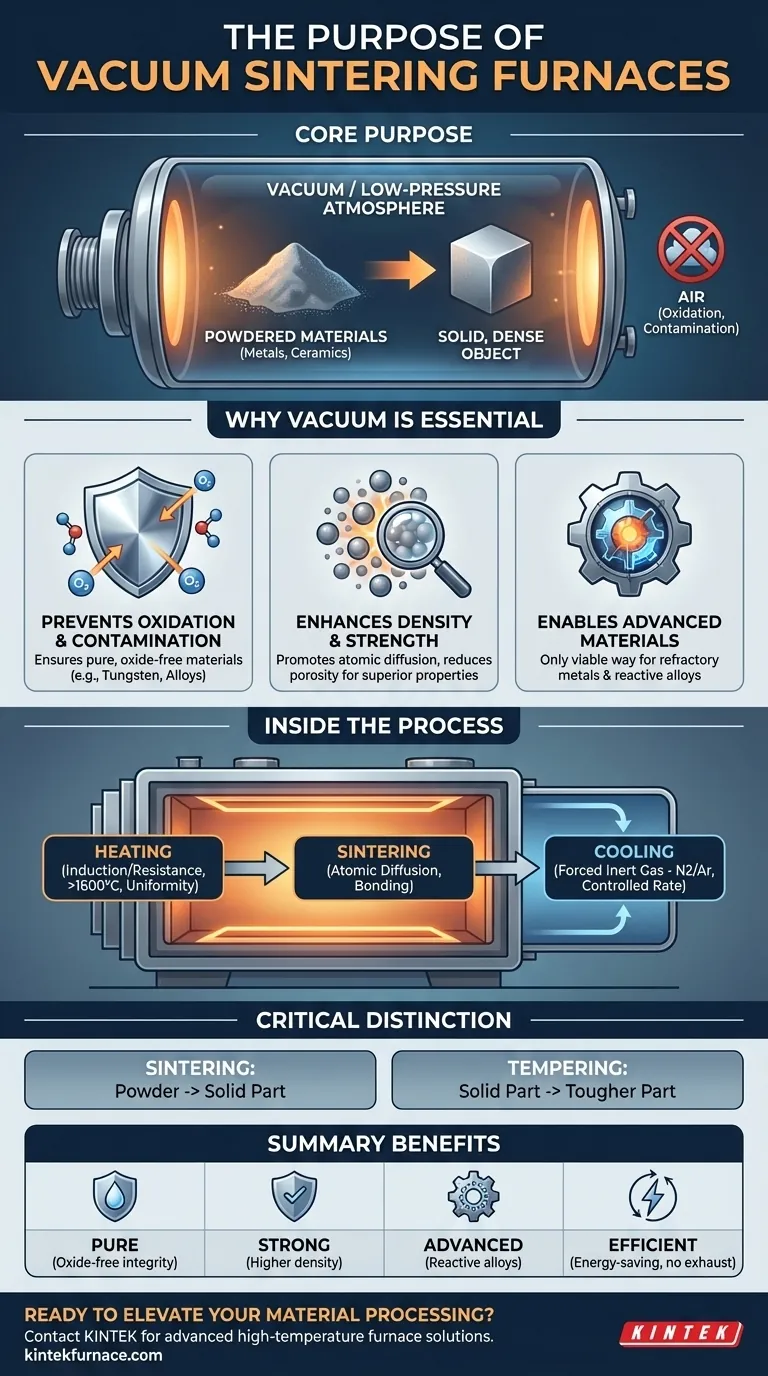
The fundamental purpose of using a vacuum is to solve a critical problem in high-temperature manufacturing: oxidation and contamination. By removing the atmosphere, the furnace creates an ultra-pure environment, allowing for the creation of superior, high-performance materials that would be impossible to produce in open air.
Why a Vacuum is Essential for Sintering
Sintering involves heating a material to just below its melting point, causing its particles to bond and form a solid piece. The use of a vacuum dramatically enhances this process.
Prevents Oxidation and Contamination
At the extreme temperatures required for sintering (often exceeding 1600°C), most advanced materials are highly reactive. Exposure to oxygen and other atmospheric gases can cause oxidation, forming an undesirable surface layer and degrading the material's integrity.
