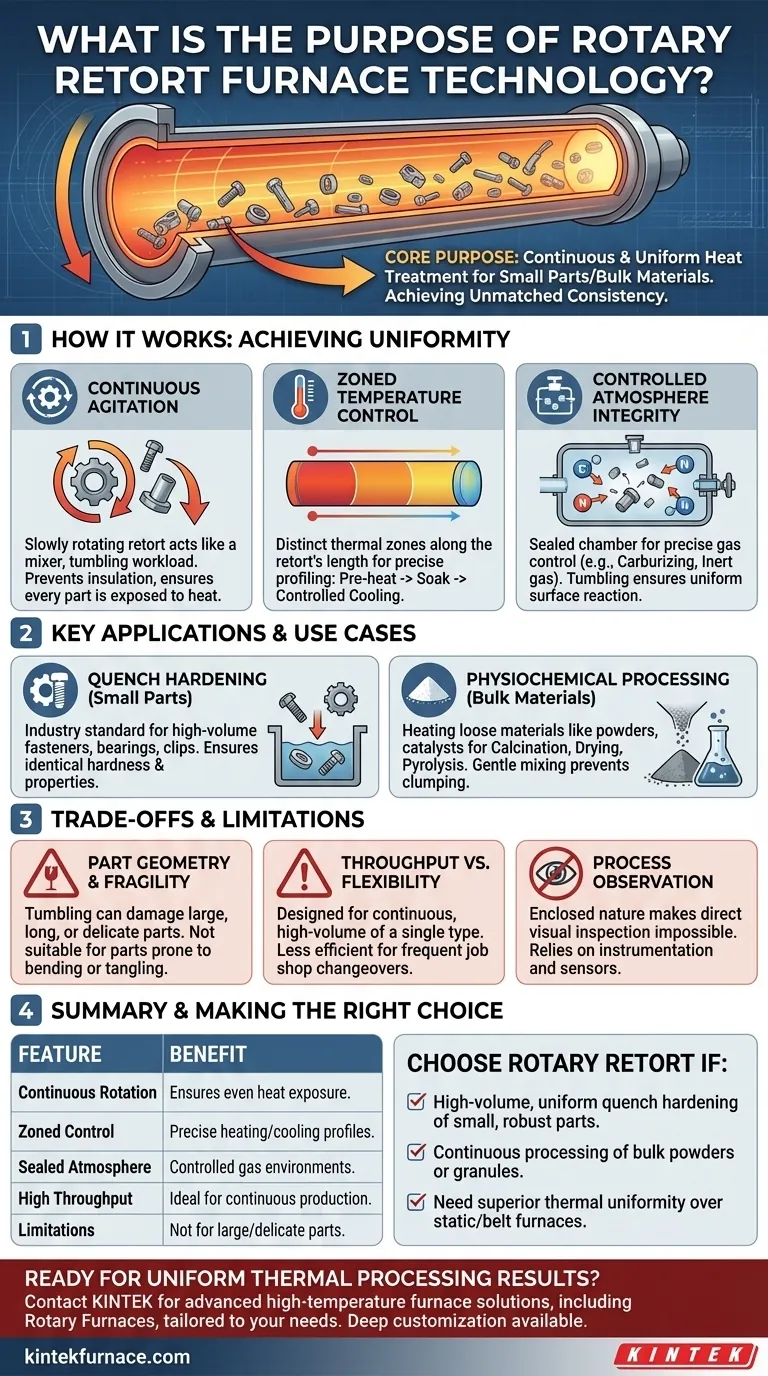
At its core, a rotary retort furnace is specialized thermal processing equipment designed for the continuous and uniform heat treatment of large quantities of small, individual parts or loose bulk materials. By tumbling the material inside a rotating cylindrical tube (the retort), it ensures every surface is evenly exposed to heat and the controlled atmosphere, achieving a level of consistency that is difficult to attain in static batch processes.
The central purpose of a rotary retort furnace is to solve the problem of non-uniformity in the heat treatment of bulk materials. Its continuous rotation guarantees that every individual part or granule receives the same thermal cycle, leading to highly consistent, repeatable, and economical results.