A vacuum furnace removes these reactive gases, ensuring the final product is pure and free of oxides. This is non-negotiable for materials like tungsten, molybdenum, and high-performance alloys.
Enhances Material Density and Strength
The vacuum environment actively promotes atomic diffusion, the mechanism by which individual particles fuse together. This leads to a more effective reduction of porosity within the material.
The result is a final product with significantly higher density and superior mechanical properties, such as hardness and strength. This is crucial for applications ranging from dental zirconia crowns to industrial cutting tools.
Enables Processing of Advanced Materials
The protective environment of a vacuum is the only viable way to process certain materials. This includes refractory metals (like tungsten), which have very high melting points, and other reactive alloys that would be ruined by atmospheric exposure.
Inside the Vacuum Sintering Process
A vacuum sintering furnace is a sophisticated system that carefully controls temperature, pressure, and cooling to achieve a precise outcome.
The Heating Mechanism
To reach the required temperatures, these furnaces employ several methods. Induction heating is common, using magnetic fields to heat a crucible containing the material. Resistance heating is another popular method.
These systems are engineered for exceptional temperature uniformity (often within ±5°C), ensuring the entire part sinters evenly.
The Cooling System
After the heating cycle, controlling the cooling rate is just as critical for determining the final microstructure of the material. Methods include natural cooling or, more commonly, forced cooling.
Forced cooling involves backfilling the chamber with a high-purity inert gas, such as nitrogen or argon, and circulating it to cool the part rapidly and uniformly.
Key Technical Parameters
The performance of a vacuum sintering furnace is defined by several key metrics. These include its maximum temperature (up to 2400°C), ultimate pressure (how strong a vacuum it can achieve), and pressure rising rate, which indicates how well the chamber is sealed.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Distinctions
While incredibly effective, vacuum sintering is a specific tool for a specific job. It's important to understand its context.
Primary Benefit: Superior Material Quality
The main reason to choose vacuum sintering is for the end result. It produces components with a clean, bright surface, high density, and mechanical properties that are far superior to those sintered in air.
The Efficiency Advantage
Modern vacuum furnaces are designed with advanced insulation to minimize heat loss, making them highly energy-efficient. Because it is a closed system, it also prevents the release of exhaust gases, making it an environmentally responsible choice.
Critical Distinction: Sintering vs. Tempering
It is crucial not to confuse vacuum sintering with vacuum tempering.
Sintering creates a solid part from powder. Tempering is a lower-temperature heat treatment applied to an already solid part to reduce its brittleness and improve toughness after it has been hardened. They are fundamentally different processes for different goals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct high-temperature process depends entirely on your material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is creating dense, pure components from reactive powders (like refractory metals or advanced ceramics): A vacuum sintering furnace is the essential and correct choice.
- If your primary focus is improving the mechanical properties of an existing hardened steel part: You require a vacuum tempering furnace, not a sintering furnace.
- If your primary focus is processing non-reactive materials where slight surface oxidation is acceptable: A conventional atmospheric furnace may be a more cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, mastering high-performance materials begins with controlling their processing environment.
Summary Table:
| Purpose | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Prevent Oxidation and Contamination | Ensures pure, oxide-free materials for superior integrity |
| Enhance Material Density and Strength | Promotes atomic diffusion for higher density and mechanical properties |
| Enable Processing of Advanced Materials | Allows sintering of reactive alloys and refractory metals |
| Improve Efficiency | Energy-efficient with minimal heat loss and no exhaust gases |
Ready to elevate your material processing with precision? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum sintering furnaces can deliver high-purity, dense results for your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
People Also Ask
- What processing conditions does a vacuum furnace provide for TiCp/Fe microspheres? Sintering at 900 °C
- What is the mechanism of a vacuum sintering furnace for AlCoCrFeNi2.1 + Y2O3? Optimize Your High-Entropy Alloy Processing
- What is the purpose of performing medium vacuum annealing on working ampoules? Ensure Pure High-Temp Diffusion
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary in copper slag impoverishment? Maximize Your Matte Separation Efficiency
- What is the role of sintering or vacuum induction furnaces in battery regeneration? Optimize Cathode Recovery



