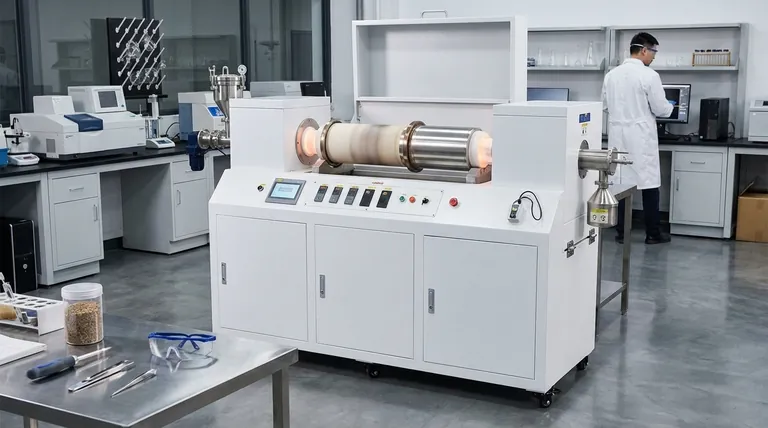

How Rotary Retorts Achieve Unmatched Uniformity
The design of a rotary retort furnace is engineered around one primary goal: overcoming the inconsistencies inherent in heating a large, static pile of material. It achieves this through a few key principles.
The Principle of Continuous Agitation
The heart of the technology is the slowly rotating retort. This constant tumbling motion acts like a mixer, continuously turning over the workload.
This agitation prevents parts in the center of the mass from being insulated by those on the outside. Every part is regularly brought to the surface, where it is directly exposed to the radiant heat of the furnace and the process atmosphere.
Zoned Temperature and Process Control
The long, tubular retort allows for the creation of multiple, distinct thermal control zones along its length.
This enables a precise process profile. Material can be pre-heated in the first zone, brought to a specific temperature and held (soaked) in the middle zones, and begin a controlled cooling process in the final zones, all within a single, continuous operation.
Controlled Atmosphere Integrity
The retort is a sealed chamber, which allows for precise control over the internal gaseous atmosphere.
This is critical for metallurgical processes like carburizing, where carbon must be introduced into the surface of steel parts, or for simply preventing oxidation by using an inert atmosphere like nitrogen. The tumbling action ensures all surfaces of the parts react uniformly with the gas.
Key Applications and Use Cases
The unique capabilities of rotary retorts make them ideal for specific industrial applications where uniformity and high throughput are paramount.
Quench Hardening of Small Parts
This is the classic application. Rotary retorts are the industry standard for hardening high-volume fasteners, bearings, clips, and other small metal components.
The uniform heating ensures that every single part has the same hardness and metallurgical properties after quenching, which is critical for performance and reliability.
Physiochemical Processing of Bulk Materials
The technology is not limited to metals. It is also used to heat loose materials like powders, catalysts, and granules for various chemical transformations.
Applications include calcination (heating to drive off impurities), drying, and pyrolysis. The gentle mixing action prevents clumping and ensures a complete reaction throughout the entire volume of material.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, rotary retort technology is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Part Geometry and Fragility
The tumbling action that creates uniformity can also cause damage. This technology is not suitable for large, long, or delicate parts that could be bent, tangled, or suffer surface damage from the constant impact.
Throughput vs. Flexibility
Rotary retort furnaces are designed for continuous, high-volume production of a single type of part. They are less efficient for job shops that require frequent changeovers between different parts and heat treatment cycles, where batch furnaces offer more flexibility.
Process Observation
Due to the enclosed nature of the retort, direct visual inspection of the workload during the process is impossible. Operators must rely on instrumentation and controls to monitor the cycle's progress.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct thermal technology depends entirely on your material, volume, and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, uniform quench hardening of small, robust parts: A rotary retort furnace is almost certainly the most efficient and consistent technology for your needs.
- If your primary focus is continuous processing of bulk powders or granular materials: This technology offers superior thermal uniformity and process control compared to static bed or belt furnaces.
- If your primary focus is heat treating large, complex, or delicate components: You should explore batch-style furnaces (like box or pit furnaces) or mesh belt furnaces that minimize part-on-part contact.
By understanding its core principle of continuous agitation, you can determine if this powerful technology is the right tool to achieve your specific processing goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Continuous Rotation | Ensures even heat exposure and prevents non-uniformity |
| Zoned Temperature Control | Allows precise process profiling for heating, soaking, and cooling |
| Sealed Atmosphere | Enables controlled gas environments for processes like carburizing |
| High Throughput | Ideal for continuous production of small, robust parts or bulk materials |
| Limitations | Not suitable for large, delicate parts; less flexible for frequent changeovers |
Ready to enhance your thermal processing with uniform results? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're processing small parts or bulk materials, contact us today via our contact form to discuss how our solutions can boost your efficiency and consistency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of rotary tube furnaces regarding heat treatment? Achieve Uniform Heating and High Throughput
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries
- What are the common applications of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating for Powders and Granules
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits



















